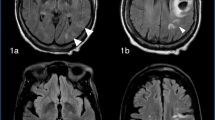
Abstract
Introduction
This study assesses the incidence and causes of hyperperfusion syndrome occurring after carotid artery stenting (CAS).
Materials and methods
We retrospectively reviewed the clinical database of 417 consecutive patients who were treated with CAS in our department to identify patients who developed hyperperfusion syndrome and/or intracranial hemorrhage. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) including fluid-attenuated inversion recovery and diffusion-weighted imaging was performed before and after CAS in 269 cases. A Spearman’s rho nonparametric correlation was performed to determine whether there was a correlation between the occurrence/development of hyperperfusion syndrome and the patient’s age, degree of stenosis on the stented and contralateral side, risk factors such as diabetes, smoking, hypertension, adiposity, gender and fluoroscopy time, and mean area of postprocedural lesions as well as preexisting lesions. Significance was established at p < 0.05.
Results
Of the 417 carotid arteries stented and where MRI was also completed, we found hyperperfusion syndrome in 2.4% (ten cases). Patients who had preexisting brain lesions (previous or acute stroke) were at a higher risk of developing hyperperfusion syndrome (p = 0.022; Spearman’s rho test). We could not validate any correlation with the other patient characteristics.
Conclusion
Extensive microvascular disease may be a predictor of hyperperfusion syndrome after carotid stent placement. We believe that further studies are warranted to predict more accurately which patients are at greater risk of developing this often fatal complication.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fiehler J, Jansen O, Berger J, Eckstein HH, Ringleb PA, Stingele R (2008) Differences in complication rates among the centres in the SPACE study. Neuroradiology 50:1049–1053 doi:10.1007/s00234-008-0459-6
Sundt TM Jr, Sharbrough FW, Piepgras DG, Kearns TP, Messick JM Jr, O’Fallon WM (1981) Correlation of cerebral blood flow and electroencephalographic changes during carotid endarterectomy: with results of surgery and hemodynamics of cerebral ischemia. Mayo Clin Proc 56:533–543
Krajickova D, Krajina A, Nova M, Raupach J (2005) Fatal intraventricular hemorrhage after the extracranial carotid artery angioplasty and stent placement. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 28:502–505 doi:10.1007/s00270-004-0155-9
McCabe DJ, Brown MM, Clifton A (1999) Fatal cerebral reperfusion hemorrhage after carotid stenting. Stroke 30:2483–2486
Gurm HS, Nallamothu BK, Yadav J (2008) Safety of carotid artery stenting for symptomatic carotid artery disease: a meta-analysis. Eur Heart J 29:113–119 doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehm362
Coutts SB, Hill MD, Hu WY (2003) Hyperperfusion syndrome: toward a stricter definition. Neurosurgery 53:1053–1058, discussion 1058–1060 doi:10.1227/01.NEU.0000088738.80838.74
Karapanayiotides T, Meuli R, Devuyst G et al (2005) Postcarotid endarterectomy hyperperfusion or reperfusion syndrome. Stroke 36:21–26 doi:10.1161/01.STR.0000149946.86087.e5
Kieburtz K, Ricotta JJ, Moxley RT 3rd (1990) Seizures following carotid endarterectomy. Arch Neurol 47:568–570
Piepgras DG, Morgan MK, Sundt TM Jr, Yanagihara T, Mussman LM (1988) Intracerebral hemorrhage after carotid endarterectomy. J Neurosurg 68:532–536
Solomon RA, Loftus CM, Quest DO, Correll JW (1986) Incidence and etiology of intracerebral hemorrhage following carotid endarterectomy. J Neurosurg 64:29–34
Kaku Y, Yoshimura S, Kokuzawa J (2004) Factors predictive of cerebral hyperperfusion after carotid angioplasty and stent placement. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1403–1408
Meyers PM, Phatouros CC, Higashida RT (2006) Hyperperfusion syndrome after intracranial angioplasty and stent placement. Stroke 37:2210–2211 doi:10.1161/01.STR.0000237208.77716.1c
Morrish W, Grahovac S, Douen A et al (2000) Intracranial hemorrhage after stenting and angioplasty of extracranial carotid stenosis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:1911–1916
Schoser BG, Heesen C, Eckert B, Thie A (1997) Cerebral hyperperfusion injury after percutaneous transluminal angioplasty of extracranial arteries. J Neurol 244:101–104 doi:10.1007/s004150050057
Yadav JS, Roubin GS, Iyer S et al (1997) Elective stenting of the extracranial carotid arteries. Circulation 95:376–381
North American Symptomatic Carotid Endarterectomy Trial Collaborators (1991) Beneficial effect of carotid endarterectomy in symptomatic patients with high-grade carotid stenosis. N Engl J Med 325:445–453
Ogasawara K, Sakai N, Kuroiwa T et al (2007) Intracranial hemorrhage associated with cerebral hyperperfusion syndrome following carotid endarterectomy and carotid artery stenting: retrospective review of 4494 patients. J Neurosurg 107:1130–1136 doi:10.3171/JNS-07/12/1130
Kadkhodayan Y, Cross DT 3rd, Derdeyn CP, Moran CJ (2007) Carotid angioplasty and stenting in the elderly. Neuroradiology 49:933–938 doi:10.1007/s00234-007-0278-1
Chamorro A, Vila N, Obach V, Macho J, Blasco J (2000) A case of cerebral hemorrhage early after carotid stenting. Stroke 31:792–793
Lovblad KO, Bassetti C, Schneider J, Ozdoba C, Remonda L, Schroth G (2000) Diffusion-weighted MRI suggests the coexistence of cytotoxic and vasogenic oedema in a case of deep cerebral venous thrombosis. Neuroradiology 42:728–731 doi:10.1007/s002340000395
Lovblad KO, Pluschke W, Remonda L et al (2000) Diffusion-weighted MRI for monitoring neurovascular interventions. Neuroradiology 42:134–138 doi:10.1007/s002340050032
Reigel MM, Hollier LH, Sundt TM Jr, Piepgras DG, Sharbrough FW, Cherry KJ (1987) Cerebral hyperperfusion syndrome: a cause of neurologic dysfunction after carotid endarterectomy. J Vasc Surg 5:628–634 doi:10.1067/mva.1987.avs0050628
Sfyroeras GS, Karkos CD, Gerassimidis TS (2008) Cerebral perfusion patterns in patients with extracranial carotid atherosclerosis and the impact of carotid stenting. A review. J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino) 49:497–502
Zahn R, Ischinger T, Hochadel M et al (2007) Carotid artery stenting in octogenarians: results from the ALKK Carotid Artery Stent (CAS) Registry. Eur Heart J 28:370–375 doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehl421
Abou-Chebl A, Reginelli J, Bajzer CT, Yadav JS (2007) Intensive treatment of hypertension decreases the risk of hyperperfusion and intracerebral hemorrhage following carotid artery stenting. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv 69:690–696 doi:10.1002/ccd.20693
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
I. Q. Grunwald and M. Politi contributed equally to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grunwald, I.Q., Politi, M., Reith, W. et al. Hyperperfusion syndrome after carotid stent angioplasty. Neuroradiology 51, 169–174 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-008-0483-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-008-0483-6