Abstract
Introduction
Lesions involving the splenium of the corpus callosum (SCC) have been rarely reported in cases of hypoglycemic brain injury.
Methods
We identified signal abnormalities in the SCC in three adult patients with hypoglycemic encephalopathy by using diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) on a 1.5-T MR scanner. Repeat DWI was performed in all patients following a marked clinical improvement, and MR angiography and routine MRI were also performed. We examined each patient’s detailed medical history and blood laboratory tests in order to exclude other conditions causing similar SCC abnormalities.
Results
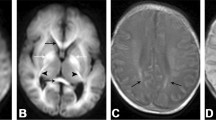
Initial DWI was performed during which each patient showed altered mental status that was attributed to profound hypoglycemia. We observed an identical pattern of DWI abnormality characterized by high signals in the SCC with apparent diffusion coefficient reductions that were reversed completely within several days following appropriate correction of hypoglycemia. T2-weighted or FLAIR images also showed no residual lesion in the SCC and MR angiography was normal in all patients.
Conclusion
These case reports suggest that the SCC should be added to the list of selective vulnerability to hypoglycemia and that hypoglycemia, in turn, be included in the differential diagnosis of reversible SCC abnormalities.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wallis WE, Donaldson I, Scott RS, Wilson J (1985) Hypoglycemia masquerading as cerebrovascular disease (hypoglycemic hemiplegia). Ann Neurol 18:510–512
Finelli PF (2001) Diffusion-weighted MR in hypoglycemic coma. Neurology 57:933–935
Chan R, Erbay S, Oljeski S, Thaler D, Bhadelia R (2003) Case report: hypoglycemia and diffusion-weighted imaging. J Comput Assist Tomogr 27:420–423
Aoki T, Sato T, Hasegawa K, Ishizaki R, Saiki M (2004) Reversible hyperintensity lesion on diffusion-weighted MRI in hypoglycemic coma. Neurology 63:392–393
Cho SJ, Minn YK, Kwon KH (2006) Severe hypoglycemia and vulnerability of the brain. Arch Neurol 63:138
Fujioka M, Okuchi K, Hiramatsu KI, Sakaki T, Sakaguchi S, Ishii Y (1997) Specific changes in human brain after hypoglycemic injury. Stroke 28:584–587
Bottcher J, Kunze A, Kurrat C, Schmidt P, Hagemann G, Witte OW, Kaiser WA (2005) Localized reversible reduction of apparent diffusion coefficient in transient hypoglycemia-induced hemiparesis. Stroke 36:e20–e22
Doherty MJ, Jayadev S, Watson NF, Konchada RS, Hallam DK (2005) Clinical implications of splenium magnetic resonance imaging signal changes. Arch Neurol 62:433–437
Lo L, Tan AC, Umapathi T, Lim CC (2006) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging in early diagnosis and prognosis of hypoglycemia. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 27:1222–1224
Oster J, Doherty C, Grant PE, Simon M, Cole AJ (2003) Diffusion-weighted imaging abnormalities in the splenium after seizures. Epilepsia 44:852–854
Chang KH, Cha SH, Han MH, Park SH, Nah DL, Hong JH (1992) Marchiafava-Bignami disease: serial changes in corpus callosum on MRI. Neuroradiology 34:480–482
Gambini A, Falini A, Moiola L, Comi G, Scotti G (2003) Marchiafava-Bignami disease: longitudinal MR imaging and MR spectroscopy study. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:249–253
Kobata R, Tsukahara H, Nakai A, Tanizawa A, Ishimori Y, Kawamura Y, Ushijima H, Mayumi M (2002) Transient MR signal changes in the splenium of the corpus callosum in rotavirus encephalopathy: value of diffusion-weighted imaging. J Comput Assist Tomogr 26:825–828
Takanashi J, Barkovich AJ, Yamaguchi K, Kohno Y (2004) Influenza-associated encephalitis/encephalopathy with a reversible lesion in the splenium of the corpus callosum: a case report and literature review. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:798–802
Tada H, Takanashi J, Barkovich AJ, Oba H, Maeda M, Tsukahara H, Suzuki M, Yamamoto T, Shimono T, Ichiyama T, Taoka T, Sohma O, Yoshikawa H, Kohno Y (2004) Clinically mild encephalitis/encephalopathy with a reversible splenial lesion. Neurology 63:1854–1858
Kim SS, Chang KH, Kim ST, Suh DC, Cheon JE, Jeong SW, Han MH, Lee SK (1999) Focal lesion in the splenium of the corpus callosum in epileptic patients: antiepileptic drug toxicity? AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:125–129
da Rocha AJ, Reis F, Gama HP, da Silva CJ, Braga FT, Junior AC, Cendes F (2006) Focal transient lesion in the splenium of the corpus callosum in three non-epileptic patients. Neuroradiology 48:731–735
Prilipko O, Delavelle J, Lazeyras F, Seeck M (2005) Reversible cytotoxic edema in the splenium of the corpus callosum related to antiepileptic treatment: report of two cases and literature review. Epilepsia 46:1633–1636
Nelles M, Bien CG, Kurthen M, von Falkenhausen M, Urbach H (2006) Transient splenium lesions in presurgical epilepsy patients: incidence and pathogenesis. Neuroradiology 48:443–448
Pekala JS, Mamourian AC, Wishart HA, Hickey WF, Raque JD (2003) Focal lesion in the splenium of the corpus callosum on FLAIR MR images: a common finding with aging and after brain radiation therapy. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:855–861
Loh Y, Watson WD, Verma A, Krapiva P (2005) Restricted diffusion of the splenium in acute Wernicke’s encephalopathy. J Neuroimaging 15:373–375
Mendelsohn DB, Levin HS, Harward H, Bruce D (1992) Corpus callosum lesions after closed head injury in children: MRI, clinical features and outcome. Neuroradiology 34:384–388
Ogura H, Takaoka M, Kishi M, Kimoto M, Shimazu T, Yoshioka T, Sugimoto H (1998) Reversible MR findings of hemolytic uremic syndrome with mild encephalopathy. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 19:1144–1145
Wong SH, Turner N, Birchall D, Walls TJ, English P, Schmid ML (2004) Reversible abnormalities of DWI in high-altitude cerebral edema. Neurology 62:335–336
Winslow H, Mickey B, Frohman EM (2006) Sympathomimetic-induced kaleidoscopic visual illusion associated with a reversible splenium lesion. Arch Neurol 63:135–137
Hasegawa Y, Formato JE, Latour LL, Gutierrez JA, Liu KF, Garcia JH, Sotak CH, Fisher M (1996) Severe transient hypoglycemia causes reversible change in the apparent diffusion coefficient of water. Stroke 27:1648–1655
de Crespigny AJ, Rother J, Beaulieu C, Moseley ME, Hoehn M (1999) Rapid monitoring of diffusion, DC potential, and blood oxygenation changes during global ischemia. Effects of hypoglycemia, hyperglycemia, and TTX. Stroke 30:2212–2222
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, J.H., Choi, J.Y., Koh, SB. et al. Reversible splenial abnormality in hypoglycemic encephalopathy. Neuroradiology 49, 217–222 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-006-0184-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-006-0184-y