Abstract
Introduction
Toxoplasmosis and lymphoma are common lesions of the central nervous system in patients with AIDS. It is often difficult to distinguish between these lesions both clinically and radiographically. Previous research has demonstrated restricted diffusion within cerebral lymphomas and bacterial abscesses. However, little work has been done to evaluate the diffusion characteristics of toxoplasmosis lesions. This study was designed to explore further the utility of diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) maps and values in making the distinction between toxoplasmosis and lymphoma.
Methods
The magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) studies of 36 patients, including 22 with toxoplasmosis (all of whom had AIDS) and 14 with lymphoma (8 of whom had AIDS), at two institutions were reviewed retrospectively. The characteristics of the lesions on DWI were evaluated, and the ADC ratios of the lesions were calculated and compared.
Results
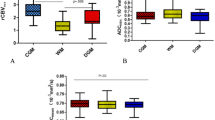
There was significant overlap of the ADC ratios of toxoplasma and lymphoma, most notably in the intermediate (1.0–1.6) range. There was variability in ADC ratios even among different lesions in the same patient. In only a minority of the lymphoma patients were the ADC ratios low enough to suggest the correct diagnosis.
Conclusion
Our study showed that toxoplasmosis exhibits a wide spectrum of diffusion characteristics with ADC ratios which have significant overlap with those of lymphoma. Therefore, in the majority of patients, ADC ratios are not definitive in making the distinction between toxoplasmosis and lymphoma.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Osborn AG, Blaser SI, Salzman KL (2004) Diagnostic imaging: brain. WB Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 122–123
Ruiz A, Ganz WI, Post MJD et al (1994) Use of Thallium-201 Brain SPECT to differentiate cerebral lymphoma from toxoplasma encephalitis in AIDS patients. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 15:1885–1894
Licho R, Litofsky NS, Senitko M et al (2002) Inaccuracy of Tl-201 brain SPECT in distinguishing cerebral infections from lymphoma in patients with AIDS. Clin Nucl Med 27:81–86
Chinn RJS, Wilkinson ID, Hall-Craggs MA et al (1995) Toxoplasmosis and primary central nervous system lymphoma in HIV infection: diagnosis with MR spectroscopy. Radiology 197:649–654
Villringer K, Jager H, Dichgans M et al (1995) Differential diagnosis of CNS lesions in AIDS patients by FDG-PET. J Comput Assist Tomogr 19:532–536
Desprechins B, Stadnik T, Koerts G, Shabana W, Breucq C, Osteaux M (1999) Use of diffusion-weighted MR imaging in differential diagnosis between intracerebral necrotic tumors and cerebral abscesses. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:1252–1257
Camacho DL, Smith JK, Castillo M (2003) Differentiation of toxoplasmosis and lymphoma in AIDS patients by using apparent diffusion coefficients. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:633–637
Dina TS (1991) Primary central nervous system lymphoma versus toxoplasmosis in AIDS. Radiology 179:823–828
Kupfer MC, Zee CS, Colletti PM et al (1990) MRI evaluation of AIDS related encephalopathy: toxoplasmosis vs lymphomas. Magn Reson Imaging 8:51–57
Rhoades RA, Tanner GA (1995) Medical physiology. Little, Brown, and Company, New York, pp 17–18
Schwartz KM, Erickson BJ, Lucchinetti C (2006) Pattern of T2 hypointensity associated with ring-enhancing brain lesions can help to differentiate pathology. Neuroradiology 48:143–149
Hawkins CP, McLaughlin JE, Kendall BE, McDonald WI (1993) Pathological findings correlated with MRI in HIV infection. Neuroradiology 35(4):264–268
Thurnher MM, Rieger A, Kleibl-Popov Ch et al (2001) Primary central nervous system lymphoma in AIDS: a wider spectrum of CT and MRI findings. Neuroradiology 43:29–35
Johnson BA, Fram EK, Johnson PC, Jacobowitz R (1997) The variable MR appearance of primary lymphoma of the central nervous system: comparison with histopathologic features. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 18:563–572
Ernst TE, Chang L, Witt MD et al (1998) Cerebral toxoplasmosis and lymphoma in AIDS: perfusion MR imaging experience in 13 patients. Radiology 208:663–669
Le Bihan D (1991) Molecular diffusion nuclear magnetic resonance imaging. Magn Reson Q 7:1–30
Guo AC, Cummings TJ, Dash RC, Provenzale JM (2002) Lymphomas and high-grade astrocytomas: comparison of water diffusibility and histologic characteristics. Radiology 224:177–183
Brightbill TC, Donovan Post MJ, Hensley GT, Ruiz A (1996) MR of toxoplasma encephalitis: signal characteristics on T2-weighted images and pathologic correlation. J Comput Assist Tomogr 20:417–422
Kessler LS, Ruiz A, Donovan Post MJ, Ganz WI, Brandon AH, Foss JN (1998) Thallium-201 brain SPECT of lymphoma in AIDS patients: pitfalls and technique optimization. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 19:1105–1109
Skiest DJ, Erdman W, Chang WE, Oz OK, Ware A, Fleckenstein J (2000) SPECT thallium-201 combined with toxoplasma serology for the presumptive diagnosis of focal central nervous system mass lesions in patients with AIDS. J Infect 40:274–281
Acknowledgements
Special thanks are due to Manuel D’Fana, RT, Ms. Jean Alli, and Ms. Winnie Tang.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schroeder, P.C., Post, M.J.D., Oschatz, E. et al. Analysis of the utility of diffusion-weighted MRI and apparent diffusion coefficient values in distinguishing central nervous system toxoplasmosis from lymphoma. Neuroradiology 48, 715–720 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-006-0123-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-006-0123-y