Abstract.
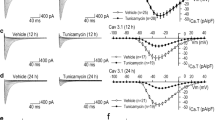
The role of glycosylation on voltage-dependent channel gating for the cloned human cardiac sodium channel (hH1a) and the adult rat skeletal muscle isoform (μl) was investigated in HEK293 cells transiently transfected with either hH1a or μl cDNA. The contribution of sugar residues to channel gating was examined in transfected cells pretreated with various glycosidase and enzyme inhibitors to deglycosylate channel proteins. Pretreating transfected cells with enzyme inhibitors castanospermine and swainsonine, or exo-glycosidase neuroaminidase caused 7 to 9 mV depolarizing shifts of V 1/2 for steady-state activation of hH1a, while deglycosylation with corresponding drugs elicited about the same amount of depolarizing shifts (8 to 9 mV) of V 1/2 for steady-state activation of μl. Elevated concentrations of extracellular Mg2+ significantly masked the castanospermine-elicited depolarizing shifts of V 1/2 for steady-state activation in both transfected hH1a and μl. For steady-state activation, deglycosylation induced depolarizing shifts of V 1/2 for hH1a (10.6 to 12 mV), but hyperpolarizing shifts for μl (3.6 to 4.4 mV). Pretreatment with neuraminidase had no significant effects on single-channel conductance, the mean open time, and the open probability. These data suggest that glycosylation differentially regulates Na channel function in heart and skeletal muscle myocytes.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 8 April 1999/Revised: 18 June 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Hartmann, H. & Satin, J. Glycosylation Influences Voltage-Dependent Gating of Cardiac and Skeletal Muscle Sodium Channels. J. Membrane Biol. 171, 195–207 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002329900571
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002329900571