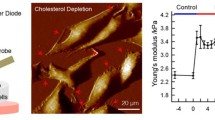
Abstract
The nonionic detergent extraction at 4 °C and the cholesterol-depletion-induced lipid raft disruption are the two widely used experimental strategies for lipid raft research. However, the effects of raft disruption and/or cold treatment on the ultrastructural and mechanical properties of cells are still unclear. Here, we evaluated the effects of raft disruption and/or cold (4 °C) treatment on these properties of living human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). At first, the cholesterol-depletion-induced raft disruption was visualized by confocal microscopy and atomic force microscopy (AFM) in combination with fluorescent quantum dots. Next, the cold-induced cell contraction and the formation of end-branched filopodia were observed by confocal microscopy and AFM. Then, the cell-surface ultrastructures were imaged by AFM, and the data showed that raft disruption and cold treatment induced opposite effects on cell-surface roughness (a significant decrease and a significant increase, respectively). Moreover, the cell-surface mechanical properties (stiffness and adhesion force) of raft-disrupted- and/or cold-treated HUVECs were measured by the force measurement function of AFM. We found that raft disruption and cold treatment induced parallel effects on cell stiffness (increase) or adhesion force (decrease) and that the combination of the two treatments caused dramatically strengthened effects. Finally, raft disruption was found to significantly impair cell migration as previously reported, whereas temporary cold treatment only caused a slight but nonsignificant decrease in cell migration performed at physiological temperature. Although the mechanisms for causing these results might be complicated and more in-depth studies will be needed, our data may provide important information for better understanding the effects of raft disruption or cold treatment on cells and the two strategies for lipid raft research.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ando K, Obara Y, Sugama J, Kotani A, Koike N, Ohkubo S, Nakahata N (2010) P2Y2 receptor-Gq/11 signaling at lipid rafts is required for UTP-induced cell migration in NG 108-15 cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 334:809–819
Bhadriraju K, Hansen LK (2002) Extracellular matrix- and cytoskeleton-dependent changes in cell shape and stiffness. Exp Cell Res 278:92–100
Bode AP, Knupp CL (1994) Effect of cold storage on platelet glycoprotein Ib and vesiculation. Transfusion 34:690–696
Byfield FJ, Aranda-Espinoza H, Romanenko VG, Rothblat GH, Levitan I (2004) Cholesterol depletion increases membrane stiffness of aortic endothelial cells. Biophys J 87:3336–3343
Chen Y, Shao L, Ali Z, Cai J, Chen ZW (2008) NSOM/QD-based nanoscale immunofluorescence imaging of antigen-specific T-cell receptor responses during an in vivo clonal Vgamma2Vdelta2 T-cell expansion. Blood 111:4220–4232
Chen Y, Qin J, Cai J, Chen ZW (2009) Cold induces micro- and nano-scale reorganization of lipid raft markers at mounds of T-cell membrane fluctuations. PLoS One 4:e5386
Fang L, Choi SH, Baek JS, Liu C, Almazan F, Ulrich F, Wiesner P, Taleb A, Deer E, Pattison J et al (2013) Control of angiogenesis by AIBP-mediated cholesterol efflux. Nature 498:118–122
Frick M, Bright NA, Riento K, Bray A, Merrified C, Nichols BJ (2007) Coassembly of flotillins induces formation of membrane microdomains, membrane curvature, and vesicle budding. Curr Biol 17:1151–1156
Fullekrug J, Simons K (2004) Lipid rafts and apical membrane traffic. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1014:164–169
Gomez-Mouton C, Abad JL, Mira E, Lacalle RA, Gallardo E, Jimenez-Baranda S, Illa I, Bernad A, Manes S, Martinez AC (2001) Segregation of leading-edge and uropod components into specific lipid rafts during T cell polarization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:9642–9647
Huang J, Shao W, Wu L, Yang W, Chen Y (2012) Effects of exogenous ganglioside GM1 on different stages of cell spreading studied by directly quantifying spreading rate. Cell Commun Adhes 19:85–95
Huttner WB, Zimmerberg J (2001) Implications of lipid microdomains for membrane curvature, budding and fission. Curr Opin Cell Biol 13:478–484
Jin H, Pi J, Huang X, Huang F, Shao W, Li S, Chen Y, Cai J (2012) BMP2 promotes migration and invasion of breast cancer cells via cytoskeletal reorganization and adhesion decrease: an AFM investigation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 93:1715–1723
Juliano RL, Gagalang E (1977) The adhesion of Chinese hamster cells. I. Effects of temperature, metabolic inhibitors and proteolytic dissection of cell surface macromolecules. J Cell Physiol 92:209–220
Kenworthy AK (2008) Have we become overly reliant on lipid rafts? Talking point on the involvement of lipid rafts in T-cell activation. EMBO Rep 9:531–535
Kiely JM, Hu Y, Garcia-Cardena G, Gimbrone MA Jr (2003) Lipid raft localization of cell surface E-selectin is required for ligation-induced activation of phospholipase C gamma. J Immunol 171:3216–3224
Lajoie P, Goetz JG, Dennis JW, Nabi IR (2009) Lattices, rafts, and scaffolds: domain regulation of receptor signaling at the plasma membrane. J Cell Biol 185:381–385
Langner M, Kubica K (1999) The electrostatics of lipid surfaces. Chem Phys Lipids 101:3–35
Liao H, He H, Chen Y, Zeng F, Huang J, Wu L, Chen Y (2014) Effects of long-term serial cell passaging on cell spreading, migration, and cell-surface ultrastructures of cultured vascular endothelial cells. Cytotechnology. doi:10.1007/s10616-013-9560-8
Lillemeier BF, Pfeiffer JR, Surviladze Z, Wilson BS, Davis MM (2006) Plasma membrane-associated proteins are clustered into islands attached to the cytoskeleton. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:18992–18997
Lingwood D, Simons K (2010) Lipid rafts as a membrane-organizing principle. Science 327:46–50
Magee AI, Adler J, Parmryd I (2005) Cold-induced coalescence of T-cell plasma membrane microdomains activates signalling pathways. J Cell Sci 118:3141–3151
Mammoto A, Huang S, Moore K, Oh P, Ingber DE (2004) Role of RhoA, mDia, and ROCK in cell shape-dependent control of the Skp2-p27kip1 pathway and the G1/S transition. J Biol Chem 279:26323–26330
Manes S, Mira E, Gomez-Mouton C, Lacalle RA, Keller P, Labrador JP, Martinez AC (1999) Membrane raft microdomains mediate front-rear polarity in migrating cells. EMBO J 18:6211–6220
Michel V, Bakovic M (2007) Lipid rafts in health and disease. Biol Cell 99:129–140
Mounier J, Laurent V, Hall A, Fort P, Carlier MF, Sansonetti PJ, Egile C (1999) Rho family GTPases control entry of Shigella flexneri into epithelial cells but not intracellular motility. J Cell Sci 112(Pt 13):2069–2080
Munro S (2003) Lipid rafts: elusive or illusive? Cell 115:377–388
Murai T, Maruyama Y, Mio K, Nishiyama H, Suga M, Sato C (2011) Low cholesterol triggers membrane microdomain-dependent CD44 shedding and suppresses tumor cell migration. J Biol Chem 286:1999–2007
Noghero A, Perino A, Seano G, Saglio E, Lo Sasso G, Veglio F, Primo L, Hirsch E, Bussolino F, Morello F (2012) Liver X receptor activation reduces angiogenesis by impairing lipid raft localization and signaling of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 32:2280–2288
Norman LL, Oetama RJ, Dembo M, Byfield F, Hammer DA, Levitan I, Aranda-Espinoza H (2010) Modification of cellular cholesterol content affects traction force, adhesion and cell spreading. Cell Mol Bioeng 3:151–162
Pierobon P, Cappello G (2012) Quantum dots to tail single bio-molecules inside living cells. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 64:167–178
Pike LJ (2006) Rafts defined: a report on the Keystone Symposium on Lipid Rafts and Cell Function. J Lipid Res 47:1597–1598
Raucher D, Sheetz MP (1999) Characteristics of a membrane reservoir buffering membrane tension. Biophys J 77:1992–2002
Rico F, Chu C, Abdulreda MH, Qin Y, Moy VT (2010) Temperature modulation of integrin-mediated cell adhesion. Biophys J 99:1387–1396
Roca-Cusachs P, Alcaraz J, Sunyer R, Samitier J, Farre R, Navajas D (2008) Micropatterning of single endothelial cell shape reveals a tight coupling between nuclear volume in G1 and proliferation. Biophys J 94:4984–4995
Rubinsky B (2003) Principles of low temperature cell preservation. Heart Fail Rev 8:277–284
Sagvolden G, Giaever I, Pettersen EO, Feder J (1999) Cell adhesion force microscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:471–476
Shao W, Jin H, Huang J, Qiu B, Xia R, Deng Z, Cai J, Chen Y (2013) AFM investigation on Ox-LDL-induced changes in cell spreading and cell-surface adhesion property of endothelial cells. Scanning 35:119–126
Shaw AS (2006) Lipid rafts: now you see them, now you don’t. Nat Immunol 7:1139–1142
Staykova M, Holmes DP, Read C, Stone HA (2011) Mechanics of surface area regulation in cells examined with confined lipid membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:9084–9088
Sun M, Northup N, Marga F, Huber T, Byfield FJ, Levitan I, Forgacs G (2007) The effect of cellular cholesterol on membrane–cytoskeleton adhesion. J Cell Sci 120:2223–2231
Wakatsuki T, Wysolmerski RB, Elson EL (2003) Mechanics of cell spreading: role of myosin II. J Cell Sci 116:1617–1625
Wang N, Ingber DE (1994) Control of cytoskeletal mechanics by extracellular matrix, cell shape, and mechanical tension. Biophys J 66:2181–2189
Wang X, He D, Cai J, Chen T, Zou F, Li Y, Wu Y, Chen ZW, Chen Y (2009a) WGA-QD probe-based AFM detects WGA-binding sites on cell surface and WGA-induced rigidity alternation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 379:335–340
Wang Y, Chen Y, Cai J, Zhong L (2009b) QD as a bifunctional cell-surface marker for both fluorescence and atomic force microscopy. Ultramicroscopy 109:268–274
Winokur R, Hartwig JH (1995) Mechanism of shape change in chilled human platelets. Blood 85:1796–1804
Zeng F, Yang W, Huang J, Chen Y (2013) Determination of the lowest concentrations of aldehyde fixatives for completely fixing various cellular structures by real-time imaging and quantification. Histochem Cell Biol 139:735–749
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31260205 & 30900340), the Scientific Research Fund of Jiangxi Provincial Education Department (GJJ10305), and the Scientific Research Foundation for Returned Overseas Chinese Scholar of State Education Ministry.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, L., Huang, J., Yu, X. et al. AFM of the Ultrastructural and Mechanical Properties of Lipid-Raft-Disrupted and/or Cold-Treated Endothelial Cells. J Membrane Biol 247, 189–200 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-013-9624-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-013-9624-x