Abstract
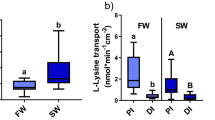
The essential amino acid histidine performs critical roles in health and disease. These functions are generally attributed to the amino acid itself, but could also be mediated by a positive effect on trace element bioavailability. Mechanistic information regarding the absorption of histidine across the gastrointestinal tract is essential for understanding the interplay between amino acid and mineral nutrients and the implications of these interactions for nutrition and toxicology. Using intestinal brush-border membrane vesicles obtained from freshwater rainbow trout, absorption of histidine over the range 0.78–780 μm was found to be saturable, with a maximal transport rate (J max) of 9.1 ± 0.8 nmol mg protein−1 min−1 and a K m (histidine concentration required to reach 50% of this level) of 339 ± 68 μm. Histidine uptake was highly specific as 10-fold elevated levels of a variety of amino acids with putative shared transporters failed to significantly inhibit uptake. Elevated levels of d-histidine, however, impaired uptake of the natural l-isomer. The presence of “luminal” copper (8.3 μm) significantly increased both the J max and K m of histidine transport. This suggests that chelated copper–histidine species cross the brush-border epithelium through transport pathways distinct from those used by histidine alone.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Babe KS Jr, Serafin WE (2000) Histamine, bradykinin, and their antagonists. In: Hardman JG, Limbird LE, Gilman AG (eds) Goodman and Gillman’s The pharmacological basis of therapeutics, 10th ed. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 581–600
Bakke-McKellep AM, Nordrum S, Krogdahl Å, Buddington RK (2000) Absorption of glucose, amino acids, and dipeptides by the intestines of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). Fish Physiol Biochem 22:33–44
Berge GE, Goodman M, Espe M, Lied E (2004) Intestinal absorption of amino acids in fish: kinetics and interaction of the in vitro uptake of l-methionine in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). Aquaculture 229:265–273
Bhardwaj RK, Herrera-Ruiz D, Eltoukhy N, Saad M, Knipp GT (2006) The functional evaluation of human peptide/histidine transporter 1 (hPHT1) in transiently transfected COS-7 cells. Eur J Pharm Sci 27:533–542
Bjerkås E, Sveier H (2004) The influence of nutritional and environmental factors on osmoregulation and cataracts in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L). Aquaculture 235:101–122
Bogé G, Roche H, Balocco C (2002) Amino acid transport by intestinal brush border vesicles of a marine fish, Boops salpa. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol 131:19–26
Bonting SL, Simon KA, Hawkins NM (1961) Studies on Na-K-ATPase. I. Quantitative distribution in several tissues of the cat. Arch Biochem Biophys 95:416–425
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of dye-binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Breck O, Sveier H (2001) Growth and cataract development in two groups of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) post smolts transferred to sea with a four-week interval. Bull Eur Assoc Fish Pathol 21:91–103
Breck O, Bjerkås E, Campbell P, Rhodes JD, Sanderson J, Waagbø R (2005) Histidine nutrition and genotype affect cataract development in Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar L. J Fish Dis 28:357–371
Bröer S (2002) Adaptation of plasma membrane amino acid transport mechanisms to physiological demands. Eur J Physiol 444:457–466
Bury NR, Walker PA, Glover CN (2003) Nutritive metal uptake in teleost fish. J Exp Biol 206:11–23
Choe KP, Kato S, Hirose S, Plata C, Sindić A, Romero MF, Claiborne JB, Evans DH (2005) NHE3 in an ancestral vertebrate: primary sequence, distribution, localization, and function in gills. Am J Physiol 289:R1520-R1534
Clearwater SJ, Farag AM, Meyer JS (2002) Bioavailability and toxicity of dietborne copper and zinc in fish. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 132:269–313
Conrad EM, Ahearn GA (2005) 3H-l-Histidine and 65Zn2+ are cotransported by a dipeptide transport system in intestine of lobster Homarus americanus. J Exp Biol 208:287–296
Daniel H, Kottra G (2004) The proton oligopeptide cotransporter family SLC15 in physiology and pharmacology. Eur J Physiol 447:610–618
Darwish HM, Cheney JC, Schmitt RC, Ettinger MJ (1984) Mobilization of copper(II) from plasma components and mechanisms of hepatic copper transport. Am J Physiol 246:G72–G79
Deschamps P, Kulkarni PP, Gautam-Basak M, Sarkar B (2005) The saga of copper(II)-l-histidine. Coord Chem Rev 249:895–909
Ferraris RP, Ahearn GA (1984) Sugar and amino acid transport in fish intestine. Comp Biochem Physiol A Physiol 77:397–413
Giordana B, Sacchi VF, Parenti P, Hanozet GM (1989) Amino acid transport systems in intestinal brush-border membranes from lepidopteran larvae. Am J Physiol 257:R494–R500
Glover CN, Hogstrand C (2002) Amino acid modulation of in vivo intestinal zinc uptake in freshwater rainbow trout. J Exp Biol 205:151–158
Glover CN, Bury NR, Hogstrand C (2003) Zinc uptake across the apical membrane of freshwater rainbow trout intestine is mediated by high affinity, low affinity and histidine-facilitated pathways. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr 1614:211–219
Glover CN, Pane EF, Wood CM (2005) Humic substances influence sodium metabolism in the freshwater crustacean, Daphnia magna. Physiol Biochem Zool 78:405–416
Glover CN, Wood CM (2008) Absorption of copper and copper-histidine complexes across the apical surface of freshwater rainbow trout intestine. J Comp Physiol B. doi:10.1007/s00360-007-0203-2
Herrera-Ruiz D, Wang Q, Gudmundsson OS, Cook TJ, Smith RL, Faria TN, Knipp GT (2001) Spatial expression patterns of peptide transporters in the human and rat gastrointestinal tracts, Caco-2 in vitro cell culture model, and multiple human tissues. AAPS PharmSci 3:E9
Huang KC, Chen TST (1975) Comparative biological aspects of intestinal absorption. In: Csáky TZ (ed) Intestinal absorption and malabsorption. Raven Press, New York, pp 187–196
Kasaoka S, Tsuboyama-Kasaoka N, Kawahara Y, Inoue S, Tsuji M, Ezaki O, Kato H, Tsuchiya T, Okuda H, Nakajima S (2004) Histidine supplementation suppresses food intake and fat accumulation in rats. Nutrition 20:991–996
Klaren PHM, Flik G, Lock RAC, Wendelaar Bonga SE (1993) Ca2+ transport across intestinal brush border membranes of the cichlid teleost Oreochromis mossambicus. J Membr Biol 132:157–166
Menzies FD, Cockford T, Breck O, Midtlyng PJ (2002) Estimation of direct costs associated with cataracts in farmed Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Bull Eur Assoc Fish Pathol 22:27–32
Midtlyng PJ, Ahrend M, Bjerkås E, Waagbø R, Wall T (1999) Current research on cataracts in fish. Bull Eur Assoc Fish Pathol 19:299–301
Nadella S, Grosell M, Wood CM (2006) Physical characterization of high affinity gastrointestinal Cu transport in vitro in freshwater rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss. J Comp Physiol B 176:793–806
National Research Council (NRC) (1993) Nutrient requirements of fish. Committee of Animal Nutrition, Board of Agriculture, National Academy Press, Washington DC
Neal JJ, Wu D, Hong YS, Reuveni M (1996) High affinity transport of histidine and methionine across Leptinotarsa decemlineata midgut brush-border membrane. J Insect Physiol 42:329–335
Read CP, Simmons JE, Campbell JW, Rothman AH (1960) Permeation and membrane transport in parasitism studies on a tapeworm-elasmobranch symbiosis. Biol Bull 119:120–133
Schneider F (1978) Histidine in enzyme active centers. Angewan Chem Int Ed 17:583–592
Steck TL, Kant JA (1974) Preparation of impermeable ghosts and inside–out vesicles from human erythrocyte membranes. Methods Enzymol 31A:172–180
Sundberg RJ, Martin RB (1974) Interactions of histidine and other imidazole derivatives with transition metal ions in chemical and biological systems. Chem Rev 74:471–514
Teillet L, Tacnet F, Ripoche P, Corman B (1995) Effect of aging on zinc and histidine transport across rat intestinal brush-border membranes. Mech Ageing Dev 79:151–167
Yamashita T, Shimada S, Guo W, Sato K, Kohmura E, Hayakawa T, Takagi T, Tohyama M (1997) Cloning and functional expression of a brain peptide/histidine transporter. J Biol Chem 272:10205–10213
Acknowledgements
We thank all members of the Wood Laboratory, McMaster University, with special gratitude reserved for the logistical and nutritive assistance of Sunita Nadella. C. M. W. was supported by the Canada Research Chair program. C. N. G. was supported by Norwegian boxer briefs.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Glover, C.N., Wood, C.M. Histidine Absorption across Apical Surfaces of Freshwater Rainbow Trout Intestine: Mechanistic Characterization and the Influence of Copper. J Membrane Biol 221, 87–95 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-007-9088-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-007-9088-y