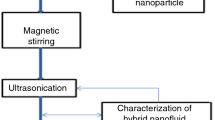
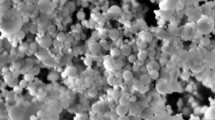
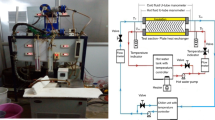
Abstract
Energetic and exergetic analyses of the plate heat exchanger are experimentally performed using Al2O3–TiO2 hybrid nanofluid as a coolant for sub-ambient temperature application to study the effect of nanoparticle volume ratio at various nanofluid flow rates ranging 2.0–4.0 lpm and inlet temperatures ranging 10–25 °C. The Al2O3–TiO2 hybrid nanofluids of 0.1% total volume concentration with different Al2O3–TiO2 ratios (5:0, 4:1, 3:2, 2:3, 1:4 and 0:5) are used as a coolant. Effects of nanoparticle mixture ratio, flow rate and inlet temperature on the heat transfer rate, heat transfer coefficient, pump work, performance index, and second law efficiency are investigated. Correlations are proposed to predict the Nusselt number for DI water as well as hybrid nanofluid. A maximum enhancement of around 16.91% and 4.5% are observed for convective heat transfer coefficient and heat transfer rate with Al2O3 (5:0) hybrid nanofluid along with 0.013% enhancement (insignificant) in the pump work for TiO2 (0:5) hybrid nanofluid. The maximum reduction in exergetic efficiency of 4.01% is observed for TiO2 (0:5) hybrid nanofluid. The study shows that the energetic and exergetic performances decrease continuously with the increase of the TiO2 ratio in the mixture, yielding no optimum nanoparticle mixture ratio.















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A:
-
Effective area of heat transfer, m2.
- cp :
-
Specific heat, J/kg. K.
- D:
-
Diameter, m.
- Dh :
-
Hydraulic diameter, m.
- E:
-
Exergy rate, W.
- G:
-
Mass velocity, kg/s.m2.
- k:
-
Thermal conductivity, W/m.K.
- m:
-
Mass, kg.
- ṁ:
-
Mass flow rate, kg/s.
- Nu:
-
Nusselt number.
- P:
-
Pump work, W.
- p:
-
Pressure, Pa.
- Pr:
-
Prandtl number.
- Q:
-
Heat transfer rate, W.
- Re:
-
Reynolds number.
- t:
-
Thickness of the plate, mm.
- T:
-
Temperature, °C.
- U:
-
Overall heat transfer coefficient, W/m2K.
- V:
-
Volume, m3.
- w:
-
Weight, N.
- X:
-
Uncertainty, %.
- AA:
-
Acetic acid
- Al2O3 :
-
Alumina nanoparticle
- CTAB:
-
Cetyl trimethyl ammonium bromide
- CuO:
-
Copper oxide nanoparticle
- DI:
-
De-ionized water
- IEP:
-
Iso-electric point
- MWCNT:
-
Multiwalled carbon nanotube
- OA:
-
Oleic acid
- PHE:
-
Plate heat exchanger
- PI:
-
Performance index
- SEM:
-
Scanning Electron Microscopy
- SDS:
-
Sodium dodecyl sulfate
- SiO2 :
-
Silica nanoparticle
- TiO2 :
-
Titania nanoparticle
- v%:
-
Percentage volume concentration
- wt.%:
-
Percentage weight concentration
- x:
-
Uncertainty
- α:
-
Heat transfer coefficient, W/m2K
- ∆p:
-
Pressure drop, Pa
- μ:
-
Dynamic viscosity, Pa.s
- ρ:
-
Density, kg/m3
- Φ:
-
Volume concentration
- η:
-
Efficiency, %
- 1:
-
First
- 2:
-
Second
- II:
-
Second law
- av:
-
Average
- c:
-
cold
- e:
-
Ambient
- h:
-
Hot
- i:
-
Inlet
- nf:
-
Nanofluid
- np:
-
Nanoparticle
- o:
-
Outlet
- w:
-
Wall
References
Abou Elmaaty TM, Kabeel AE, Mahgoub M (2017) Corrugated plate heat exchanger review. Renew Sust Energ Rev 70:852–860
Sarkar J, Ghosh P, Adil A (2015) A review on hybrid nanofluids : recent research, development and applications. Renew Sust Energ Rev 43:164–177
Gupta M, Singh V, Kumar S, Kumar S, Dilbaghi N, Said Z (2018) Up to date review on the synthesis and thermophysical properties of hybrid nanofluids. J Clean Prod 190:169–192
Sundar LS, Sharma KV, Singh MK, Sousa ACM (2017) Hybrid nanofluids preparation, thermal properties, heat transfer and friction factor – a review. Renew Sust Energ Rev 68:185–198
Zaraki A, Ghalambaz M, Chamkha AJ, Ghalambaz M, Rossi DD (2015) Theoretical analysis of natural convection boundary layer heat and mass transfer of nanofluids: effects of size, shape and type of nanoparticles, type of base fluid and working temperature. Adv Powder Technol 26:935–946
Ghalambaz M, Doostani A, Chamkha AJ, Ismael MA (2017) Melting of nanoparticles-enhanced phase-change materials in an enclosure: effect of hybrid nanoparticles. Int J Mech Sci 134:85–97
Ghalambaz M, Doostani A, Izadpanahi E, Chamkha AJ (2017) Phase-change heat transfer in a cavity heated from below: the effect of utilizing single or hybrid nanoparticles as additives. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 72:104–115
Ghalambaz M, Doostani A, Izadpanahi E, Chamkha AJ (2020) Conjugate natural convection flow of Ag–MgO/water hybrid nanofluid in a square cavity. J Therm Anal Calorim 139:2321–2336
Sidik NAC, Jamil MM, Aziz-Japar WMA, Adamu IM (2017) A review on preparation methods, stability and applications of hybrid nanofluids. Renew Sust Energ Rev 80:1112–1122
Sridhara V, Satapathy LN (2011) Al2O3-based nanofluids: a review. Nanoscale Res Lett 6:456
Yang L, Du K (2017) A comprehensive review on heat transfer characteristics of TiO2 nanofluids. Int J Heat Mass Transf 108:11–31
Qi C, Wan YL, Wang GQ, Han DT (2018) Study on stabilities, thermophysical properties and natural convective heat transfer characteristics of TiO2-water nanofluids. Indian J Phys 92(4):461–478
Alkasmoul FS, Al-Asadi MT, Myers TG, Thompson HM, Wilson MCT (2018) A practical evaluation of the performance of Al2O3-water, TiO2-water and CuO-water nanofluids for convective cooling. Int J Heat Mass Transf 126:639–651
Maddah H, Aghayari R, Mirzaee M, Hossein M (2018) Factorial experimental design for the thermal performance of a double pipe heat exchanger using Al2O3-TiO2 hybrid nanofluid. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 97:92–102
Das PK, Mallik AK, Ganguly R, Santra AK (2016) Synthesis and characterization of TiO2-water nanofluids with different surfactants. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 75:341–348
Pandey SD, Nema VK (2012) Experimental analysis of heat transfer and friction factor of nanofluid as a coolant in a corrugated plate heat exchanger. Exp Thermal Fluid Sci 38:248–256
Javadi FS, Sadeghipour S, Saidur R, BoroumandJazi G, Rahmati B, Elias MM, Sohel MR (2013) The effects of nanofluid on thermophysical properties and heat transfer characteristics of a plate heat exchanger. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 44:58–63
Tiwari AK, Ghosh P, Sarkar J (2013) Performance comparison of the plate heat exchanger using different nanofluids. Exp Thermal Fluid Sci 49:141–151
Tiwari AK, Ghosh P, Sarkar J (2015) Particle concentration levels of various nanofluids in plate heat exchanger for best performance. Int J Heat Mass Transf 89:1110–1118
Barzegarian R, Moraveji MK, Aloueyan A (2016) Experimental investigation on heat transfer characteristics and pressure drop of BPHE (brazed plate heat exchanger) using TiO2-water nanofluid. Exp Thermal Fluid Sci 74:11–18
Tabari ZT, Heris SZ, Moradi M, Kahani M (2016) The study on application of TiO2/water nanofluid in plate heat exchanger of milk pasteurization industries. Renew Sust Energ Rev 58:1318–1326
Huang D, Wu Z, Sunden B (2016) Effects of hybrid nanofluid mixture in plate heat exchangers. Exp Thermal Fluid Sci 72:190–196
Bhattad A, Sarkar J, Ghosh P (2020) Hydrothermal performance of different alumina hybrid nanofluid types in plate heat exchanger. J Therm Anal Calorim 139:3777–3787
Hamid KA, Azmi WH, Nabil MF, Mamat R, Sharma KV (2018) Experimental investigation of thermal conductivity and dynamic viscosity on nanoparticle mixture ratios of TiO2-SiO2nanofluids. Int J Heat Mass Transf 116:1143–1152
Charab AA, Movahedirad S, Norouzbeigi R (2017) Thermal conductivity of Al2O3+TiO2/water nanofluid: model development and experimental validation. Appl Therm Eng 119:42–51
Hamid KA, Azmi WH, Nabil MF, Mamat R (2018) Experimental investigation of nanoparticle mixture ratios on TiO2–SiO2 nanofluids heat transfer performance under turbulent flow. Int J Heat Mass Transf 118:617–627
Zawawi NNM, Azmi WH, Sharif MZ, Najafi G (2019) Experimental investigation on stability and thermo-physical properties of Al2O3–SiO2/PAG nanolubricants with different nanoparticle ratios. J Therm Anal Calorim 135:1243–1255
Nimmagadda R, Venkatasubbaiah K (2015) Conjugate heat transfer analysis of micro-channel using novel hybrid nanofluids (Al2O3+Ag/water). Eur J Mech B/Fluids 52:19–27
Bhattad A, Sarkar J, Ghosh P (2019) Experimentation on effect of particle ratio on hydrothermal performance of plate heat exchanger using hybrid nanofluid. Appl Therm Eng 162:114309
Bhattad A, Sarkar J, Ghosh P (2018) Discrete phase numerical model and experimental study of hybrid nanofluid heat transfer and pressure drop in plate heat exchanger. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf 91:262–273
Bhattad A, Sarkar J, Ghosh P (2020) Energetic and exergetic performances of plate heat exchanger using brine based hybrid nanofluid for milk chilling application. Heat Transfer Eng 41:522–535
Stogiannis IA, Mouza AA, Paras SV (2015) Efficacy of SiO2 nanofluids in a miniature plate heat exchanger with undulated surface. Int J Therm Sci 92:230–238
Pantzali MN, Kanaris AG, Antoniadis KD, Mouza AA, Paras SV (2009) Effect of nanofluids on the performance of a miniature plate heat exchanger with modulated surface. Int J Heat Fluid Flow 30:691–699
Huang D, Wu Z, Sunden B (2015) Pressure drop and convective heat transfer of Al2O3/waterand MWCNT/water nanofluids in a chevron plate heat exchanger. Int J Heat Mass Transf 89:620–626
Kakac S, Liu H (2002) Heat exchangers: selection, rating and thermal design, 2nd ed. CRC Press LLC, Florida, USA
Bhattad A, Sarkar J, Ghosh P (2018) Improving the performance of refrigeration systems by using nanofluids: a comprehensive review. Renew Sust Energ Rev 82:3656–3669
Ghalambaz M, Chamkha AJ, Wen D (2019) Natural convective flow and heat transfer of Nano-encapsulated phase change materials (NEPCMs) in a cavity. Int J Heat Mass Transf 138:738–749
Ghalambaz M, Groşan T, Pop I (2019) Mixed convection boundary layer flow and heat transfer over a vertical plate embedded in a porous medium filled with a suspension of nano-encapsulated phase change materials. J Mol Liq 293:111432
Hajjar A, Mehryan SAM, Ghalambaz M (2020) Time periodic natural convection heat transfer in a nano-encapsulated phase-change suspension. Int J Mech Sci 166:105243
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhattad, A., Sarkar, J. & Ghosh, P. Heat transfer characteristics of plate heat exchanger using hybrid nanofluids: effect of nanoparticle mixture ratio. Heat Mass Transfer 56, 2457–2472 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00231-020-02877-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00231-020-02877-y