Abstract
Computational investigations are reported on the local flow and heat transfer characteristics from staggered, multiple circular air jets impinging on a flat surface with effusion holes. The geometrical and flow parameters for the computational study are chosen as per the experimental arrangement of Cho and Rhee J Turbomachinery 123:601–608, (14) so as to explain salient features observed in these experiments. The two peaks in the Nusselt number observed in the case of H/D = 6 and three peaks in the case of H/D = 2 are attributed to the flow characteristics such as primary vortices forming an up-wash region, followed by secondary vortices resulting in a secondary stagnation zone. The magnitude of local peak in heat transfer increases up to 88% with increasing values of D/d from 0.5 to 1.5 at Re = 10,000.






















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- c:
-
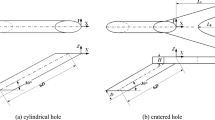
Center to center distance of jet holes, m
- D:
-
Diameter of jet hole, m
- d:
-
Diameter of film hole, m
- H:
-
Distance between target surface and jet hole exit, m
- kf :
-
Thermal conductivity of fluid, W/m–K
- m:
-
Mass flow rate, kg/sec
- Nu:
-
Nusselt number
- q″:
-
Local heat flux, W/m2
- p:
-
Local static pressure, N/m2
- pmax :
-
Maximum local static pressure, N/m2
- Cp :
-
Pressure coefficient (p/p max)
- p0 :
-
Stagnation pressure, N/m2
- Tj :
-
Jet temperature, K
- Ttp :
-
Target plate temperature, K
- v:
-
Velocity magnitude in y—direction, m/s
- U:
-
Jet exit velocity, m/s
- t1 :
-
Jet plate thickness, m
- t2 :
-
Target plate thickness, m
- x:
-
x-co-ordinate, m
- y:
-
y-co-ordinate, m
- z:
-
z-co-ordinate, m
References
Livingood NB, Hrycay P (1973) Impingement heat transfer from turbulent air jets to flat plates: a literature survey. NASA TM X- 2778
Martin H (1977) Heat and mass transfer between impinging gas jets and solid surfaces. Adv Heat Transf 13:1–60
Downs SJ, James EH (1987) Jet impingement heat transfer: a literature survey. ASME 87-H-35, proceedings of the national heat transfer conference. Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, August 9–12
Jambunathan K, Lai E, Moss MA, Button BL (1992) A review of heat transfer data for single circular jet impingement. Int J Heat Fluid Flow 13–2:106–115
Viskanta R (1993) Heat transfer to impinging isothermal gas and flame jets. Exp Ther Fluid Sci 6:111–134
Sezai I, Mohamad AA (1999) Three dimensional stimulation of laminar rectangular impinging jets, flow structure, and heat transfer. Trans ASME J Heat Transf 121:50–56
Aldabagh LBY, Sezai I, Mohamad AA (2003) Three dimensional investigation of a laminar impinging square jet interaction with cross-flow. ASME J Heat Transf 125:243–249
Aldabagh LBY, Mohamad AA (2007) Effect of jet-to-plate spacing in laminar array jets impinging. Heat Mass Transf 43:265–273
Aldabbagh LBY, Mohamad AA (2009) Mixed convection in an impinging laminar single square jet. ASME J Heat Transf 131(022201):1–7
Aldabbag LBY, Mohamad AA (2009) A three dimensional numerical simulation of impinging jet arrays on a moving plate. Int J Heat and Mass Transf 52:4894–4900
Hollworth BR, Dangan L (1980) Arrays of impinging jets with spent fluid removal through vent holes on the target surface part I: average heat transfer. Trans ASME J Eng Power 102:994–999
Hollworth BR, Lehmann G, Rosiczkowski J (1983) Arrays of impinging jets with spent fluid removal through vent holes on the target surface part II: local heat transfer. Trans ASME J Eng Power 105:393–402
Ekkad SV, Huang Y, Han JC (1999) Impingement heat transfer on a target plate with film cooling holes. AIAA J Thermophys Heat Transf 13(4):522–528
Cho HH, Rhee DH (2001) Local heat/mass transfer measurement on the effusion plate in impingement/effusion cooling systems. J Turbomachinery 123:601–608
Ramakumar BVN, Prasad BVSSS (2008) Computational flow and heat transfer of a circular jets impinging on a concave surface. Heat Mass Transf 44(6):667–678
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ashok kumar, M., Prasad, B.V.S.S.S. Computational flow and heat transfer of multiple circular jets impinging on a flat surface with effusion. Heat Mass Transfer 47, 1121–1132 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00231-011-0776-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00231-011-0776-x