Abstract
Purpose
We aimed to quantitatively assess the effects of short-term statin use on delayed ischemic neurologic deficits (DINDs) and clinical outcomes in patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) through a meta-analysis of the available evidence.
Methods
We searched the electronic databases up to April 8, 2016 to retrieve relevant studies comparing the outcomes between immediate statin-treated in statin-naïve patients and untreated patients following aneurysmal SAH. Meta-analysis was performed using Review Manager 5.3.
Results
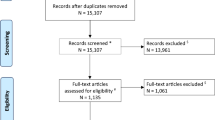
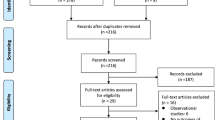
Eight randomized controlled clinical trials (RCTs) and 5 observational studies involving 2148 patients met the eligibility criteria. In the RCTs, statins were found to significantly reduce the occurrence of DINDs (relative risk (RR), 0.76; 95% confidence interval (CI), 0.61–0.94; P = 0.01), but did not significantly reduce poor functional outcomes (RR, 1.01; 95% CI, 0.87–1.16; P = 0.93) or mortality (RR, 0.80; 95% CI, 0.58–1.11; P = 0.18). In observational studies, statin use was not associated with any reduction in DINDs, poor outcome, or mortality. Meta-analysis of RCTs indicated a significant reduction in DINDs and mortality in patients with high-dose statin use (RR, 0.63; 95% CI, 0.42–0.95; P = 0.03; I 2 = 0%; and RR, 0.36; 95% CI, 0.15–0.86; P = 0.02; I 2 = 0%, respectively).
Conclusion
The present meta-analysis suggests that statin use may prevent DINDs in patients with aneurysmal SAH. Based on our findings, the role of statins in improving neurological outcome was limited. However, the risk of DINDs and mortality decreased with higher statin doses in a dose-dependent manner. Hence, further well-designed RCTs with modified protocols in specific patients are required.






Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
31 July 2017
An erratum to this article has been published.
References
Connolly ES Jr, Rabinstein AA, Carhuapoma JR, Derdeyn CP, Dion J, Higashida RT, Hoh BL, Kirkness CJ, Naidech AM, Ogilvy CS, Patel AB, Thompson BG, Vespa P, American Heart Association Stroke Council, Council on Cardiovascular Radiology and Intervention, Council on Cardiovascular Nursing, Council on Cardiovascular Surgery and Anesthesia, Council on Clinical Cardiology (2012) Guidelines for the management of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 43:1711–1737
Yundt KD, Grubb RL Jr, Diringer MN, Powers WJ (1998) Autoregulatory vasodilation of parenchymal vessels is impaired during cerebral vasospasm. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 18:419–424
Takeuchi H, Handa Y, Kobayashi H, Kawano H, Hayashi M (1991) Impairment of cerebral autoregulation during the development of chronic cerebral vasospasm after subarachnoid hemorrhage in primates. Neurosurgery 28:41–48
Kassell NF, Torner JC, Haley EC Jr, Jane JA, Adams HP, Kongable GL (1990) The International Cooperative Study on the Timing of Aneurysm Surgery. Part 1: overall management results. J Neurosurg 73:18–36
Bederson JB, Connolly ES, Batjer HH, Dacey RG, Dion JE, Diringer MN, Duldner JE Jr, Harbaugh RE, Patel AB, Rosenwasser RH, American Heart Association (2009) Guidelines for the management of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: a statement for healthcare professionals from a special writing group of the stroke council, American Heart Association. Stroke 40:994–1025
Macdonald RL, Pluta RM, Zhang JH (2007) Cerebral vasospasm after subarachnoid hemorrhage: the emerging revolution. Nat Clin Pract Neurol 3:256–263
Rabinstein AA, Lanzino G, Wijdicks EF (2010) Multidisciplinary management and emerging therapeutic strategies in aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage. Lancet Neurol 9:504–519
McGirt MJ, Lynch JR, Parra A, Sheng H, Pearlstein RD, Laskowitz DT, Pelligrino DA, Warner DS (2002) Simvastatin increases endothelial nitric oxide synthase and ameliorates cerebral vasospasm resulting from subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke 33:2950–2956
Sabri M, Ai J, Marsden PA, Macdonald RL (2011) Simvastatin re-couples dysfunctional endothelial nitric oxide synthase in experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage. PLoS One 6:e17062
Tseng M, Czosnyka M, Richards H, Pickard JD, Kirkpatrick PJ (2005) Effects of acute treatment with pravastatin on cerebral vasospasm, autoregulation, and delayed ischemic deficits after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: a phase II randomized placebo-controlled trial. Stroke 36:1627–1632
Lynch JR, Wang H, McGirt MJ, Floyd J, Friedman AH, Coon AL, Blessing R, Alexander MJ, Graffagnino C, Warner DS, Laskowitz DT (2005) Simvastatin reduces vasospasm after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke 36:2024–2026
Chou SH, Smith EE, Badjatia N, Nogueira RG, Sims JR II, Ogilvy CS, Rordorf GA, Ayata C (2008) A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot study of simvastatin in aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke 39:2891–2893
Kirkpatrick PJ, Turner CL, Smith C, Hutchinson PJ, Murray GD, STASH Collaborators (2014) Simvastatin in aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage (STASH): a multicentre randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Neurol 13:666–675
Wong GK, Chan DY, Siu DY, Zee BC, Poon WS, Chan MT, Gin T, Leung M, HDS-SAH Investigators (2015) High-dose simvastatin for aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: multicenter randomized controlled double-blinded clinical trial. Stroke 46:382–328
Su SH, Xu W, Hai J, Wu YF, Yu F (2014) Effects of statins-use for patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Sci Rep 20144:4573
Higgins JP, Green S Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0. http://www.cochrane-handbook.org
DerSimonian R, Laird N (1986) Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials 7:177–188
Higgins JP, Thompson SG (2002) Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med 21:1539–1558
Vergouwen M, Meijers J, Geskus RB, Coert BA, Horn J, Stroes ES, van der Poll T, Vermeulen M, Roos YB (2009) Biological effects of simvastatin in patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: a double-blind, placebo-controlled randomized trial. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 29:1444–1453
Jaschinski U, Scherer K, Lichtwarck M, Forst H (2008) Impact of treatment with pravastatin on delayed ischemic disease and mortality after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Crit Care 12:P112
Macedo S, Belio Y, Siqueria C, Siqueria S, Brito L (2009) Effects of simvastatin in prevention of vasospasm in nontraumatic subarachnoid hemorrhage: preliminary data. Crit Care 13:P103
Garg K, Sinha S, Kale SS, Chandra PS, Suri A, Singh MM, Kumar R, Sharma MS, Pandey RM, Sharma BS, Mahapatra AK (2013) Role of simvastatin in prevention of vasospasm and improving functional outcome after aneurysmal sub-arachnoid hemorrhage: a prospective, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot trial. Br J Neurosurg 27:181–186
Kramer AH, Gurka MJ, Nathan B, Dumont AS, Kassell NF, Bleck TP (2008) Statin use was not associated with less vasospasm or improved outcome after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurosurgery 62:422–427
Kerz T, Victor A, Beyer C, Trapp I, Heid F, Reisch R (2008) A case control study of statin and magnesium administration in patients after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: incidence of delayed cerebral ischemia and mortality. Neurol Res 30:893–897
Kern M, Lam MM, Knuckey NW, Lind CR (2009) Statins may not protect against vasospasm in subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Clin Neurosci 16:527–530
McGirt MJ, Garces Ambrossi GL, Huang J, Tamargo RJ (2009) Simvastatin for the prevention of symptomatic cerebral vasospasm following aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: a single-institution prospective cohort study. J Neurosurg 110:968–974
Sanchez-Peña P, Nouet A, Clarençon F, Colonne C, Jean B, Le Jean L, Fonfrede M, Aout M, Vicaut E, Puybasset L (2012) Atorvastatin decreases computed tomography and S100-assessed brain ischemia after subarachnoid aneurysmal hemorrhage: a comparative study. Crit Care Med 40:594–602
Vergouwen MD, Etminan N, Ilodigwe D, Macdonald RL (2011) Lower incidence of cerebral infarction correlates with improved functional outcome after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 31:1545–1553
Etminan N, Vergouwen MD, Ilodigwe D, Macdonald RL (2011) Effect of pharmaceutical treatment on vasospasm, delayed cerebral ischemia, and clinical outcome in patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 31:1443–1451
Cahill J, Zhang JH (2009) Subarachnoid hemorrhage: is it time for a new direction? Stroke 40:S86–S87
Ma J, Huang S, Ma L, Liu Y, Li H, You C (2012) Endothelin-receptor antagonists for aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: an updated meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Crit Care 16:R198
Shen J, Pan JW, Fan ZX, Xiong XX, Zhan RY (2013) Dissociation of vasospasm-related morbidity and outcomes in patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage treated with clazosentan: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Neurosurg 119:180–189
Golan E, Vasquez DN, Ferguson ND, Adhikari NK, Scales DC (2013) Prophylactic magnesium for improving neurologic outcome after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Crit Care 28:173–181
Diringer MN, Bleck TP, Claude Hemphill IIIJ, Menon D, Shutter L, Vespa P, Bruder N, Connolly ES Jr, Citerio G, Gress D, Hänggi D, Hoh BL, Lanzino G, Le Roux P, Rabinstein A, Schmutzhard E, Stocchetti N, Suarez JI, Treggiari M, Tseng MY, Vergouwen MD, Wolf S, Zipfel G, Neurocritical Care Society (2011) Critical care management of patients following aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: recommendations from the Neurocritical Care Society’s Multidisciplinary Consensus Conference. Neurocrit Care 15:211–240
Sabri M, Macdonald RL (2010) Statins: a potential therapeutic addition to treatment for aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage? World Neurosurg 73:646–653
Violi F, Calvieri C, Ferro D, Pignatelli P (2013) Statins as antithrombotic drugs. Circulation 127:251–257
Endres M (2005) Statins and stroke. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 25:1093–1110
Scheitz JF, Seiffge DJ, Tütüncü S, Gensicke H, Audebert HJ, Bonati LH, Fiebach JB, Tränka C, Lyrer PA, Endres M, Engelter ST, Nolte CH (2014) Dose-related effects of statins on symptomatic intracerebral hemorrhage and outcome after thrombolysis for ischemic stroke. Stroke 45:509–514
Dormuth CR, Hemmelgarn BR, Paterson JM, James MT, Teare GF, Raymond CB, Lafrance JP, Levy A, Garg AX, Ernst P, Canadian Network for Observational Drug Effect Studies (2013) Use of high potency statins and rates of admission for acute kidney injury: multicenter, retrospective observational analysis of administrative databases. BMJ 346:f880
Egger M, Davey Smoth G, Altman DG (2001) Systematic reviews in healthcare: meta-analysis in context. BMJ Publishing Group, London, pp 211–227
Ní Chróinín D, Asplund K, Åsberg S, Callaly E, Cuadrado-Godia E, Díez-Tejedor E, Di Napoli M, Engelter ST, Furie KL, Giannopoulos S, Gotto AM Jr, Hannon N, Jonsson F, Kapral MK, Martí-Fàbregas J, Martínez-Sánchez P, Milionis HJ, Montaner J, Muscari A, Pikija S, Probstfield J, Rost NS, Thrift AG, Vemmos K, Kelly PJ (2013) Statin therapy and outcome after ischemic stroke: systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies and randomized trials. Stroke 44:448–456
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by a grant of the Korea Health Technology R&D Project through the Korea Health Industry Development Institute (KHIDI), funded by the Ministry of Health & Welfare, Republic of Korea (grant number: HC15C1234).
Author contributions
All authors contributed to the design of the study. K.-S.C., T.L., W.K., and Y.C. undertook the searches and screened studies for eligibility. K.-S.C., J.M.K., and H.-J.Y. assessed the quality of papers and performed statistical analyses. K.-S.C. and S.H-.L. drafted the manuscript. T.L., W.K., and J.-H.C. moderated disagreements during data collection and analyzed the data. K.-S.C. and S.-H.L. critically revised the manuscript for important intellectual content. All authors revised the manuscript and approved the final version.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
An erratum to this article is available at https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-017-2294-3.
Electronic supplementary material
Online Resource 1
(DOCX 15 kb)
Online Resource 2
(DOCX 267 kb)
Online Resource 3
(DOCX 21 kb)
Online Resource 4
(DOCX 20 kb)
Online Resource 5
(DOCX 33 kb)
Online Resource 6
(DOCX 33 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, KS., Kim, J.M., Yi, HJ. et al. Dose-related effect of statins in patients with endovascular coiling or microsurgical clipping for aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: updated study-level meta-analysis. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 73, 1071–1081 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-017-2221-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-017-2221-7