Abstract
Purpose
Anticholinergic drugs are known to cause physical and cognitive impairment, particularly in older patients. The total of all anticholinergic influences to which a patient is exposed is referred to as anticholinergic load. Because the anticholinergic load is defined in various ways, this review aimed to describe differences in the development and evaluation of available methods calculating the anticholinergic load.
Methods
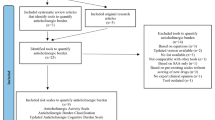
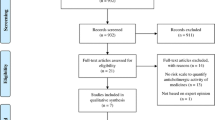
From September 2014 to August 2015, two reviewers performed a literature search in PubMed considering relevant items of the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guideline. We aimed to identify articles which calculated the anticholinergic load with a scale or equation and investigated its association with patient-related outcomes. From the included studies, we descriptively analyzed the identification and scoring criteria of the scales and equations with a main emphasis on their association to the reported outcomes.
Results
Out of 465 articles, 55 were included referring to 12 scales and one equation. Main discrepancies were located in eight different identification criteria for anticholinergic drugs, two different scoring principles, and 118 tests used for assessing outcomes. The methods most frequently detecting a significant association between the anticholinergic load and outcomes took into account the drugs’ dosages and anticholinergic potencies. Interestingly, none of the methods included the patient’s susceptibility for anticholinergic effects and they only rarely considered modulators of drug exposure.
Conclusions
Due to hugely varying tests for assessing outcomes, the methods are scarcely comparable. For a more valuable comparison, the anticholinergic load should be calculated with all scales and the equation and correlated with patient-related outcomes.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Durán CE, Azermai M, Vander Stichele RH (2013) Systematic review of anticholinergic risk scales in older adults. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 69:1485–1496. doi:10.1007/s00228-013-1499-3
Mintzer J, Burns A (2000) Anticholinergic side-effects of drugs in elderly people. J R Soc Med 93:457–462
Minzenberg MJ, Poole JH, Benton C, Vinogradov S (2004) Association of anticholinergic load with impairment of complex attention and memory in schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 161:116–124
Rudolph JL, Salow MJ, Angelini MC, McGlinchey RE (2008) The anticholinergic risk scale and anticholinergic adverse effects in older persons. Arch Intern Med 168:508–513
Mangoni AA, van Munster BC, Woodman RJ, de Rooij SE (2013) Measures of anticholinergic drug exposure, serum anticholinergic activity, and all-cause postdischarge mortality in older hospitalized patients with hip fractures. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry 21:785–793. doi:10.1016/j.jagp.2013.01.012
Kumpula EK, Bell JS, Soini H, Pitkälä KH (2011) Anticholinergic drug use and mortality among residents of long-term care facilities: a prospective cohort study. J Clin Pharmacol 51:256–263. doi:10.1177/0091270010368410
Wilson NM, Hilmer SN, March LM, Chen JS, Gnjidic D, Mason RS, Cameron ID, Sambrook PN (2012) Associations between drug burden index and mortality in older people in residential aged care facilities. Drugs Aging 29:157–165. doi:10.2165/11598570-000000000-00000
Lampela P, Lavikainen P, Garcia-Horsman JA, Bell JS, Huupponen R, Hartikainen S (2013) Anticholinergic drug use, serum anticholinergic activity, and adverse drug events among older people: a population-based study. Drugs Aging 30:321–330. doi:10.1007/s40266-013-0063-2
Kashyap M, Belleville S, Mulsant BH, Hilmer SN, Paquette A, Tu le M, Tannenbaum C (2014) Methodological challenges in determining longitudinal associations between anticholinergic drug use and incident cognitive decline. J Am Geriatr Soc 62:336–341. doi:10.1111/jgs.12632
Pasina L, Djade CD, Lucca U, Nobili A, Tettamanti M, Franchi C, Salerno F, Corrao S, Marengoni A, Iorio A, Marcucci M, Violi F, Mannucci PM (2013) Association of anticholinergic burden with cognitive and functional status in a cohort of hospitalized elderly: comparison of the anticholinergic cognitive burden scale and anticholinergic risk scale: results from the REPOSI study. Drugs Aging 30:103–112. doi:10.1007/s40266-012-0044-x
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, PRISMA Group (2010) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Int J Surg 8:336–341. doi:10.1016/j.ijsu.2010.02.007
Kersten H, Wyller TB (2014) Anticholinergic drug burden in older people’s brain—how well is it measured? Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 114:151–159. doi:10.1111/bcpt.12140
Lertxundi U, Domingo-Echaburu S, Hernandez R, Peral J, Medrano J (2013) Expert-based drug lists to measure anticholinergic burden: similar names, different results. Psychogeriatrics 13:17–24. doi:10.1111/j.1479-8301.2012.00418.x
Gerretsen P, Pollock BG (2011) Drugs with anticholinergic properties: a current perspective on use and safety. Expert Opin Drug Saf 10:751–765. doi:10.1517/14740338.2011.579899
Slattum PW, Vargas-Irwin C, Dharia SP, Robles JR (2008) Comparison of two drug-burden computational procedures applied to anticholinergic drugs. AMIA Annu Symp Proc. xx:1138.
Rudd KM, Raehl CL, Bond CA, Abbruscato TJ, Stenhouse AC (2005) Methods for assessing drug-related anticholinergic activity. Pharmacotherapy 25:1592–1601
Faure R, Dauphinot V, Krolak-Salmon P, Mouchoux C (2013) A standard international version of the Drug Burden Index for cross-national comparison of the functional burden of medications in older people. J Am Geriatr Soc 61:1227–1228. doi:10.1111/jgs.12343
Peron EP, Gray SL, Hanlon JT (2011) Medication use and functional status decline in older adults: a narrative review. Am J Geriatr Pharmacother 9:378–391. doi:10.1016/j.amjopharm.2011.10.002
Salahudeen MS, Hilmer SN, Nishtala PS (2015) Comparison of anticholinergic risk scales and associations with adverse health outcomes in older people. J Am Geriatr Soc 63:85–90. doi:10.1111/jgs.13206
Kouladjian L, Gnjidic D, Chen TF, Mangoni AA, Hilmer SN (2014) Drug Burden Index in older adults: theoretical and practical issues. Clin Interv Aging 9:1503–1515. doi:10.2147/CIA.S66660
Hilmer SN, Mager DE, Simonsick EM, Cao Y, Ling SM, Windham BG, Harris TB, Hanlon JT, Rubin SM, Shorr RI, Bauer DC, Abernethy DR (2007) A drug burden index to define the functional burden of medications in older people. Arch Intern Med 167:781–787
Hilmer SN, Mager DE, Simonsick EM, Ling SM, Windham BG, Harris TB, Shorr RI, Bauer DC, Abernethy DR, Health ABC Study (2009) Drug burden index score and functional decline in older people. Am J Med 122:1142–1149.e1-2. doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2009.02.021
Wilson NM, Hilmer SN, March LM, Cameron ID, Lord SR, Seibel MJ, Mason RS, Chen JS, Cumming RG, Sambrook PN (2011) Associations between drug burden index and falls in older people in residential aged care. J Am Geriatr Soc 59:875–880. doi:10.1111/j.1532-5415.2011.03386.x
Wilson NM, Hilmer SN, March LM, Cameron ID, Lord SR, Seibel MJ, Sambrook PN (2010) Associations between drug burden index and physical function in older people in residential aged care facilities. Age Ageing 39:503–507. doi:10.1093/ageing/afq053
Cao YJ, Mager DE, Simonsick EM, Hilmer SN, Ling SM, Windham BG, Crentsil V, Yasar S, Fried LP, Abernethy DR (2008) Physical and cognitive performance and burden of anticholinergics, sedatives, and ACE inhibitors in older women. Clin Pharmacol Ther 83:422–429
Gnjidic D, Cumming RG, Le Couteur DG, Handelsman DJ, Naganathan V, Abernethy DR, Hilmer SN (2009) Drug Burden Index and physical function in older Australian men. Br J Clin Pharmacol 68:97–105. doi:10.1186/s12877-015-0029-9
Gnjidic D, Le Couteur DG, Naganathan V, Cumming RG, Creasey H, Waite LM, Sharma A, Blyth FM, Hilmer SN (2012) Effects of drug burden index on cognitive function in older men. J Clin Psychopharmacol 32:273–277. doi:10.1097/JCP.0b013e3182487825
Gnjidic D, Bell JS, Hilmer SN, Lönnroos E, Sulkava R, Hartikainen S (2012) Drug Burden Index associated with function in community-dwelling older people in Finland: a cross-sectional study. Ann Med 44:458–467. doi:10.3109/07853890.2011.573499
Gnjidic D, Le Couteur DG, Abernethy DR, Hilmer SN (2012) Drug burden index and beers criteria: impact on functional outcomes in older people living in self-care retirement villages. J Clin Pharmacol 52:258–265. doi:10.1177/0091270010395591
Gnjidic D, Hilmer SN, Hartikainen S, Tolppanen AM, Taipale H, Koponen M, Bell JS (2014) Impact of high risk drug use on hospitalization and mortality in older people with and without Alzheimer’s disease: a national population cohort study. PLoS One 9:e83224. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0083224
Best O, Gnjidic D, Hilmer SN, Naganathan V, McLachlan AJ (2013) Investigating polypharmacy and drug burden index in hospitalised older people. Intern Med J 43:912–918. doi:10.1111/imj.12203
Lönnroos E, Gnjidic D, Hilmer SN, Bell JS, Kautiainen H, Sulkava R, Hartikainen S (2012) Drug Burden Index and hospitalization among community-dwelling older people. Drugs Aging 29:395–404. doi:10.2165/11631420-000000000-00000
Nishtala PS, Narayan SW, Wang T, Hilmer SN (2014) Associations of drug burden index with falls, general practitioner visits, and mortality in older people. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf 23:753–758. doi:10.1002/pds.3624
Lowry E, Woodman RJ, Soiza RL, Hilmer SN, Mangoni AA (2012) Drug burden index, physical function, and adverse outcomes in older hospitalized patients. J Clin Pharmacol 52:1584–1591
Bosboom PR, Alfonso H, Almeida OP, Beer C (2012) Use of potentially harmful medications and health-related quality of life among people with dementia living in residential aged care facilities. Dement Geriatr Cogn Dis Extra 2:361–371. doi:10.1159/000342172
Dispennette R, Elliott D, Nguyen L, Richmond R (2014) Drug Burden Index score and anticholinergic risk scale as predictors of readmission to the hospital. Consult Pharm 29:158–168. doi:10.4140/TCP.n.2014.158
Carnahan RM, Lund BC, Perry PJ, Culp KR, Pollock BG (2002) The relationship of an anticholinergic rating scale with serum anticholinergic activity in elderly nursing home residents. Psychopharmacol Bull 36:14–19
Carnahan RM, Lund BC, Perry PJ, Pollock BG, Culp KR (2006) The anticholinergic drug scale as a measure of drug-related anticholinergic burden: associations with serum anticholinergic activity. J Clin Pharmacol 46:1481–1486
Juliebø V, Bjøro K, Krogseth M, Skovlund E, Ranhoff AH, Wyller TB (2009) Risk factors for preoperative and postoperative delirium in elderly patients with hip fracture. J Am Geriatr Soc 57:1354–1361. doi:10.1111/j.1532-5415.2009.02377.x
Low LF, Anstey KJ, Sachdev P (2009) Use of medications with anticholinergic properties and cognitive function in a young-old community sample. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry 24:578–584. doi:10.1002/gps.2157
Kersten H, Molden E, Willumsen T, Engedal K, Bruun Wyller T (2013) Higher anticholinergic drug scale (ADS) scores are associated with peripheral but not cognitive markers of cholinergic blockade. Cross sectional data from 21 Norwegian nursing homes. Br J Clin Pharmacol 75:842–849. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2125.2012.04411.x
Agar M, Currow D, Plummer J, Seidel R, Carnahan R, Abernethy AP (2009) Changes in anticholinergic load from regular prescribed medications in palliative care as death approaches. Palliat Med 23:257–265. doi:10.1177/0269216309102528
Ancelin ML, Artero S, Portet F, Dupuy AM, Touchon J, Ritchie K (2006) Non-degenerative mild cognitive impairment in elderly people and use of anticholinergic drugs: longitudinal cohort study. BMJ 332:455–459
Han L, McCusker J, Cole M, Abrahamowicz M, Primeau F, Elie M (2001) Use of medications with anticholinergic effect predicts clinical severity of delirium symptoms in older medical inpatients. Arch Intern Med 161:1099–1105
Han L, Agostini JV, Allore HG (2008) Cumulative anticholinergic exposure is associated with poor memory and executive function in older men. J Am Geriatr Soc 56:2203–2210. doi:10.1111/j.1532-5415.2008.02009.x
Wawruch M, Macugova A, Kostkova L, Luha J, Dukat A, Murin J, Drobna V, Wilton L, Kuzelova M (2012) The use of medications with anticholinergic properties and risk factors for their use in hospitalised elderly patients. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf 21:170–176. doi:10.1002/pds.2169
Lowry E, Woodman RJ, Soiza RL, Mangoni AA (2011) Associations between the anticholinergic risk scale score and physical function: potential implications for adverse outcomes in older hospitalized patients. J Am Med Dir Assoc 12:565–572. doi:10.1016/j.jamda.2011.03.006
Teramura-Grönblad M, Muurinen S, Soini H, Suominen M, Pitkälä KH (2011) Use of anticholinergic drugs and cholinesterase inhibitors and their association with psychological well-being among frail older adults in residential care facilities. Ann Pharmacother 45:596–602. doi:10.1345/aph.1P650
Koshoedo S, Soiza RL, Purkayastha R, Mangoni AA (2012) Anticholinergic drugs and functional outcomes in older patients undergoing orthopaedic rehabilitation. Am J Geriatr Pharmacother 10:251–257. doi:10.1016/j.amjopharm.2012.06.003
Zimmerman KM, Salow M, Skarf LM, Kostas T, Paquin A, Simone MJ, Rudolph J (2014) Increasing anticholinergic burden and delirium in palliative care inpatients. Palliat Med 28:335–341. doi:10.1177/0269216314522105
Walter PJ, Dieter AA, Siddiqui NY, Weidner AC, Wu JM (2014) Perioperative anticholinergic medications and risk of catheterization after urogynecologic surgery. Female Pelvic Med Reconstr Surg 20:163–167. doi:10.1097/SPV.0000000000000075
Landi F, Dell’Aquila G, Collamati A, Martone AM, Zuliani G, Gasperini B, Eusebi P, Lattanzio F, Cherubini A (2014) Anticholinergic drug use and negative outcomes among the frail elderly population living in a nursing home. J Am Med Dir Assoc 15:825–829. doi:10.1016/j.jamda.2014.08.002
Ehrt U, Broich K, Larsen JP, Ballard C, Aarsland D (2010) Use of drugs with anticholinergic effect and impact on cognition in Parkinson’s disease: a cohort study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 81:160–165. doi:10.1136/jnnp.2009.186239
Jessen F, Kaduszkiewicz H, Daerr M, Bickel H, Pentzek M, Riedel-Heller S, Wagner M, Weyerer S, Wiese B, van den Bussche H, Broich K, Maier W (2010) Anticholinergic drug use and risk for dementia: target for dementia prevention. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 260(Suppl 2):S111–S115. doi:10.1007/s00406-010-0156-4
Sittironnarit G, Ames D, Bush AI, Faux N, Flicker L, Foster J, Hilmer S, Lautenschlager NT, Maruff P, Masters CL, Martins RN, Rowe C, Szoeke C, Ellis KA, AIBL research group (2011) Effects of anticholinergic drugs on cognitive function in older Australians: results from the AIBL study. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 31:173–178. doi:10.1159/000325171
Campbell N, Perkins A, Hui S, Khan B, Boustani M (2011) Association between prescribing of anticholinergic medications and incident delirium: a cohort study. J Am Geriatr Soc 59(Suppl 2):S277–S281. doi:10.1111/j.1532-5415.2011.03676.x
Kolanowski A, Fick DM, Campbell J, Litaker M, Boustani M (2009) A preliminary study of anticholinergic burden and relationship to a quality of life indicator, engagement in activities, in nursing home residents with dementia. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 10:252–257. doi:10.1016/j.jamda.2008.11.005
Fox C, Richardson K, Maidment ID, Savva GM, Matthews FE, Smithard D, Coulton S, Katona C, Boustani MA, Brayne C (2011) Anticholinergic medication use and cognitive impairment in the older population: the medical research council cognitive function and ageing study. J Am Geriatr Soc 59:1477–1483. doi:10.1111/j.1532-5415.2011.03491.x
Fox C, Livingston G, Maidment ID, Coulton S, Smithard DG, Boustani M, Katona C (2011) The impact of anticholinergic burden in Alzheimer’s dementia-the LASER-AD study. Age Ageing 40:730–735. doi:10.1093/ageing/afr102
Campbell NL, Boustani MA, Lane KA, Gao S, Hendrie H, Khan BA, Murrell JR, Unverzagt FW, Hake A, Smith-Gamble V, Hall K (2010) Use of anticholinergics and the risk of cognitive impairment in an African American population. Neurology 75:152–159. doi:10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181e7f2ab
Cai X, Campbell N, Khan B, Callahan C, Boustani M (2013) Long-term anticholinergic use and the aging brain. Alzheimers Dement 9:377–385. doi:10.1016/j.jalz.2012.02.005
Shah RC, Janos AL, Kline JE, Yu L, Leurgans SE, Wilson RS, Wei P, Bennett DA, Heilman KM, Tsao JW (2013) Cognitive decline in older persons initiating anticholinergic medications. PLoS One 8:e64111. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0064111
Lanctôt KL, O’Regan J, Schwartz Y, Swardfager W, Saleem M, Oh PI, Herrmann N (2014) Assessing cognitive effects of anticholinergic medications in patients with coronary artery disease. Psychosomatics 55:61–68. doi:10.1016/j.psym.2013.04.004
Whalley LJ, Sharma S, Fox HC, Murray AD, Staff RT, Duthie AC, Deary IJ, Starr JM (2012) Anticholinergic drugs in late life: adverse effects on cognition but not on progress to dementia. J Alzheimers Dis 30:253–261. doi:10.3233/JAD-2012-110935
Aizenberg D, Sigler M, Weizman A, Barak Y (2002) Anticholinergic burden and the risk of falls among elderly psychiatric inpatients: a 4-year case-control study. Int Psychogeriatr 14:307–310
Cancelli I, Valentinis L, Merlino G, Valente M, Gigli GL (2008) Drugs with anticholinergic properties as a risk factor for psychosis in patients affected by Alzheimer’s disease. Clin Pharmacol Ther 84:63–68
Cancelli I, Gigli GL, Piani A, Zanchettin B, Janes F, Rinaldi A, Valente M (2008) Drugs with anticholinergic properties as a risk factor for cognitive impairment in elderly people: a population-based study. J Clin Psychopharmacol 28:654–659. doi:10.1097/JCP.0b013e31818ce849
Chew ML, Mulsant BH, Pollock BG, Lehman ME, Greenspan A, Mahmoud RA, Kirshner MA, Sorisio DA, Bies RR, Gharabawi G (2008) Anticholinergic activity of 107 medications commonly used by older adults. J Am Geriatr Soc 56:1333–1341. doi:10.1111/j.1532-5415.2008.01737.x
Boustani M, Campbell N, Munger S, Maidment I, Fox C (2008) Impact of anticholinergics on the ageing brain: a review and practical application. Aging Health 4:311–320. doi:10.2217/1745509X.4.3.311
Summers WK (1978) A clinical method of estimating risk of drug induced delirium. Life Sci 22:1511–1516
Kay GG, Abou-Donia MB, Messer Jr WS, Murphy DG, Tsao JW, Ouslander JG (2005) Antimuscarinic drugs for overactive bladder and their potential effects on cognitive function in older patients. J Am Geriatr Soc 53:2195–2201
Renner UD, Oertel R, Kirch W (2005) Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics in clinical use of scopolamine. Ther Drug Monit 27:655–665
Chew ML, Mulsant BH, Pollock BG, Lehman ME, Greenspan A, Kirshner MA, Bies RR, Kapur S, Gharabawi G (2006) A model of anticholinergic activity of atypical antipsychotic medications. Schizophr Res 88:63–72
Olianas MC, Maullu C, Onali P (1999) Mixed agonist-antagonist properties of clozapine at different human cloned muscarinic receptor subtypes expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Neuropsychopharmacology 20:263–270
Fick DM, Cooper JW, Wade WE, Waller JL, Maclean JR, Beers MH (2003) Updating the beers criteria for potentially inappropriate medication use in older adults: results of a US consensus panel of experts. Arch Intern Med 163:2716–2724
Schliebs R, Arendt T (2011) The cholinergic system in aging and neuronal degeneration. Behav Brain Res 221:555–563. doi:10.1016/j.bbr.2010.11.058
Salahudeen MS, Duffull SB, Nishtala PS (2015) Anticholinergic burden quantified by anticholinergic risk scales and adverse outcomes in older people: a systematic review. BMC Geriatr 15:31. doi:10.1186/s12877-015-0029-9
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mayer, T., Haefeli, W.E. & Seidling, H.M. Different methods, different results—how do available methods link a patient’s anticholinergic load with adverse outcomes?. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 71, 1299–1314 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-015-1932-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-015-1932-x