Abstract
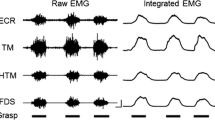
In 12 subjects, each sitting on an armchair with the right forearm prone, the H-reflex elicited in the resting flexor carpi radialis muscle underwent cyclic excitability changes correlated with rhythmic flexion-extension movements of the ipsilateral foot (frequency of oscillations between 1.5 and 2.5 Hz). During foot plantar flexion, the H-reflex underwent a clear-cut increase, the maximum facilitation falling, in most subjects, within the second half of that phase; then, a gradual reduction in size led the reflex amplitude back to the initial value at the end of foot dorsal extension. If present also when the wrist and the ankle are moved together, this facilitation should favour the in-phase (isodirectional) association between movements and, conversely, hinder the anti-phase coupling.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 16 June 1997 / Accepted: 10 July 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baldissera, F., Cavallari, P. & Leocani, L. Cyclic modulation of the H-reflex in a wrist flexor during rhythmic flexion-extension movements of the ipsilateral foot. Exp Brain Res 118, 427–430 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002210050297
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002210050297