Abstract
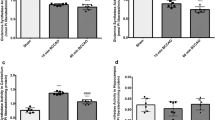
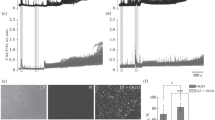
The present study was undertaken to investigate the effects of the α2 adrenergic agonist, clonidine, on the near complete cerebral ischemia (NCFI) evoked release of glutamate and aspartate from normo- and hyperglycemic rodent brain tissue using microdialysis tissue techniques. Hemodynamic variables, blood lactate, and glucose levels were monitored throughout the 40 min NCFI occlusion period. After 48 h, rats were killed and the extent of neuronal injury was determined in the cortex, striatum, and hippocampus. Hemodynamic variables recorded during ischemia improved with clonidine treatment in both normo- and hyperglycemic groups. Glutamate and aspartate levels were greatly increased over control values during normo- and hyperglycemic NCFI treatment. Clonidine pretreatment suppressed the release of both glutamate and aspartate during NCFI in normo- and hyperglycemic rodents when compared with NCFI-treated normo- and hyperglycemic rats without the drug. Significant neuroprotection of cells in the cortex, striatum, and hippocampus was also observed in drug-treated animals 48 h postischemia. The combined effects of diminished glutamate release after NCFI and reduced neuronal injury in both normo- and hyperglycemic states suggests that clonidine treatment during NCFI is neuroprotective. The neuroprotective effect of clonidine during ischemia may be ascribed to both a sensitization of central sympathetic activity and a reduced release of glutamate thereby reducing NMDA receptor activation and neuronal damage.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bickler PE, Buck LT, Feiner JR (1995) Volatile and intravenous anesthetics decrease glutamate release from cortical brain slices during anoxia. Anesthesiology 83:1233–1240
Dolphin AC (1982) Noradrenergic modulation of glutamate release in the cerebellum. Brain Res 252:111–116
Engelhard K, Werner C, Kaspar S, Mollenberg O, Blobner M, Bachl M, Kochs E (2002) Effect of the α2-agonist dexmedetomidine on cerebral neurotransmitter concentrations during cerebral ischemia in rats. Anesthesiology 96:450–457
Engelhard K, Werner C, Eberspacher E, Bachl M, Blobner M, Hildt E, Hutzler P, Kochs E (2003) The effect of the α2-agonist dexmedetomidine and the N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonist S(+)-ketamine on the expression of apoptosis-regulating proteins after incomplete cerebral ischemia and reperfusion in rats. Anesth Analg 96:524–531 (table of contents)
Gartshore G, Patterson J, Macrae IM (1997) Influence of ischemia and reperfusion on the course of brain tissue swelling and blood–brain barrier permeability in a rodent model of transient focal cerebral ischemia. Exp Neurol 147:353–360
Hoffman WE, Cheng MA, Thomas C, Baughman VL, Albrecht RF (1991a) Clonidine decreases plasma catecholamines and improves outcome from incomplete ischemia in the rat. Anesth Analg 73:460–464
Hoffman WE, Kochs E, Werner C, Thomas C, Albrecht RF (1991b) Dexmedetomidine improves neurologic outcome from incomplete ischemia in the rat. Reversal by the α2-adrenergic antagonist atipamezole. Anesthesiology 75:328–332
Karlsson BR, Loberg EM, Steen PA (1995) Dexmedetomidine, a potent α2-agonist, does not affect neuronal damage following severe forebrain ischaemia in the rat. Eur J Anaesthesiol 12:281–285
Kawasaki Y, Kumamoto E, Furue H, Yoshimura M (2003) Alpha2 adrenoceptor-mediated presynaptic inhibition of primary afferent glutamatergic transmission in rat substantia gelatinosa neurons. Anesthesiology 98:682–689
Kubo T, Nagura J, Kihara M, Misu Y (1986) Cardiovascular effects of L-glutamate and gamma-amino butyric acid injected into the rostral venrolateral medulla in normotensive and spontaneously hypertensive rats. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther 279:150–161
Lanier WL, Stangland KJ, Scheithauer BW, Milde JH, Michenfelder JD (1987) The effects of dextrose infusion and head position on neurologic outcome after complete cerebral ischemia in primates: examination of a model. Anesthesiology 66:39–48
Li PA, Kristian T, Shamloo M, Siesjo K (1996) Effects of preischemic hyperglycemia on brain damage incurred by rats subjected to 2.5 or 5 minutes of forebrain ischemia. Stroke 27:1592–1601 (discussion 1601–1592)
Maier C, Steinberg GK, Sun GH, Zhi GT, Maze M (1993) Neuroprotection by the α2-adrenoreceptor agonist dexmedetomidine in a focal model of cerebral ischemia. Anesthesiology 79:306–312
Miura Y, Grocott HP, Bart RD, Pearlstein RD, Dexter F, Warner DS (1998) Differential effects of anesthetic agents on outcome from near-complete but not incomplete global ischemia in the rat. Anesthesiology 89:391–400
Miyazaki M, Nazarali AJ, Boisvert DP, Bayens-Simmonds J, Baker GB (1989) Inhibition of ischemia-induced brain catecholamine alterations by clonidine. Brain Res Bull 22:207–211
Naruse T, Ishida T, Ishii R, Tagawa T, Namba K (1994) Relationship between hypotensive effects and plasma concentrations of clonidine in spontaneously hypertensive rats: continuous treatment and sudden termination of clonidine infusion. Gen Pharmacol 25:1421–1425
Niddam R, Angel I, Bidet S, Langer SZ (1990) Pharmacological characterization of alpha-2 adrenergic receptor subtype involved in the release of insulin from isolated rat pancreatic islets. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 254:883–887
Nishizawa Y (2001) Glutamate release and neuronal damage in ischemia. Life Sci 69:369–381
Pan Y-Z, Li D-P, Pan H-L (2002) Inhibition of glutamatergic synaptic input to spinal lamina iio neurons by presynaptic alpha 2-adrenergic receptors. J Neurophysiol 87:1938–1947
Szabo B (2002) Imidazoline antihypertensive drugs: a critical review on their mechanism of action. Pharmacol Ther 93:1–35
Talke P, Bickler PE (1996) Effects of dexmedetomidine on hypoxia-evoked glutamate release and glutamate receptor activity in hippocampal slices. Anesthesiology 85:551–557
Wagner SRt, Lanier WL (1994) Metabolism of glucose, glycogen, and high-energy phosphates during complete cerebral ischemia. A comparison of normoglycemic, chronically hyperglycemic diabetic, and acutely hyperglycemic nondiabetic rats. Anesthesiology 81:1516–1526
Wang WZ, Yuan WJ, Pan YX, Tang CS, Su DF (2004) Interaction between clonidine and N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors in the caudal ventrolateral medulla of rats. Exp Brain Res 158:259–264
Zhang X, Kindel G, Wulfert E, Hanin I (1998) Mivazerol inhibits intrathecal release of glutamate evoked by halothane withdrawal in rats. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 42:1004–1009
Zhang X, Kindel G, Jellish WS (2003) An improved method for measurement of glutamate and aspartate by high-performance liquid chromatography with 0-phthalaldenyde manual derivatization. Preclinica 1:87–91
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank the Department of Anesthesiology at Loyola University Medical Center for their financial support and Dr. Stephen Slogoff, M.D, Professor, for his editorial critique of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jellish, W.S., Murdoch, J., Kindel, G. et al. The effect of clonidine on cell survival, glutamate, and aspartate release in normo- and hyperglycemic rats after near complete forebrain ischemia. Exp Brain Res 167, 526–534 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-005-0064-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-005-0064-4