Abstract
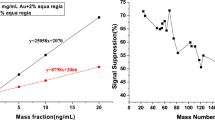
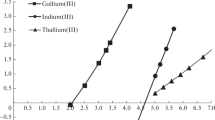
The possibility of using ETAAS or ICP-AES for the determination of trace amounts of Ag, Bi, Cd, Co, Cr, Cu, Fe, Mn, Ni, Pb, Pd, Pt and Sb in pure gold is investigated. The influence of the matrix element on the atomization of the trace analytes is studied and optimal instrumental parameters are defined. An analytical method based on matrix element reductive separation followed by spectrometric determination of trace analytes is proposed as an alternative for the analysis of high purity gold. Advantages and disadvantages of proposed analytical procedures from the viewpoint of achieved repeatability, reproducibility and detection limits and of the duration of analysis are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 16 August 1999 / Revised: 23 November 1999 / Accepted: 27 November 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karadjova, I., Arpadjan, S. & Jordanova, L. Determination of trace metals in high purity gold. Fresenius J Anal Chem 367, 146–150 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002160051615
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002160051615