Abstract
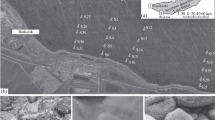
The aim of the present study was to optimize a protocol for extracting extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) from biofilms on rocky substrata, as the EPS matrix is considered key to understanding the biofilm mode of life. For this purpose, we tested the extraction efficacy of NaOH and H2SO4 at different concentrations, temperatures and times for obtaining EPS from multi-species subaerial biofilms grown on granite blocks under laboratory conditions. Two experimental designs (Box-Behnken design and full factorial design) were used in testing each extractant. The extraction efficiency was determined by analysing the carbohydrate, protein and DNA contents of the extracts obtained. H2SO4 proved unsuitable as an extractant as it caused excessive cell lysis. However, response surface optimization of NaOH-mediated extraction enabled cell lysis to be minimized. Confirmation experiments were performed under the optimal conditions established and a protocol for extracting EPS is proposed, yielding the first quantitative data on EPS extracted from subaerial biofilms developed on rocky substrata.

Development of a method for extracting EPS from subaerial biofilms on rocky substrata




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Costerton JW. The biofilm primer. Heidelberg: Springer; 2007.
Flemming HC, Wingender J. The biofilm matrix. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2010;8:623–33.
Gorbushina AA. Life on the rocks. Environ Microbiol. 2007;9:1613–31.
Kemmling A, Kämper M, Flies C, Schieweck O, Hoppert M. Biofilms and extracellular matrices on geomaterials. Environ Geol. 2004;46:429–35.
Viles HA. Microbial geomorphology: a neglected link between life and landscape. Geomorphology. 2012;157-158:6-16.
Warscheid T, Braams J. Biodeterioration of stone: a review. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad. 2000;46:343–68.
Hoppert M, Berker R, Flies C, Kämper M, Pohl W, Schneider J, et al. Biofilms and their extracellular environment on geomaterials: methods for investigation down to nanometer scale. Geol Soc Lond, Spec Publ. 2002;205:207–15.
Perry TD, Duckworth OW, McNamara CJ, Martin ST, Mitchell R. Effects of the biologically produced polymer alginic acid on macroscopic and microscopic calcite dissolution rates. Environ Sci Technol. 2004;38:3040–6.
Tourney J, Ngwenya BT. The role of bacterial extracellular polymeric substances in geomicrobiology. Chem Geol. 2014;386:115–32.
Sheng G-P, Yu H-Q, Li X-Y. Extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) of microbial aggregates in biological wastewater treatment systems: a review. Biotechnol Adv. 2010;28:882–94.
Perkins RG, Paterson DM, Sun H, Watson J, Player MA. Extracellular polymeric substances: quantification and use in erosion experiments. Cont Shelf Res. 2004;24:1623–35.
Takahashi E, Ledauphin J, Goux D, Orvain F. Optimizing extraction of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) from benthic diatoms: comparison of the efficiency of six EPS extraction methods. Mar Freshw Res. 2009;60:1201–10.
Liu H, Fang HHP. Extraction of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) of sludges. J Biotechnol. 2002;95:249–56.
Zhu L, Yu H, Liu Y, Qi H, Xu X. Optimization for extracellular polymeric substances extraction of microbial aggregates. Water Sci Technol. 2015;71:1106–12.
Sheng G-P, Yu H-Q, Yu Z. Extraction of extracellular polymeric substances from the photosynthetic bacterium Rhodopseudomonas acidophila. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2005;67:125–30.
Jachlewski S, Jachlewski WD, Linne U, Bräsen C, Wingender J, Siebers B. Isolation of extracellular polymeric substances from biofilms of the thermoacidophilic archaeon Sulfolobus acidocaldarius. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2015;3:123.
Barranguet C, van Beusekom SAM, Veuger B, Neu TR, Manders EMM, Sinke JJ, et al. Studying undisturbed autotrophic biofilms: still a technical challenge. Aquat Microb Ecol. 2004;34:1–9.
Redmile-Gordon MA, Brookes PC, Evershed RP, Goulding KWT, Hirsch PR. Measuring the soil-microbial interface: extraction of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) from soil biofilms. Soil Biol Biochem. 2014;72:163–71.
Vázquez-Nion D, Rodríguez-Castro J, López-Rodríguez MC, Fernández-Silva I, Prieto B. Subaerial biofilms on granitic historic buildings: microbial diversity and development of phototrophic multi-species cultures. Biofouling. 2016;32:657–69.
Rippka R, Deruelles J, Waterbury JB, Herdman M, Stanier RY. Genetic assignments, strain histories and properties of pure cultures of cyanobacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1979;111:1–61.
Prieto B, Silva B, Lantes O. Biofilm quantification on stone surfaces: comparison of various methods. Sci Total Environ. 2004;333:1–7.
Sanmartín P, Vázquez-Nion D, Silva B, Prieto B. Spectrophotometric color measurement for early detection and monitoring of greening on granite buildings. Biofouling. 2012;28:329–38.
Prieto B, Sanmartín P, Silva B, Martínez-Verdú F. Measuring the color of granite rocks: a proposed procedure. Color Res Appl. 2010;35:368–75.
CIE. Colorimetry CIE Publication 15-2. Vienna: Central Bureau of the Commission Internationale l’Eclairage (CIE); 1986.
Comte S, Guibaud G, Baudu M. Relations between extraction protocols for activated sludge extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) and EPS complexation properties: part I. Comparison of the efficiency of eight EPS extraction methods. Enzym Microb Technol. 2006;38:237–45.
Alcamo IE. Fundamentals of microbiology. Menlo Park: Benjamin Cummings; 1997.
Bezerra MA, Santelli RE, Oliveira EP, Villar LS, Escaleira LA. Response surface methodology (RSM) as a tool for optimization in analytical chemistry. Talanta. 2008;76:965–77.
Wingender J, Neu TR, Flemming HC. Microbial extracellular polymeric substances: characterisation, structure and function. Berlin: Springer; 1999.
Dubois M, Gilles KA, Hamilton JK, Rebers PA, Smith F. Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal Chem. 1956;28:350–6.
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951;193:265–75.
Burton K. Study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1956;62:315–23.
Box GEP, Wilson KB. The exploration and exploitation of response surfaces: some general considerations and examples. Biometrics. 1954;10:16–60.
Adav SS, Lee D-J. Extraction of extracellular polymeric substances from aerobic granule with compact interior structure. J Hazard Mater. 2008;154:1120–6.
Montgomery DC. Design and analysis of experiments. New York: John Wiley & Sons; 1997.
Haaland PD. Experimental design in biotechnology. New York: Marcel Dekker; 1989.
Acknowledgments
The first author was financially supported by “Programa de axudas predoutorais financiadas polos grupos de investigación da Universidade de Santiago de Compostela no marco do Estatuto do Persoal de Investigación en Formación” through PhD grant 2011/AX461.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Daniel Vázquez-Nion declares that he has no conflict of interest. María Echeverri declares that she has no conflict of interest. Benita Silva declares that she has no conflict of interest. Beatriz Prieto declares that she has no conflict of interest. This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors. All authors have seen and agree with the contents of the manuscript.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 51.7 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vázquez-Nion, D., Echeverri, M., Silva, B. et al. Response surface optimization of a method for extracting extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) from subaerial biofilms on rocky substrata. Anal Bioanal Chem 408, 6369–6379 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-016-9752-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-016-9752-0