Abstract
Quaternized chitosan is a cationic biopolymer with good antibacterial activity, biocompatibility, and biodegradability, and it has been widely applied in many fields. We have developed a convenient method to evaluate the antibacterial activity of hydroxypropyltrimethylammonium chloride chitosan (HACC) with a nonionic surfactant poloxamer in aqueous solution by monitoring the change of the oxidation peak current in cyclic voltammetry. Increasing values of the oxidation peak current were positively correlated with the antibacterial activity of HACC–poloxamer solutions. Optical microscope images, the zeta potential, and fluorescence spectroscopy showed that the aggregation state of HACC–poloxamer was related to the ratio of the two polymers and also to the antibacterial activity and oxidation peak current. At an HACC-to-poloxamer ratio of 1:0.75, the maximum surface charge density and the smooth edge of HACC–poloxamer aggregates can accelerate diffusion in aqueous solution. It is expected that this convenient method can be applied for a quick evaluation of the antibacterial activity of cationic biopolymers in aqueous solution.

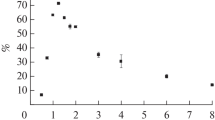
The cyclic voltammograms of MB in HACC/poloxamer solution, and the antibacterial efficiency against S. aureus after incubated with HACC (a) and 1/0.75 of HACC/poloxamer (b)





Similar content being viewed by others
References
An NT, Thien DT, Dong NT, Dung PL. Water-soluble N-carboxymethylchitosan derivatives: preparation, characteristics and its application. Carbohydr Polym. 2009;75:489–97.
Rinaudo M, Auzely R, Vallin C, Mullagaliev I. Specific interactions in modified chitosan systems. Biomacromolecules. 2005;6:2396–407.
De Leeuw BJ, Junginger HE, Verhoef JC. N-Trimethyl chitosan chloride as a potential absorption enhancer across mucosal surfaces in vitro evaluation in intestinal epithelial cells. Pharm Res. 1997;14:1197–202.
Babak V, Lukina I, Vikhoreva G, Desbrieres J, Rinaudo M. Interfacial properties of dynamic association between chitin derivatives and surfactants. Colloid Surf A-Physicochem Eng. 1999;147
Sandri G, Rossi S, Bonferoni MC, Ferrari F, Zambito Y, Colo GD, et al. Buccal penetration enhancement properties of N-trimethyl chitosan: influence of quaternization degree on absorption of a high molecular weight molecule. Int J Pharm. 2005;297:146–55.
Tan H, Ma R, Lin C, Liu Z, Tang T. Quaternized chitosan as an antimicrobial agent: antimicrobial activity, mechanism of action and biomedical applications in orthopedics. Int J Mol Sci. 2013;14:1854–69.
Sahariah P, Benediktssdóttir BE, Hjálmarsdóttir MÁ, Sigurjonsson OE, Sørensen KK, Thygesen MB, et al. Impact of chain length on antibacterial activity and hemocompatibility of quaternary N-alkyl and N, N-dialkyl chitosan derivatives. Biomacromolecules. 2015;16:1449–60.
Másson M, Holappa J, Hjálmarsdóttir M, Rúnarsson ÖV, Nevalainen T, Järvinen T. Antimicrobial activity of piperazine derivatives of chitosan. Carbohydr Polym. 2008;74:566–71.
Yang T, Chou C, Li C. Antibacterial activity of N-alkylated disaccharide chitosan derivatives. Int J Food Microbiol. 2005;97:237–45.
Sajomsang W, Gonil P, Saesoo S. Synthesis and antibacterial activity of methylated N-(4-N, N-dimethylaminocinnamyl) chitosan chloride. Eur Polym J. 2009;45:2319–28.
Peng Z, Wang L, Du L, Guo S, Wang X, Tang T. Adjustment of the antibacterial activity and biocompatibility of hydroxypropyltrimethyl ammonium chloride chitosan by varying the degree of substitution of quaternary ammonium. Carbohydr Polym. 2010;81:275–83.
Guo Z, Xing R, Song L, Zhong Z, Xia J, Wang L, et al. The influence of molecular weight of quaternized chitosan on antifungal activity. Carbohydr Polym. 2008;71:694–7.
Chi W, Qin C, Zeng L, Li W, Wang W. Microbiocidal activity of chitosan-N-2-hydroxypropyl trimethyl ammonium chloride. J Appl Polym Sci. 2007;103:3851–6.
Yin Y, Zhang H, Nishinari K. Voltammetric characterization on the hydrophobic interaction in polysaccharide hydrogels. J Phys Chem B. 2007;111:1590–6.
Fan L, Yang J, Wu H, Hu Z, Yi J, Tong J, et al. Preparation and characterization of quaternary ammonium chitosan hydrogel with significant antibacterial activity. Int J Biol Macromol. 2015;79:830–6.
Jin Z, Li W, Cao H, Zhang X, Chen G, Wu H, et al. Antimicrobial activity and cytotoxicity of N-2-HACC and characterization of nanoparticles with N-2-HACC and CMC as a vaccine carrier. Chem Eng J. 2013;221:331–41.
Sahariah P, Snorradóttir BS, Hjálmarsdóttir MÁ, Sigurjónsson ÓE, Másson M. Experimental design for determining quantitative structure activity relationship for antibacterial chitosan derivatives. J Mater Chem B. 2016;4:4762–70.
Sajomsang W, Gonil P, Tantayanon S. Antibacterial activity of quaternary ammonium chitosan containing mono or disaccharide moieties: preparation and characterization. Int J Biol Macromol. 2009;44:419–27.
Bhowmick A, Jana P, Pramanik N, Mitra T, Banerjee SL, Gnanamani A, et al. Multifunctional zirconium oxide doped chitosan based hybrid nanocomposites as bone tissue engineering materials. Carbohydr Polym. 2016;151:879–88.
Tamer TM, Hassan MA, Omer AM, Baset WMA, Hassan ME, El-Shafeey MEA, et al. Synthesis, characterization and antimicrobial evaluation of two aromatic chitosan Schiff base derivatives. Process Biochem. 2016;51:1721–30.
Yang X, Guo Y, Liu J, Yan L, Zhong J, Feng R. Study of the effects of pyrene probe concentration and solution polarity on the self-association behavior of hydrophobically associating polymer by steady-state fluorescence. Appl Chem Ind. 2013;42:195–9.
Liu P, Meng W, Wang S, Sun Y, Ashraf MA. Quaternary ammonium salt of chitosan: preparation and antimicrobial property for paper. Open Med. 2015;10:473–8.
Vallapa N, Wiarachai O, Thongchul N, Pan J, Tangpasuthadol V, Kiatkamjornwong S, et al. Enhancing antibacterial activity of chitosan surface by heterogeneous quaternization. Carbohydr Polym. 2011;83:868–75.
Shen H, Yin Y, Zhang H. An electrochemical study of the hydrophobic interaction of methylcellulose. Acta Chim Sin. 2005;63:1621–5.
Carter MT, Rodriguez M, Bard AJ. Voltammetric Studies of the interaction of metal chelates with DNA. 2. Tris-chelated complexes of cobalt(111) and iron(11) with 1,10-phenanthroline and 2,2'-bipyridine. J Am Chem Soc. 1989;111:8901–11.
Fu X, Shen W, Yao T, Hou W. Physical chemistry. 5th ed. Beijing: Higher Education Press; 2006.
Grant J, Lee H, Liu RCW, Allen C. Intermolecular interactions and morphology of aqueous polymer/surfactant mixtures containing cationic chitosan and nonionic sorbitan esters. Biomacromolecules. 2008;9:2146–52.
Siu H, Duhamel J. Associations between a pyrene-labeled hydrophobically modified alkali swellable emulsion copolymer and sodium dodecyl sulfate probed by fluorescence, surface tension, and viscometry. Macromolecules. 2006;39:1144–55.
Worm M, Kang B, Dingels C, Wurm FR, Frey H. Acid-labile amphiphilic PEO-b-PPO-b-PEO copolymers: degradable poloxamer analogs. Macromol Rapid Commun. 2016;37:775–80.
Schillén K, Jansson J, Löf D, Costa T. Mixed micelles of a PEO-PPO-PEO triblock copolymer (P123) and a nonionic surfactant (C12EO6) in water. a dynamic and static light scattering study. J Phys Chem B. 2008;112:5551–62.
Nambam JS, Philip J. Effects of interaction of ionic and nonionic surfactants on self-assembly of PEO–PPO–PEO triblock copolymer in aqueous solution. J Phys Chem B. 2012;116:1499–507.
Li Y, Hao J, Li G. Electrochemical behavior of cationic‐anionic surfactant solutions by cyclic voltammetry. J Dispers Sci Technol. 2006.
Bard AJ, Faulkner LR. Electrochemistry methods fundamentals and applications. 2nd ed. New York: Wiley; 2003.
Li W, Xiao L, Qin C. Synthesis and relevant electrochemical properties of 2-hydroxypropyltrimethyl ammonium chloride chitosan-grafted multiwalled carbon nanotubes. J Mater Sci. 2010;45:5915–22.
Tsai G, Hwang S. In vitro and in vivo antibacterial activity of shrimp chitosan against some intestinal bacteria. Fish Sci. 2004;70:675–81.
Je J, Kim S. Chitosan derivatives killed bacteria by disrupting the outer and inner membrane. J Agric Food Chem. 2006;54:6629–33.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Nature Science Foundations of China (81571812), the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (1107047002), and Hydron Contact Lens Co. (8507040152).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 212 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Guo, Q., Wang, H. et al. Evaluation of the antibacterial activity of a cationic polymer in aqueous solution with a convenient electrochemical method. Anal Bioanal Chem 409, 1627–1633 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-016-0105-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-016-0105-9