Abstract
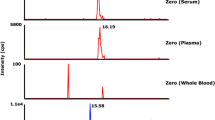
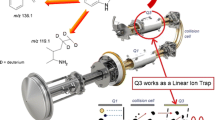
In the present study, a rapid and sensitive LC-ESI-MS/MS method for quantification of (S)-fluoxetine as a native marker in mass spectrometry (MS) binding assays addressing the human serotonin transporter (hSERT) was developed and validated. The concept of MS binding assays based on mass spectrometric quantification of a nonlabeled marker recently introduced by us represents a promising alternative to conventional radioligand binding without the drawbacks inherently connected with radioisotope labeling. For high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), a 20 × 2-mm RP-18 column with a mobile phase composed of acetonitrile and ammonium bicarbonate buffer (5 mmol L−1, pH 9.5) at a ratio of 80:20 (v/v) and a flow rate of 800 μL min−1 in an isocratic mode were used, resulting in a chromatographic cycle time of 60 s. Employing [2H5]fluoxetine as internal standard enabled ESI-MS/MS quantification of (S)-fluoxetine between 3 nmol L−1 and 50 pmol L−1 (LLOQ) in matrix obtained from binding experiments without the need of any sample preparation. Validation of the method showed that linearity, intra-, and inter-batch accuracy as well as precision meet the requirements of the FDA guidance for bioanalytical method validation. Considering sensitivity and speed, the established method is clearly superior to those published for biological matrices so far. Furthermore, the method was transferred to other RP-18 columns of different lengths and respective validation experiments demonstrated its versatility and chromatographic robustness. Finally, the newly developed method was successfully applied to MS binding assays for hSERT. The affinity determined for (S)-fluoxetine in saturation experiments was in good agreement with literature data obtained in respective radioligand binding assays.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Höfner G, Zepperitz C, Wanner KT (2007) Mass spectrometry in medicinal chemistry. Wiley, Weinheim
de Jong LAA, Uges DRA, Franke JP, Bischoff R (2005) J Chromatogr B 829:1–25
Haylett DG (2003) Direct measurement of drug binding to receptors. In: Foreman JC, Johansen T (eds) Textbook of receptor pharmacology, 2nd edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Williams M, Mehlin C, Triggle DJ (2003) Receptor targets in drug discovery and development. In: Abraham DJ (ed) Burger’s medicinal chemistry and drug discovery, vol 2: drug development. Wiley, New York
Siegel MM (2005) Mass-spectrometry-based drug screening assays for early phases in drug discovery. In: Lee MS (ed) Integrated strategies for drug discovery using mass spectrometry. Wiley, New York
Zepperitz C, Höfner G, Wanner KT (2006) Chem Med Chem 1:208–217
Murphy DL, Lerner A, Rudnick G, Lesch KP (2004) Mol Interv 4:109–123
Owens MJ, Morgan WN, Plott SJ, Nemeroff CB (1997) J Pharm Exp Ther 283:1305–1322
Tatsumi M, Groshan K, Blakely RD, Richelson R (1997) Eur J Pharmacol 340:249–258
Koch S, Perry KW, Nelson DL, Conway RG, Threlkeld PG, Bymaster FP (2002) Neuropsychopharmacol 27:949–959
Wong DT, Bymaster FP, Engleman EE (1995) Life Sci 57:411–441
Wong DT, Horng JS, Bymaster FP, Hauser KL, Molloy BB (1974) Life Sci 15:471–479
Zhou Z, Zhen J, Karpowich NK, Law CJ, Reith MEA, Wong DN (2009) Nat Struct Mol Biol 16:652–658
Chen F, Larsen MB, Sánchez C, Wiborg O (2005) Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 15:193–198
Wong DT, Bymaster FP, Reid LR, Fuller RW, Perry KW (1985) Drug Dev Res 6:398–403
Elfving B, Madsen J, Knudsen GM (2007) Synapse 61:882–888
Wong DT, Bymaster FP (1983) Fed Proc 42:1164
Bennett JP Jr, Yamamura HI (1985) Neurotransmitter, hormone, or drug receptor binding methods. In: Yamamura HI, Enna SJ, Kuhar MJ (eds) Neurotransmitter receptor binding, 2nd edn. Raven, New York
Bylund DB, Deupreee JD, Toews ML (2004) Radioligand-binding methods for membrane preparations and intact cells. In: Willars GB, Challiss RAJ (eds) Methods in molecular biology, vol. 259: receptor signal transduction protocols, 2nd edn. Humana Press, Totowa
Li C, Ji Z, Nan F, Shao Q, Liu P, Dai J, Zhen J, Yuan H, Xu F, Cui J, Huang B, Zhang M, Yu C (2002) Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 16:1844–1850
de Castro M, Concheiro M, Quintela Q, Cruz A, López-Rivadulla M (2008) J Pharm Biomed Anal 48:183–193
Queiroz ME, Oliveira EB, Breton F, Pawliszyn J (2007) J Chromatogr A 1174:72–77
Lajeunesse A, Gagnon C, Sauvé S (2008) Anal Chem 80:5325–5333
Souverain S, Mottaz M, Cherkaoui S, Veuthey JL (2003) Anal Bioanal Chem 377:880–885
Smyth WF, Leslie JC, McClean S, Hannigan B, McKenna HP, Doherty B, Joyce C, E O’Kane (2006) Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 20:1637–1642
US FDA (2001) Guidance for industry, bioanalytical method validation. United States Food and Drug Administration, Washington. Available at: http://www.fda.gov/downloads/Drugs/GuidanceComplianceRegulatoryInformation/Guidances/ucm070107.pdf. Accessed 10 Aug 2010
Bradford M (1976) Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Niessen WMA (2006) In: Cazes J (ed) Chromatographic science series, vol. 97: liquid chromatography–mass specrometry, 3rd edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Taylor PJ (2005) Clin Biochem 38:328–334
Mei H, Hsieh Y, Nardo C, Xu X, Wang S, Ng K, Korfmacher WA (2003) Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 17:97–103
Hopfgartner G, Varesio E (2005) Trends Analyt Chem 308:127–133
Snyder LR, Kirkland JJ, Dolan JW (2010) Ionic samples: reversed-phase, ion-pair, and ion-exchange chromatography. In: Introduction to modern liquid chromatography, 3rd edn. Wiley, New Jersey
Peng L, Farkas T (2008) J Chromatogr A 1179:131–144
Schellinger AP, Carr PW (2006) J Chromatogr A 1109:253–266
Unger KK, Weber E (1995) Bestimmung der Totzeit. In: Handbuch der HPLC Teil 1, 2nd edn. GIT Verlag, Darmstadt
Binsumait IA, Hadidi KA, Abu-Al Raghib S (2001) Pharmazie 56:311–313
Acknowledgments
We thank Theo Rein for providing pcDNA3.1(+) containing the cDNA coding for hSERT. For technical support in cell culture, we thank Silke Duensing-Kropp and Ljiljana Galogaza. We also thank Katharina Heimberger for article editing and proofreading.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hess, M., Höfner, G. & Wanner, K.T. Development and validation of a rapid LC-ESI-MS/MS method for quantification of fluoxetine and its application to MS binding assays. Anal Bioanal Chem 400, 3505–3515 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-011-4997-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-011-4997-0