Abstract
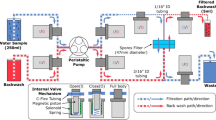
Trace analysis of microorganisms in real biological samples needs very sensitive methods for their detection. Most procedures for detecting and quantifying pathogens require a sample preparation step including concentrating microorganisms from large sample volumes with high and reproducible efficiency. Electromigration techniques have great potential to include the preconcentration, separation, and detection of whole cells and therefore they can rapidly indicate the presence of pathogens. The preconcentration and separation of microorganisms from real suspensions utilising a combination of filtration and capillary isoelectric focusing was developed and the possibility for its application to real samples was verified. For our experiments, spores of Monilinia species and of Penicillium expansum were selected as model bioparticles, as they cause major losses in agrosystems. The isoelectric points of the spores of M. laxa, M. fructigena, M. fruticola, and P. expansum were determined and the method was verified using real samples taken directly from infected apples. The coupling of a filtration cartridge with a separation capillary can improve the detection limit of isoelectric focusing with UV detection by at least 4 orders of magnitude. Spores of M. fructigena and of M. laxa in numbers of hundreds of particles per milliliter were detected on a visually noninfected apple surface which was cross-contaminated during handling and storage. The efficiency of preconcentration and a preliminary identification was verified by the phenotyping technique after cultivation of the spores sampled from the apple surface.

The pre-concentration and separation of spores of Monilinia species and of Penicillium expansum from the real suspensions including combination of filtration and capillary isoelectric focusing were developed and the possibility of their application to real samples was verified. The coupling of the filtration cartridge with the separation capillary can improve the detection limit of the isoelectric focusing with the UV-detection by at least four orders of magnitude.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arai F, Ichikawa A, Ogawa M, Fukuda T, Horio K, Itoigawa K (2001) Electrophoresis 22:283–288
Fenselau C, Pribil P (2006) In: Wilkins CL, Lay JO (eds) Identification of microorganisms by mass spectrometry. Totowa, Wiley
O’Connell S, Lawson RD, Watwood ME, Lehman RM (2000) J Microbiol Methods 40:213–220
Alvarez AM (2004) Annu Rev Phytopathol 42:339–366
Dawyndt P, Vancanneyt M, Snauwaert C, De Baets B, De Meyer H, Swings J (2006) J Microbiol Methods 66:410–433
Lantz AW, Bisha B, Tong M-Y, Nelson RE, Brehm-Stecher BF, Armstrong DW (2010) Electrophoresis 31:2849–2853
Boonham N, Glover R, Tomlinson J, Mumford R (2008) Eur J Plant Pathol 121:355–363
Wahl KL, Wunschel SC, Jarman KH, Valentine NB, Petersen CE, Kingsley KA, Saenz AJ (2002) Anal Chem 74:6191–6199
Parisi D, Magliulo M, Nanni P, Casale M, Forina M, Roda A (2008) Anal Bioanal Chem 391:2127–2134
Rotem S, Raz N, Kashi Y, Mor A (2010) Appl Environ Microbiol 76:3301–3307
Mach AJ, Carlo DD (2010) Biotechnol Bioeng 107:302–311
Berry ED, Siragusa GR (1997) Appl Environ Microbiol 63:4069–4074
Košťál V, Arriaga EA (2008) Electrophoresis 29:2578–2586
Horká M, Růžička F, Holá V, Šlais K (2009) Electrophoresis 30:2134–2141
Liu Z, Wu SS, Pawliszyn J (2007) J Chromatogr A 1140:213–218
Lantz AW, Bao Y, Armstrong DW (2007) Anal Chem 79:1720–1724
Horká M, Růžička F, Horký J, Holá V, Šlais K (2006) Anal Chem 78:8438–8444
Dolník V (2006) Electrophoresis 27:126–141
Jung B, Bharadwaj R, Santiago JG (2006) Anal Chem 78:2319–2327
Gebauer P, Bocek P (2002) Electrophoresis 23:3858–3864
Wang J, Zhang Y, Mohamadi MR, Kaji N, Tokeshi M, Baba Y (2009) Electrophoresis 30:3250–3256
Lichtenberg J, Verpoorte E, De Rooij NF (2001) Electrophoresis 22:258–271
Burgi DS, Chien RL (1991) Anal Chem 63:2042–2047
Quirino JP, Terabe S (1998) Science 282:465–468
Britz-McKibbin P, Ichihashi T, Tsubota K, Chen DDY, Terabe S (2003) J Chromatogr A 1013:65–76
Tempels FWA, Underberg WJM, Somsen GW, de Jong GJ (2008) Electrophoresis 29:108–128
Puig P, Borrull F, Calull M, Aguilar C (2008) Anal Chim Acta 616:1–18
Ramautar R, Sosen GW, de Jong GJ (2010) Electrophoresis 31:44–54
Petr J, Jiang Ch, Sevcik J, Tesarova E, Armstrong DW (2009) Electrophoresis 30:3870–3876
Shen Y, Berger SJ, Smith RD (2000) Anal Chem 72:4603–4607
Yu L, Li SFY (2007) J Chromatogr A 1161:308–313
Pfetsch A, Welsch T (1997) Fresenius J Anal Chem 359:198–201
Kutter JP, Jacobson SC, Ramsey JM (2000) J Microcolumn Sep 12:93–97
Munoz Z, Moret A, Bech J (2008) Agrociencia 42:119–128
van Brouwershaven IR, Bruil ML, van Leeuwen GCM, Kox LFF (2009) Plant Pathol 59:548–555
Okull DO, Laborde LF (2004) J Food Sci 69:23–27
Hirokawa T, Nishino M, Aoki N, Sawamoto YKTY, Akiyama J-I (1983) J Chromatogr A 271:D1–D106
Acevedo F (1991) J Chromatogr A 545:391–396
Horká M, Růžička F, Holá V, Šlais K (2006) Anal Bioanal Chem 385:840–846
Šťastná M, Trávníček M, Šlais K (2005) Electrophoresis 26:53–59
Šťastná M, Šlais K (2003) J Chromatogr A 1008:193–203
Horká M, Willimann T, Blum M, Nordig P, Friedl Z, Šlais K (2001) J Chromatogr A 916:65–71
Horká M, Růžička F, Horký J, Holá V, Šlais K (2006) J Chromatogr B 841:152–159
Horká M, Růžička F, Kubesová A, Holá V, Šlais K (2009) Anal Chem 81:3997–4004
Doyle RJ (2000) Microbes Infect 2:391–400
Rijnaarts HHM, Norde W, Lyklema J, Zehnder AJB (1995) Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 4:191–197
Willetts HJ, Byrde RJW, Fielding AH, Wong AL (1977) J Gen Microbiol 103:77–83
Šťastná M, Šlais K (2008) Electrophoresis 29:4503–4507
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Grant Agency of the Academy of Sciences of the Czech Republic (no. IAAX00310701) and by the institutional research plan AVO Z40310501.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Horká, M., Horký, J., Kubesová, A. et al. The trace analysis of microorganisms in real samples by combination of a filtration microcartridge and capillary isoelectric focusing. Anal Bioanal Chem 400, 3133–3140 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-011-4975-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-011-4975-6