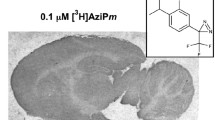
Abstract
Rationale
While neurosteroids are well-described positive allosteric modulators of gamma-aminobutyric acid type A (GABAA) receptors, the binding sites that mediate these actions have not been definitively identified.
Objectives
This study was conducted to synthesize neurosteroid analogue photolabeling reagents that closely mimic the biological effects of endogenous neurosteroids and have photochemical properties that will facilitate their use as tools for identifying the binding sites for neurosteroids on GABAA receptors.
Results
Two neurosteroid analogues containing a trifluromethyl-phenyldiazirine group linked to the steroid C11 position were synthesized. These reagents, CW12 and CW14, are analogues of allopregnanolone (5α-reduced steroid) and pregnanolone (5β-reduced steroid), respectively. Both reagents were shown to have favorable photochemical properties with efficient insertion into the C–H bonds of cyclohexane. They also effectively replicated the actions of allopregnanolone and pregnanolone on GABAA receptor functions: they potentiated GABA-induced currents in Xenopus laevis oocytes transfected with α1β2γ2L subunits, modulated [35S]t-butylbicyclophosphorothionate binding in rat brain membranes, and were effective anesthetics in Xenopus tadpoles. Studies using [3H]CW12 and [3H]CW14 showed that these reagents covalently label GABAA receptors in both rat brain membranes and in a transformed human embryonal kidney (TSA) cells expressing either α1 and β2 subunits or β3 subunits of the GABAA receptor. Photolabeling of rat brain GABAA receptors was shown to be both concentration-dependent and stereospecific.
Conclusions
CW12 and CW14 have the appropriate photochemical and pharmacological properties for use as photolabeling reagents to identify specific neurosteroid-binding sites on GABAA receptors.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akk G, Bracamontes JR, Covey DF, Evers A, Dao T, Steinbach JH (2004) Neuroactive steroids have multiple actions to potentiate GABAA receptors. J Physiol 558:59–74
Akk G, Shu HJ, Wang C, Steinbach JH, Zorumski CF, Covey DF, Mennerick S (2005) Neurosteroid access to the GABAA receptor. J Neurosci 25:11605–11613
Akk G, Covey DF, Evers AS, Steinbach JH, Zorumski CF, Mennerick S (2007) Mechanisms of neurosteroid interactions with GABA(A) receptors. Pharmacol Ther 116:35–57
Akk G, Li P, Bracamontes J, Reichert DE, Covey DF, Steinbach JH (2008) Mutations of the GABA-A receptor alpha1 subunit M1 domain reveal unexpected complexity for modulation by neuroactive steroids. Mol Pharmacol 74:614–627
Akk G, Covey DF, Evers AS, Mennerick S, Zorumski CF, Steinbach JH (2010) Kinetic and structural determinants for GABA-A receptor potentiation by neuroactive steroids. Curr Neuropharmacol 8:18–25
Atkinson RM, Davis B, Pratt MA, Sharpe HM, Tomich EG (1965) Action of some steroids on the central nervous system of the mouse: II. Pharmacology. J Med Chem 8:426–432
Brunner J (1993) New photolabeling and crosslinking methods. Annu Rev Biochem 62:483–514
Brunner J, Senn H, Richards FM (1980) 3-Trifluoromethyl-3-phenyldiazirine. A new carbene generating group for photolabeling reagents. J Biol Chem 255:3313–3318
Bureau MH, Olsen RW (1993) GABAA receptor subtypes: ligand binding heterogeneity demonstrated by photoaffinity labeling and autoradiography. J Neurochem 61:1479–1491
Chen ZW, Chen LH, Akentieva N, Lichti CF, Darbandi R, Hastings R, Covey DF, Reichert DE, Townsend RR, Evers AS (2012a) A neurosteroid analogue photolabeling reagent labels the colchicine-binding site on tubulin: a mass spectrometric analysis. Electrophoresis 33:666–674
Chen ZW, Manion B, Townsend RR, Reichert DE, Covey DF, Steinbach JH, Sieghart W, Fuchs K, Evers AS (2012b) Neurosteroid analog photolabeling of a site in the third transmembrane domain of the β3 subunit of the GABAA receptor. Mol Pharmacol 82:408–419
Chiara DC, Jayakar SS, Zhou X, Zhang X, Savechenkov PY, Bruzik KS, Miller KW, Cohen JB (2013) Specificity of intersubunit general anesthetic-binding sites in the transmembrane domain of the human α1β3γ2 gamma-aminobutyric acid type A (GABAA) receptor. J Biol Chem 288:19343–19357
Chisari M, Eisenman LN, Krishnan K, Bandyopadhyaya AK, Wang C, Taylor A, Benz A, Covey DF, Zorumski CF, Mennerick S (2009) The influence of neuroactive steroid lipophilicity on GABAA receptor modulation: evidence for a low-affinity interaction. J Neurophysiol 102:1254–1264
Chisari M, Eisenman LN, Covey DF, Mennerick S, Zorumski CF (2010) The sticky issue of neurosteroids and GABA(A) receptors. Trends Neurosci 33:299–306
Covey DF, Nathan D, Kalkbrenner M, Nilsson KR, Hu Y, Zorumski CF, Evers AS (2000) Enantioselectivity of pregnanolone-induced gamma-aminobutyric acid(A) receptor modulation and anesthesia. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 293:1009–1016
Darbandi-Tonkabon R, Hastings WR, Zeng CM, Akk G, Manion BD, Bracamontes JR, Steinbach JH, Mennerick SJ, Covey DF, Evers AS (2003) Photoaffinity labeling with a neuroactive steroid analogue. 6-azi-pregnanolone labels voltage-dependent anion channel-1 in rat brain. J Biol Chem 278:13196–13206
Darbandi-Tonkabon R, Manion BD, Hastings WR, Craigen WJ, Akk G, Bracamontes JR, He Y, Sheiko TV, Steinbach JH, Mennerick SJ, Covey DF, Evers AS (2004) Neuroactive steroid interactions with voltage-dependent anion channels: lack of relationship to GABA(A) receptor modulation and anesthesia. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 308:502–511
Evers AS, Chen ZW, Manion BD, Han M, Jiang X, Darbandi-Tonkabon R, Kable T, Bracamontes J, Zorumski CF, Mennerick S, Steinbach JH, Covey DF (2010) A synthetic 18-norsteroid distinguishes between two neuroactive steroid binding sites on GABAA receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 333:404–413
Franks NP (2008) General anaesthesia: from molecular targets to neuronal pathways of sleep and arousal. Nat Rev Neurosci 9:370–386
Gyermek L, Soyka LF (1975) Steroid anesthetics. Anesthesiology 42:331–344
Harrison NL, Majewska MD, Harrington JW, Barker JL (1987) Structure–activity relationships for steroid interaction with the γ-aminobutyric acid A receptor complex. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 241:346–353
Hawkinson JE, Kimbrough CL, McCauley LD, Bolger MB, Lan NC, Gee KW (1994) The neuroactive steroid 3 alpha-hydroxy-5 beta-pregnan-20-one is a two-component modulator of ligand binding to the GABAA receptor. Eur J Pharmacol 269:157–163
Hosie AM, Wilkins ME, da Silva HM, Smart TG (2006) Endogenous neurosteroids regulate GABAA receptors through two discrete transmembrane sites. Nature 444:486–489
Hosie AM, Wilkins ME, Smart TG (2007) Neurosteroid binding sites on GABA(A) receptors. Pharmacol Ther 116:7–19
Hosie AM, Clarke L, da Silva H, Smart TG (2009) Conserved site for neurosteroid modulation of GABAA receptors. Neuropharmacology 56:149–154
Li P, Bracamontes J, Katona BW, Covey DF, Steinbach JH, Akk G (2007) Natural and enantiomeric etiocholanolone interact with distinct sites on the rat α1β2γ2L GABAA receptor. Mol Pharmacol 71:1582–1590
Li P, Bandyopadhyaya AK, Covey DF, Steinbach JH, Akk G (2009) Hydrogen bonding between the 17b-substituent of a neurosteroid and the GABA(A) receptor is not obligatory for channel potentiation. Br J Pharmacol 158:1322–1329
Pratt MB, Husain SS, Miller KW, Cohen JB (2000) Identification of sites of incorporation in the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor of a photoactivatible general anesthetic. J Biol Chem 275:29441–29451
Selye H (1941) Anesthetic effect of steroid hormones. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 46:116–121
Shu HJ, Zeng CM, Wang C, Covey DF, Zorumski CF, Mennerick S (2007) Cyclodextrins sequester neuroactive steroids and differentiate mechanisms that rate limit steroid actions. Br J Pharmacol 150:164–175
Srinivasan S, Sapp DW, Tobin AJ, Olsen RW (1999) Biphasic modulation of GABA(A) receptor binding by steroids suggests functional correlates. Neurochem Res 24:1363–1372
Wittig I, Braun HP, Schagger H (2006) Blue native PAGE. Nat Protoc 1:418–428
Wittmer LL, Hu Y, Kalkbrenner M, Evers AS, Zorumski CF, Covey DF (1996) Enantioselectivity of steroid-induced gamma-aminobutyric acid A receptor modulation and anesthesia. Mol Pharmacol 50:1581–1586
Ziebell MR, Nirthanan S, Husain SS, Miller KW, Cohen JB (2004) Identification of binding sites in the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor for [3H]azietomidate, a photoactivatable general anesthetic. J Biol Chem 279:17640–17649
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grant PO1-GM47969 from the National Institute of General Medical Sciences to A.S.E, D.F.C., J.H.S and C.F.Z and by grant MH099658 to S.M. from the National Institute of Mental Health. Washington University receives income and equity based on a license of related technology to Sage Therapeutics. D.F.C., C.F.Z. and A.S.E. have equity holdings in Sage Therapeutics, Inc. Sage Therapeutics, Inc. did not support this research or have any other role in the research or its conclusions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Figure 1
(PDF 33 kb)
Supplementary Figure 2
(PDF 40 kb)
Supplementary Figure 3
(PDF 34 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, ZW., Wang, C., Krishnan, K. et al. 11-trifluoromethyl-phenyldiazirinyl neurosteroid analogues: potent general anesthetics and photolabeling reagents for GABAA receptors. Psychopharmacology 231, 3479–3491 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-014-3568-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-014-3568-4