Abstract
Rationale
Negative motivational withdrawal from acute opiate dependence was induced by an opioid antagonist, and the withdrawal signs prevented by pretreatment with nicotine.
Objectives
The present study was undertaken to examine the mechanism of nicotine-induced attenuation of withdrawal precipitated by naloxone in rats administered a single dose of morphine.
Methods
Conditioned place aversion (CPA) was precipitated by naloxone in rats exposed once to morphine. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR) agonists were microinjected into the central amygdaloid nucleus (CeA) before naloxone was administered. Additionally, c-Fos expression in the amygdala was measured in rats exposed to α7 nAChR ligands.
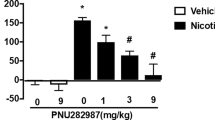
Results
The microinjection of nicotine (0.3 and 1.0 μg/μl) into the CeA dose-dependently inhibited naloxone-induced CPA. This inhibition of CPA was reversed by methyllycaconitine (MLA), an α7 nAChR antagonist. CPA was also significantly attenuated by the microinjection of tropisetron (3.0 μg/μl), an α7 nAChR agonist and 5-hydroxytriptamine 3 (5-HT3) receptor antagonist, but not by ondansetron (1.0 and 3.0 μg/μl), a 5-HT3 receptor antagonist. The microinjection of PNU-282987 (3.0 μg/μl), a selective α7 nAChR agonist, into the CeA also inhibited CPA. Furthermore, nicotine increased c-Fos expression in the CeA, but not the medial or basolateral amygdaloid nucleus. The increase of c-Fos in the CeA was significantly inhibited by MLA.
Conclusion
Nicotine-induced attenuation of CPA precipitated by naloxone is mediated by the α7 nAChR subtype, and the CeA is one of the regions of the brain involved in the effect of nicotine on acutely opiate-dependent subjects.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Araki H, Kawakami KY, Jin C, Suemaru K, Kitamura Y, Nagata M, Futagami K, Shibata K, Kawasaki H, Gomita Y (2004) Nicotine attenuates place aversion induced by naloxone in single-dose, morphine-treated rats. Psychopharmacology 171:398–404
Azar MR, Jones BC, Schulteis G (2003) Conditioned place aversion is a highly sensitive index of acute opioid dependence and withdrawal. Psychopharmacology 170:42–50
Bhatnagar S, Sun LM, Raber J, Maren S, Julius D, Dallman MF (2004) Changes in anxiety-related behaviors and hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal activity in mice lacking the 5-HT-3A receptor. Physiol Behav 81:545–555
Bickel WK, Stitzer ML, Liebson IA, Bigelow GE (1988) Acute physical dependence in man: effects of naloxone after brief morphine exposure. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 244:126–132
Bodnar AL, Cortes-Burgos LA, Cook KK, Dinh DM, Groppi VE, Hajos M, Higdon NR, Hoffmann WE, Hurst RS, Myers JK, Rogers BN, Wall TM, Wolfe ML, Wong E (2005) Discovery and structure-activity relationship of quinuclidine benzamides as agonists of alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. J Med Chem 48:905–908
Carboni E, Acquas E, Leone P, Perezzani L, Di Chiara G (1988) 5-HT3 receptor antagonists block morphine- and nicotine-induced place-preference conditioning. Eur J Pharmacol 22:159–160
Chartoff EH, Mague SD, Barhight MF, Smith AM, Carlezon WA Jr (2006) Behavioral and molecular effects of dopamine D1 receptor stimulation during naloxone-precipitated morphine withdrawal. J Neurosci 26:6450–6457
Chu LF, Liang DY, Li X, Sahbaie P, D’arcy N, Liao G, Peltz G, David Clark J (2009) From mouse to man: the 5-HT3 receptor modulates physical dependence on opioid narcotics. Pharmacogenet Genomics 19:193–205
Cui R, Suemaru K, Li B, Kohnomi S, Araki H (2009) Tropisetron attenuates naloxone-induced place aversion in single-dose morphine-treated rats: role of alpha7 nicotinic receptors. Eur J Pharmacol 609:74–77
Davis M, Rainnie D, Cassell M (1994) Neurotransmission in the rat amygdala related to fear and anxiety. Trends Neurosci 17:208–214
Easterling KW, Holtzman SG (1997) Intracranial self-stimulation in rats: sensitization to an opioid antagonist following acute or chronic treatment with mu opioid agonists. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 281:188–199
Frenois F, Cador M, Caillé S, Stinus L, Le Moine C (2002) Neural correlates of the motivational and somatic components of naloxone-precipitated morphine withdrawal. Eur J Neurosci 16:1377–1389
Georges F, Stinus L, Bloch B, Le Moine C (1999) Chronic morphine exposure and spontaneous withdrawal are associated with modifications of dopamine receptor and neuropeptide gene expression in the rat striatum. Eur J Neurosci 11:481–490
Gracy KN, Dankiewicz LA, Koob GF (2001) Opiate withdrawal-induced fos immunoreactivity in the rat extended amygdala parallels the development of conditioned place aversion. Neuropsychopharmacology 24:152–160
Haertzen CA, Hooks NT Jr (1969) Changes in personality and subjective experience associated with the chronic administration and withdrawal of opiates. J Nerv Ment Dis 148:606–614
Han ZY, Zoli M, Cardona A, Bourgeois JP, Changeux JP, Le Novère N (2003) Localization of [3H]nicotine, [3H]cytisine, [3H]epibatidine, and [125I]alpha-bungarotoxin binding sites in the brain of Macaca mulatta. J Comp Neurol 461:49–60
Higgins GA, Nguyen P, Joharchi N, Sellers EM (1991) Effects of 5-HT3 receptor antagonists on behavioural measures of naloxone-precipitated opioid withdrawal. Psychopharmacology 105:322–328
Jin C, Araki H, Nagata M, Suemaru K, Shibata K, Kawasaki H, Hamamura T, Gomita Y (2004) Withdrawal-induced c-Fos expression in the rat centromedial amygdala 24 h following a single morphine exposure. Psychopharmacology 175:428–435
Jin C, Araki H, Nagata M, Shimosaka R, Shibata K, Suemaru K, Kawasaki H, Gomita Y (2005) Expression of c-Fos in the rat central amygdala accompanies the acquisition but not expression of conditioned place aversion induced by withdrawal from acute morphine dependence. Behav Brain Res 161:107–112
Kankaanpää A, Meririnne E, Seppälä T (2002) 5-HT3 receptor antagonist MDL 72222 attenuates cocaine- and mazindol-, but not methylphenidate-induced neurochemical and behavioral effects in the rat. Psychopharmacology 159:341–350
Kelsey JE, Arnold SR (1994) Lesions of the dorsomedial amygdala, but not the nucleus accumbens, reduce the aversiveness of morphine withdrawal in rats. Behav Neurosci 108:1119–1127
Koob GF (1999) The role of the striatopallidal and extended amygdala systems in drug addiction. Ann N Y Acad Sci 877:445–460
Koob GF, Le Moal M (2005) Neurobiology of addiction. Academic, San Diego
Liu J, Schulteis G (2004) Brain reward deficits accompany naloxone-precipitated withdrawal from acute opioid dependence. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 79:101–108
Loughlin SE, Islas MI, Cheng MY, Lee AG, Villegier AS, Leslie FM (2006) Nicotine modulation of stress-related peptide neurons. J Comp Neurol 497:575–588
Macor JE, Gurley D, Lanthorn T, Loch J, Mack RA, Mullen G, Tran O, Wright N, Gordon JC (2001) The 5-HT3 antagonist tropisetron (ICS 205-930) is a potent and selective alpha7 nicotinic receptor partial agonist. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 11:319–321
Martin WR, Eades CG (1964) A comparison between acute and chronic physical dependence in the chronic spinal dog. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 146:385–394
Mathieu-Kia AM, Pages C, Besson MJ (1998) Inducibility of c-Fos protein in visuo-motor system and limbic structures after acute and repeated administration of nicotine in the rat. Synapse 29:343–354
McDonald RV, Parker LA, Siegel S (1997) Conditioned sucrose aversions produced by naloxone-precipitated withdrawal from acutely administered morphine. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 58:1003–1008
Motoshima S, Suemaru K, Kawasaki Y, Jin C, Kawasaki H, Gomita Y, Araki H (2005) Effects of alpha4beta2 and alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor antagonists on place aversion induced by naloxone in single-dose morphine-treated rats. Eur J Pharmacol 519:91–95
Panagis G, Hildebrand BE, Svensson TH, Nomikos GG (2000) Selective c-fos induction and decreased dopamine release in the central nucleus of amygdala in rats displaying a mecamylamine-precipitated nicotine withdrawal syndrome. Synapse 35:15–25
Parker LA, Joshi A (1998) Naloxone-precipitated morphine withdrawal induced place aversions: effect of naloxone at 24 hours postmorphine. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 61:331–333
Parker LA, Cyr JA, Santi AN, Burton PD (2002) The aversive properties of acute morphine dependence persist 48 h after a single exposure to morphine: evaluation by taste and place conditioning. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 72:87–92
Paxinos G, Watson C (1997) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Academic, San Diego
Rodríguez de Fonseca F, Navarro M (1998) Role of the limbic system in dependence on drugs. Ann Med 30:397–405
Salminen O, Seppä T, Gäddnäs H, Ahtee L (1999) The effects of acute nicotine on the metabolism of dopamine and the expression of Fos protein in striatal and limbic brain areas of rats during chronic nicotine infusion and its withdrawal. J Neurosci 19:8145–8151
Schulteis G, Heyser CJ, Koob GF (1997) Opiate withdrawal signs precipitated by naloxone following a single exposure to morphine: potentiation with a second morphine exposure. Psychopharmacology 129:56–65
Schulteis G, Heyser CJ, Koob GF (1999) Differential expression of response-disruptive and somatic indices of opiate withdrawal during the initiation and development of opiate dependence. Behav Pharmacol 10:235–242
Séguéla P, Wadiche J, Dineley-Miller K, Dani JA, Patrick JW (1993) Molecular cloning, functional properties, and distribution of rat brain alpha 7: a nicotinic cation channel highly permeable to calcium. J Neurosci 13:596–604
Shram MJ, Funk D, Li Z, Lê AD (2007) Acute nicotine enhances c-fos mRNA expression differentially in reward-related substrates of adolescent and adult rat brain. Neurosci Lett 18:286–291
Simpson K, Spencer CM, McClellan KJ (2000) Tropisetron: an update of its use in the prevention of chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting. Drugs 59:1297–1315
Taraschenko OD, Panchal V, Maisonneuve IM, Glick SD (2005) Is antagonism of alpha3beta4 nicotinic receptors a strategy to reduce morphine dependence? Eur J Pharmacol 513:207–218
Veinante P, Stoeckel ME, Lasbennes F, Freund-Mercier MJ (2003) c-Fos and peptide immunoreactivities in the central extended amygdala of morphine-dependent rats after naloxone-precipitated withdrawal. Eur J Neurosci 18:1295–1305
Watanabe T, Nakagawa T, Yamamoto R, Maeda A, Minami M, Satoh M (2002) Involvement of glutamate receptors within the central nucleus of the amygdala in naloxone-precipitated morphine withdrawal-induced conditioned place aversion in rats. Jpn J Pharmacol 88:399–406
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by a grant from the Smoking Research Foundation of Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ishida, S., Kawasaki, Y., Araki, H. et al. α7 Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in the central amygdaloid nucleus alter naloxone-induced withdrawal following a single exposure to morphine. Psychopharmacology 214, 923–931 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-010-2101-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-010-2101-7