Abstract
Rationale and objectives
Sigma receptors have been implicated in appetitive effects of psychostimulants and in high levels of ethanol intake. This study tested the hypothesis that the sigma-1 receptor subtype (Sig-1R) may modulate ethanol intake.
Material and methods
The effects of acute and repeated treatment with the potent, selective Sig-1R antagonist NE-100 on ethanol intake (10%) were studied in adult, male Sardinian alcohol-preferring (sP) rats, a model of genetic predisposition to high ethanol drinking. To assess the specificity of action, the acute effects of NE-100 on intake of an equally preferred sucrose solution and of a higher concentration of ethanol that sP rats did not prefer over water (28%), were determined. Finally, the ability of NE-100 administration to prevent the increased ethanol intake that occurs after deprivation was evaluated.
Results
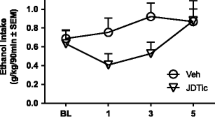
Acute treatment with NE-100 dose-dependently (10–30 mg/kg) reduced 1- and 3-h intake of 10% ethanol solution in sP rats, while increasing concurrent water intake and not affecting food intake. NE-100 (17.8–30 mg/kg) comparably reduced intake of the 28% ethanol solution, while not suppressing 1.25% sucrose solution intake, suggesting selectivity of action against ethanol intake. Acute NE-100 (30 mg/kg) also prevented an increase in ethanol intake after a 7-day deprivation period. Repeated, daily NE-100 (30 mg/kg) treatment continued to reduce 24-h ethanol intake across 7 days of administration, with some, but incomplete, tolerance, evident by day 6.
Conclusions
The results implicate the Sig-1R system in alcohol drinking, identifying a potential therapeutic target for the treatment of alcohol use disorders.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agabio R, Carai MA, Lobina C, Pani M, Reali R, Vacca G, Gessa GL, Colombo G (2000) Development of short-lasting alcohol deprivation effect in Sardinian alcohol-preferring rats. Alcohol 21:59–62
Alonso G, Phan V, Guillemain I, Saunier M, Legrand A, Anoal M, Maurice T (2000) Immunocytochemical localization of the sigma(1) receptor in the adult rat central nervous system. Neuroscience 97:155–170
Bastianetto S, Rouquier L, Perrault G, Sanger DJ (1995) DTG-induced circling behaviour in rats may involve the interaction between sigma sites and nigro-striatal dopaminergic pathways. Neuropharmacology 34:281–287
Berardi F, Ferorelli S, Colabufo NA, Leopoldo M, Perrone R, Tortorella V (2001) A multireceptorial binding reinvestigation on an extended class of sigma ligands: N-[omega-(indan-1-yl and tetralin-1-yl) alkyl] derivatives of 3,3-dimethylpiperidine reveal high affinities towards sigma1 and EBP sites. Bioorg Med Chem 9:1325–1335
Boening JA, Lesch OM, Spanagel R, Wolffgramm J, Narita M, Sinclair D, Mason BJ, Wiesbeck GA (2001) Pharmacological relapse prevention in alcohol dependence: from animal models to clinical trials. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 25:127S–131S
Bouchard P, Quirion R (1997) [3H]1, 3-di(2-tolyl) guanidine and [3H](+) pentazocine binding sites in the rat brain: autoradiographic visualization of the putative sigma1 and sigma2 receptor subtypes. Neuroscience 76:467–477
Brammer MK, Gilmore DL, Matsumoto RR (2006) Interactions between 3, 4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine and sigma1 receptors. Eur J Pharmacol 553:141–145
Carelli RM, Wightman RM (2004) Functional microcircuitry in the accumbens underlying drug addiction: insights from real-time signaling during behavior. Curr Opin Neurobiol 14:763–768
Cloninger CR, Bohman M, Sigvardsson S (1981) Inheritance of alcohol abuse. Cross-fostering analysis of adopted men. Arch Gen Psychiatry 38:861–868
Colombo G (1997) ESBRA-Nordmann 1996 Award Lecture: ethanol drinking behaviour in Sardinian alcohol-preferring rats. Alcohol Alcohol 32:443–453
Colombo G, Lobina C, Carai MA, Gessa GL (2006) Phenotypic characterization of genetically selected Sardinian alcohol-preferring (sP) and -non-preferring (sNP) rats. Addict Biol 11:324–338
Cowen MS, Rezvani AH, Jarrott B, Lawrence AJ (1999) Ethanol consumption by Fawn-Hooded rats following abstinence: effect of naltrexone and changes in mu-opioid receptor density. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 23:1008–1014
Gundlach AL, Largent BL, Snyder SH (1985) Phencyclidine and sigma opiate receptors in brain: biochemical and autoradiographical differentiation. Eur J Pharmacol 113:465–466
Hanner M, Moebius FF, Flandorfer A, Knaus HG, Striessnig J, Kempner E, Glossmann H (1996) Purification, molecular cloning, and expression of the mammalian sigma1-binding site. Proc Natl Acad Sic USA 93:8072–8077
Heilig M, Egli M (2006) Pharmacological treatment of alcohol dependence: target symptoms and target mechanisms. Pharmacol Ther 111:855–876
Iyengar S, Dilworth VM, Mick SJ, Contreras PC, Monahan JB, Rao TS, Wood PL (1990) Sigma receptors modulate both A9 and A10 dopaminergic neurons in the rat brain: functional interaction with NMDA receptors. Brain Res 524:322–326
Koob GF (2000) Animal models of craving for ethanol. Addiction 95(Suppl 2):S73–S81
Li TK (2000) Clinical perspectives for the study of craving and relapse in animal models. Addiction 95(Suppl 2):S55–S60
Martin WR, Eades CG, Thompson JA, Huppler RE, Gilbert PE (1976) The effects of morphine- and nalorphine-like drugs in the nondependent and morphine-dependent chronic spinal dog. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 197:517–532
Martin-Fardon R, Maurice T, Aujla H, Bowen WD, Weiss F (2007) Differential effects of sigma1 receptor blockade on self-administration and conditioned reinstatement motivated by cocaine vs natural reward. Neuropsychopharmacology 32:1967–1973
Matsumoto RR, Mack AL (2001) (+/-)-SM 21 attenuates the convulsive and locomotor stimulatory effects of cocaine in mice. Eur J Pharmacol 417:R1–R2
Matsumoto RR, McCracken KA, Pouw B, Zhang Y, Bowen WD (2002) Involvement of sigma receptors in the behavioral effects of cocaine: evidence from novel ligands and antisense oligodeoxynucleotides. Neuropharmacology 42:1043–1055
Matsumoto RR, Pouw B, Mack AL, Daniels A, Coop A (2007) Effects of UMB24 and (+/-)-SM 21, putative sigma2-preferring antagonists, on behavioral toxic and stimulant effects of cocaine in mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 86:86–91
Maurice T (2004) Neurosteroids and sigma1 receptors, biochemical and behavioral relevance. Pharmacopsychiatry 37(Suppl 3):S171–S182
Maurice T, Romieu P (2004) Involvement of the sigma1 receptor in the appetitive effects of cocaine. Pharmacopsychiatry 37(Suppl 3):S198–S207
Maurice T, Martin-Fardon R, Romieu P, Matsumoto RR (2002) Sigma(1) (sigma(1)) receptor antagonists represent a new strategy against cocaine addiction and toxicity. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 26:499–527
Maurice T, Casalino M, Lacroix M, Romieu P (2003) Involvement of the sigma 1 receptor in the motivational effects of ethanol in mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 74:869–876
McBride WJ, Li TK (1998) Animal models of alcoholism: neurobiology of high alcohol-drinking behavior in rodents. Crit Rev Neurobiol 12:339–369
McBride WJ, Le AD, Noronha A (2002) Central nervous system mechanisms in alcohol relapse. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 26:280–286
McLellan AT, Lewis DC, O’Brien CP, Kleber HD (2000) Drug dependence, a chronic medical illness: implications for treatment, insurance, and outcomes evaluation. JAMA 284:1689–1695
Menkel M, Terry P, Pontecorvo M, Katz JL, Witkin JM (1991) Selective sigma ligands block stimulant effects of cocaine. Eur J Pharmacol 201:251–252
Minabe Y, Matsuno K, Ashby CR Jr (1999) Acute and chronic administration of the selective sigma1 receptor agonist SA4503 significantly alters the activity of midbrain dopamine neurons in rats: an in vivo electrophysiological study. Synapse 33:129–140
Miyatake R, Furukawa A, Matsushita S, Higuchi S, Suwaki H (2004) Functional polymorphisms in the sigma1 receptor gene associated with alcoholism. Biol Psychiatry 55:85–90
Moebius FF, Burrows GG, Hanner M, Schmid E, Striessnig J, Glossmann H (1993) Identification of a 27-kDa high affinity phenylalkylamine-binding polypeptide as the sigma 1 binding site by photoaffinity labeling and ligand-directed antibodies. Mol Pharmacol 44:966–971
Nuwayhid SJ, Werling LL (2006) Sigma(2) (sigma(2)) receptors as a target for cocaine action in the rat striatum. Eur J Pharmacol
Overstreet DH, Kampov-Polevoy AB, Rezvani AH, Braun C, Bartus RT, Crews FT (1999) Suppression of alcohol intake by chronic naloxone treatment in P rats: tolerance development and elevation of opiate receptor binding. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 23:1761–1771
Parkes H, Sinclair JD (2000) Reduction of alcohol drinking and upregulation of opioid receptors by oral naltrexone in AA rats. Alcohol 21:215–221
Prescott CA, Kendler KS (1999) Genetic and environmental contributions to alcohol abuse and dependence in a population-based sample of male twins. Am J Psychiatry 156:34–40
Quirion R, Hammer RP Jr, Herkenham M, Pert CB (1981) Phencyclidine (angel dust)/sigma “opiate” receptor: visualization by tritium-sensitive film. Proc Natl Acad Sic USA 78:5881–5885
Romieu P, Martin-Fardon R, Maurice T (2000) Involvement of the sigma1 receptor in the cocaine-induced conditioned place preference. Neuroreport 11:2885–2888
Romieu P, Meunier J, Garcia D, Zozime N, Martin-Fardon R, Bowen WD, Maurice T (2004) The sigma1 (sigma1) receptor activation is a key step for the reactivation of cocaine conditioned place preference by drug priming. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 175:154–162
Sabino V, Cottone P, Zhao Y, Iyer MR, Steardo LJ, Steardo L, Rice KC, Conti B, Koob GF, Zorrilla EP (2009) The sigma-receptor antagonist BD-1063 decreases ethanol intake and reinforcement in animal models of excessive drinking. Neuropsychopharmacology 34(6):1482–1493
Sanchez-Arroyos R, Guitart X (1999) Electrophysiological effects of E-5842, a sigma1 receptor ligand and potential atypical antipsychotic, on A9 and A10 dopamine neurons. Eur J Pharmacol 378:31–37
Serra S, Brunetti G, Vacca G, Lobina C, Carai MA, Gessa GL, Colombo G (2003) Stable preference for high ethanol concentrations after ethanol deprivation in Sardinian alcohol-preferring (sP) rats. Alcohol 29:101–108
Sigvardsson S, Bohman M, Cloninger CR (1996) Replication of the Stockholm Adoption Study of alcoholism. Confirmatory cross-fostering analysis. Arch Gen Psychiatry 53:681–687
Steinfels GF, Tam SW (1989) Selective sigma receptor agonist and antagonist affect dopamine neuronal activity. Eur J Pharmacol 163:167–170
Tanaka M, Shirasaki T, Kaku S, Muramatsu M, Otomo S (1995) Characteristics of binding of [3H]NE-100, a novel sigma-receptor ligand, to guinea-pig brain membranes. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 351:244–251
Ueda H, Yoshida A, Tokuyama S, Mizuno K, Maruo J, Matsuno K, Mita S (2001) Neurosteroids stimulate G protein-coupled sigma receptors in mouse brain synaptic membrane. Neurosci Res 41:33–40
Ujike H, Kanzaki A, Okumura K, Akiyama K, Otsuki S (1992) Sigma (sigma) antagonist BMY 14802 prevents methamphetamine-induced sensitization. Life Sic 50:PL129–PL134
Walker JM, Bowen WD, Walker FO, Matsumoto RR, De CB, Rice KC (1990) Sigma receptors: biology and function. Pharmacol. Rev. 42:355–402
Weatherspoon JK, Werling LL (1999) Modulation of amphetamine-stimulated [3H]dopamine release from rat pheochromocytoma (PC12) cells by sigma type 2 receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 289:278–284
Weiser SD, Patrick SL, Mascarella SW, Downing-Park J, Bai X, Carroll FI, Walker JM, Patrick RL (1995) Stimulation of rat striatal tyrosine hydroxylase activity following intranigral administration of sigma receptor ligands. Eur J Pharmacol 275:1–7
Acknowledgements
Research was supported by grants from the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (5K99AA016731-02, 2P60AA006420-25, and 5R01AA012602-09) and by the Pearson Center for Alcoholism and Addiction Research. This is manuscript number 19878 from The Scripps Research Institute. The authors thank Taisho Pharmaceuticals for the gift of NE-100, the excellent technical assistance of Maury Cole, Molly Brennan, Jeanette Helfers and Robert Lintz, and the editorial assistance of Mike Arends.
Disclosure/conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Valentina Sabino and Pietro Cottone contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sabino, V., Cottone, P., Zhao, Y. et al. Selective reduction of alcohol drinking in Sardinian alcohol-preferring rats by a sigma-1 receptor antagonist. Psychopharmacology 205, 327–335 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-009-1548-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-009-1548-x