Abstract
Rationale
Administration of an opiate antagonist following acute morphine exposure elevates the startle response in rodents, a phenomenon that may reflect the anxiogenic effects of withdrawal. Previous acute dependence studies have demonstrated escalated withdrawal severity following multiple withdrawal episodes.
Objectives
To examine the effects of prior opiate exposure on the magnitude of withdrawal-potentiated startle and an additional measure of acute dependence, withdrawal-induced hyperalgesia.
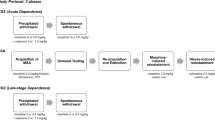
Methods
The effects of repeated naloxone-precipitated morphine withdrawals on acoustic startle responding were evaluated in experiments that varied either the dose of the opiate antagonist (8-day, repeated measures procedure) or agonist (3-day procedure). Additional experiments examined withdrawal-induced hyperalgesia utilizing either a single-day dependence paradigm or the same 3-day procedure as in the startle experiment.
Results
Repeated naloxone-precipitated withdrawals from acute morphine exacerbated withdrawal severity in both startle procedures, although this effect varied biphasically (inverted-U function) with morphine dose in the 3-day dependence paradigm. Withdrawal from a single morphine exposure also induced hyperalgesia, and this effect was intensified by prior withdrawal episodes.
Conclusions
These data demonstrate that repeated withdrawals from acute morphine exacerbate the severity of potentiated startle and hyperalgesia. These paradigms may be useful in examining the neural plasticity underlying the development of opiate dependence.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams JU, Holtzman SG (1990) Pharmacologic characterization of the sensitization to the rate-decreasing effects of naltrexone induced by acute opioid pretreatment in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 253:483–489
American Psychiatric Association (1994) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 4th edn. American Psychiatric Association, Washington D.C.
Azar MR, Jones BC, Schulteis G (2003) Conditioned place aversion is a highly sensitive index of acute opioid dependence and withdrawal. Psychopharmacology 70:42–50
Azorlosa JL, Stitzer ML, Greenwald MK (1994) Opioid physical dependence development: effects of single versus repeated morphine pretreatments and of subjects’ opioid exposure history. Psychopharmacology 114:71–80
Bickel WK, Stitzer ML, Liebson IA, Bigelow GE (1988) Acute physical dependence in man: effects of naloxone after brief morphine exposure. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 244:126–132
Blasig J, Herz A, Reinhold K, Zieglgansberger S (1973) Development of physical dependence on morphine in respect to time and dosage and quantification of the precipitated withdrawal syndrome in rats. Psychopharmacologia 33:19–38
Davis M (1979) Morphine and naloxone: effects on conditioned fear as measured with the potentiated startle paradigm. Eur J Pharmacol 54:341–347
Davis M (1998) Are different parts of the extended amygdala involved in fear versus anxiety? Biol Psychiatry 44:1239–1247
Davis M, Astrachan DI (1978) Conditioned fear and startle magnitude: effects of different footshock or backshock intensities used in training. J Exp Psychol [Anim Behav Proc] 4:95–103
Dwoskin LP, Neal BS, Sparber SB (1983) Yohimbine exacerbates and clonidine attenuates acute morphine withdrawal in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 90:269–273
Fendt M, Fanselow MS (1999) The neuroanatomical and neurochemical basis of conditioned fear. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 23:743–760
Fendt M, Mucha RF (2001) Anxiogenic-like effects of opiate withdrawal seen in the fear-potentiated startle test, an interdisciplinary probe for drug-related motivational states. Psychopharmacology 155:242–250
Gewirtz JC, McNish KA, Davis M (1998) Lesions of the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis block sensitization of the acoustic startle reflex produced by repeated stress, but not fear-potentiated startle. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 22:625–648
Gold MS, Pottash AL, Sweeney DR, Davies RK, Kleber HD (1980) Clonidine decreases opiate withdrawal-related anxiety: possible opiate noradrenergic interaction in anxiety and panic. Subst Alcohol Actions Misuse 1:239–246
Hamilton KL, Harris AC, Sparber SB, Gewirtz JC, Schrott LM (2003) Prenatal opiate exposure differentially affects acoustic startle responding and thermal nociception in male and female rats. College on Problems of Drug Dependence, National Institute on Drug Abuse, Rockville, Md.
Hargreaves K, Dubner R, Brown F, Flores C, Joris J (1988) A new and sensitive method for measuring thermal nociception in cutaneous hyperalgesia. Pain 32:77–88
Harris AC, Gewirtz JC (2004) Elevated startle during withdrawal from acute morphine: a model of opiate withdrawal and anxiety. Psychopharmacology 171:140–147
Kalinichev M, Holtzman SG (2003) Changes in urination/defecation, auditory startle response, and startle-induced ultrasonic vocalizations in rats undergoing morphine withdrawal: similarities and differences between acute and chronic dependence. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 304:603–609
Kayan S, Woods LA, Mitchell CL (1971) Morphine-induced hyperalgesia in rats tested on the hot plate. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 177:509–513
Kim DH, Fields HL, Barbaro NM (1990) Morphine analgesia and acute physical dependence: rapid onset of two opposing, dose-related processes. Brain Res 516:37–40
Koob GF, Le Moal M (1997) Drug abuse: hedonic homeostatic dysregulation. Science 278:52–58
Koob GF, Le Moal M (2001) Drug addiction, dysregulation of reward, and allostasis. Neuropsychopharmacology 24:97–129
Maldonado R (1997) Participation of noradrenergic pathways in the expression of opiate withdrawal: biochemical and pharmacological evidence. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 21:91–104
Mansbach RS, Gold LH, Harris LS (1992) The acoustic startle response as a measure of behavioral dependence in rats. Psychopharmacology 108:40–46
Mayo-Smith MF (1997) Pharmacological management of alcohol withdrawal. A meta-analysis and evidence-based practice guideline. American Society of Addiction medicine working group on pharmacological management of alcohol withdrawal. JAMA 278:144–151
Meyer DR, Sparber SB (1977) Evidence of possible opiate dependence during the behavioral depressant action of a single dose of morphine. Life Sci 21:1087–1093
Risbrough VB, Hauger RL, Pelleymounter MA, Geyer MA (2003) Role of corticotropin releasing factor (CRF) receptors 1 and 2 in CRF-potentiated acoustic startle in mice. Psychopharmacology 170:178–187
Schulteis G, Koob GF (1996) Reinforcement processes in opiate addiction: a homeostatic model. Neurochem Res 21:1437–1454
Schulteis G, Heyser CJ, Koob GF (1997) Opiate withdrawal signs precipitated by naloxone following a single exposure to morphine: potentiation with a second morphine exposure. Psychopharmacology 129:56–65
Schulteis G, Heyser CJ, Koob GF (1999) Differential expression of response-disruptive and somatic indices of opiate withdrawal during the initiation and development of opiate dependence. Behav Pharmacol 10:235–242
Schulteis G, Morse AC, Liu J (2003) Repeated experience with naloxone facilitates acute morphine withdrawal: potential role for conditioning processes in acute opioid dependence. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 76:493–503
Sparber SB, Gellert VF, Lichtblau L, Eisenberg R (1978) The use of operant behavior methods to study aggression and effects of acute and chronic morphine administration in rats. In: Adler ML, Manara L, Samanin R (eds) Factors affecting the action of narcotics. Raven, New York, pp 63–91
Swerdlow NR, Geyer MA, Vale WW, Koob GF (1986) Corticotropin-releasing factor potentiates acoustic startle in rats: blockade by chlordiazepoxide. Psychopharmacology 88:147–152
Tilson HA, Rech RH, Stolman S (1973) Hyperalgesia during withdrawal as a means of measuring the degree of dependence in morphine dependent rats. Psychopharmacologia 28:287–300
Walker DL, Cassella JV, Lee Y, De Lima TC, Davis M (1997) Opposing roles of the amygdala and dorsolateral periaqueductal gray in fear-potentiated startle. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 21:743–753
White DA, Holtzman SG (2001) Acute opioid pretreatment potentiates naltrexone-induced drinking suppression in water-deprived rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 298:156–164
Yoburn BC, Chen J, Huang T, Inturrisi CE (1985) Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of subcutaneous morphine pellets in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 235:282–286
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank Darrin Aase, David Atkinson, Annette Kenzler, Mark Liszewski, and Claire Smith for their assistance in conducting the experiments. This work was supported by the National Institute of Drug Abuse T32 DA07097 and the University of Minnesota.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Harris, A.C., Hanes, S.L. & Gewirtz, J.C. Potentiated startle and hyperalgesia during withdrawal from acute morphine: effects of multiple opiate exposures. Psychopharmacology 176, 266–273 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-004-1889-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-004-1889-4