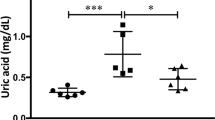
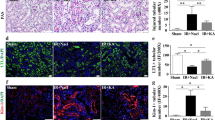
Abstract
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a type of chronic disease in which multiple factors are responsible for the structural and functional disorders of the kidney. Piperazine ferulate (PF) has anti-platelet and anti-fibrotic effects, and its mechanism of action remains to be elucidated. This study aimed to investigate the protective effect of PF against CKD in rats and to determine its mechanism of action. Network pharmacology was used to predict potential PF action targets in the treatment of CKD and to further validate them. A rat model of CKD was established; blood was collected, etc., for the assessment of the renal function; renal pathologic damage was examined using hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining and Masson staining; changes in the levels of TGF-β1 and α-SMA were determined with ELISA; EPOR, FN, and COL I expression were detected utilizing immunohistochemistry; and HIF-1α, HIF-2α, and EPO protein molecules were analyzed deploying western blotting. PF reduces Scr, BUN, and 24 h UP levels; decreases FN and COL I expression; and attenuates renal injury. Additionally, PF inhibited TGF-β1 and stimulated the production of HIF-1α and HIF-2α, which downregulated α-SMA and upregulated EPO. PF attenuated the progression of the CKD pathology, and the mechanism of its action is possibly associated with the promotion of HIF-1α/HIF-2α/EPO production and TGF-β1 reduction.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- α-SMA:
-
α-Smooth muscle actin
- BC:
-
Betweenness centrality
- BCL-2:
-
B-cell lymphoma-2
- BUN:
-
Blood urea nitrogen
- CASP3:
-
Caspase-3
- CKD:
-
Chronic kidney disease
- DC:
-
Degree centrality
- ECM:
-
Extracellular matrix
- ELISA:
-
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
- EPO:
-
Erythropoietin
- EPOR:
-
Erythropoietin receptor
- ESKD:
-
End-stage renal disease
- FN:
-
Fibronectin
- COL I:
-
Collagen I
- HE:
-
Hematoxylin and eosin
- HIF :
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor
- HIF -1a:
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor-1a
- HIF -2a:
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor-2a
- MDM2 :
-
Murine double minute2
- PARP1:
-
Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1
- PLT:
-
Platelet count
- Scr:
-
Serum creatinine
- TGF-β1:
-
Transforming growth factor-β1
- UP:
-
Urine protein
References
Babitt JL, Lin HY (2012) Mechanisms of anemia in CKD. J Am Soc Nephrol 23:1631–1634. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2011111078
Cai H (2017) Study on the improvement effort and mechanism of salvia miltiorrhiza stem-leaf on chronic renal function injury (master). Nanjing University Of Chinese Medicine
Cehn Q, Ma X, Mao N, Fan J (2022) Advances in the relationship between regulatory T cells and chronic kidney disease. J Chengdu Med Coll 17:267–272
Chen J, Li D (2018) Telbivudine attenuates UUO-induced renal fibrosis via TGF-β/Smad and NF-κB signaling. Int Immunopharmacol 55:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2017.11.043
Chen M, Chen L, Zhou Z, Liu H, Gu B (2020) Examination of the dissolution curve of piperazine ferulate tablets. Pharm Clin Res 28:443–446. https://doi.org/10.13664/j.cnki.pcr.2020.06.010
Chou Y-H, Pan S-Y, Shih H-M, Lin S-L (2023) Update of pericytes function and their roles in kidney diseases. J Formos Med Assoc. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfma.2023.08.002
Dai W, Wu R, Zhang Y, Hou X, Peng D (2023) Tissue distribution of the five main components of Taohong Siwu decoction in a rat model of cerebral ischemia/reperfusion. J Anhui Univ Tradit Chin Med 42:88–96
Dang J, Jia R, Tu Y, Xiao S, Ding G (2010) Erythropoietin prevents reactive oxygen species generation and renal tubular cell apoptosis at high glucose level. Biomed Pharmacother 64:681–685. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2010.06.011
Deng R, Yao L, Xiang D (2018) Pharmacological effect of piperazine ferulate. Cent South Pharm 16:1575–1578
Djudjaj S, Boor P (2019) Cellular and molecular mechanisms of kidney fibrosis. Mol Aspects Med 65:16–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mam.2018.06.002
Dong X (2021) Effects of Liu Wei Di Huang Tang on HIF-1α, Twist and E-cadherin in renal tissues of 5/6 nephrectomized rats (Master). Hunan University of Chinese Medicine
El-Mesallamy HO, Gawish RA, Sallam A-AM, Fahmy HA, Nada AS (2018) Ferulic acid protects against radiation-induced testicular damage in male rats: impact on SIRT1 and PARP1. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 25:6218–6227. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0873-6
Gonzalez-Flores A, Aguilar-Quesada R, Siles E, Pozo S, Rodríguez-Lara MI, López-Jiménez L, López-Rodríguez M, Peralta-Leal A, Villar D, Martín-Oliva D, del Peso L, Berra E, Oliver FJ (2014) Interaction between PARP-1 and HIF-2α in the hypoxic response. Oncogene 33:891–898. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2013.9
Hafizi R, Imeri F, Wenger RH, Huwiler A (2021) S1P stimulates erythropoietin production in mouse renal interstitial fibroblasts by S1P1 and S1P3 receptor activation and HIF-2α stabilization. Int J Mol Sci 22:9467. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22179467
Hain D, Bednarski D, Cahill M, Dix A, Foote B, Haras MS, Pace R, Gutiérrez OM (2023) Iron-deficiency anemia in CKD: a narrative review for the kidney care team. Kidney Med 5:100677. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xkme.2023.100677
Hayashi K, Shimokawa T, Yamagata M, Yoneda K (2021) Inhibition of α2-adrenoceptor is renoprotective in 5/6 nephrectomy-induced chronic kidney injury rats. J Pharmacol Sci 145:79–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphs.2020.11.001
Hofni A, El-Moselhy MA, Taye A, Khalifa MM (2014) Combination therapy with spironolactone and candesartan protects against streptozotocin-induced diabetic nephropathy in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 744:173–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2014.10.021
Hong Q, Ma Z-C, Huang H, Wang Y-G, Tan H-L, Xiao C-R, Liang Q-D, Zhang H-T, Gao Y (2016) Antithrombotic activities of ferulic acid via intracellular cyclic nucleotide signaling. Eur J Pharmacol 777:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2016.01.005
Hu B, Song J-T, Ji X-F, Liu Z-Q, Cong M-L, Liu D-X (2017) Sodium ferulate protects against angiotensin II-induced cardiac hypertrophy in mice by regulating the MAPK/ERK and JNK pathways. Biomed Res Int 2017:3754942. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3754942
Huang R, Fu P, Ma L (2023) Kidney fibrosis: from mechanisms to therapeutic medicines. Signal Transduct Target Ther 8:129. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-023-01379-7
Jelkmann W (2011) Regulation of erythropoietin production. J Physiol 589:1251–1258. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.2010.195057
Kadatane SP, Satariano M, Massey M, Mongan K, Raina R (2023) The Role of Inflammation in CKD. Cells 12:1581. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12121581
Koltai K, Kesmarky G, Feher G, Tibold A, Toth K (2017) Platelet aggregometry testing: molecular mechanisms, techniques and clinical implications. Int J Mol Sci 18:1803. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18081803
Koury MJ, Haase VH (2015) Anaemia in kidney disease: harnessing hypoxia responses for therapy. Nat Rev Nephrol 11:394–410. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneph.2015.82
Kumar H, Choi D-K (2015) Hypoxia inducible factor pathway and physiological adaptation: a cell survival pathway? Mediators Inflamm 2015:584758. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/584758
Li D, Li B, Rui Y, Xie H, Zhang X, Liu R, Zeng N (2022) Piperazine ferulate attenuates gentamicin-induced acute kidney injury via the NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway. Phytomedicine 99:154021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154021
Li Wge, Li Gsen, Yao L, Cheng Q (2021) Expert consensus on clinical application of piperazineferulate tablets on kidney diseases. Chin J Pract Int Med 41:584–589. https://doi.org/10.19538/j.nk2021070107
Liu Y, Shi G, Cao D, Wan Y, Wu W, Tu Y, Liu B, Han W, Yao J (2018) Pathomechanisms of pericyte-myofibroblast transition in kidney and interventional effects of Chinese herbal medicine. China J ChinMater Med 43:4192–4197
Liu H, Shen X, Zhou Z (2020) Determination of the related substances and assay of piperazine ferulate tablets by HPLC. Drug Standards of China 21:69–75. https://doi.org/10.19778/j.chp.2020.01.013
Liu Yu, Liu Z, Liu X (2021) Chronic kidney disease treatment. Chin Remedies Clin 21:1100–1102
Lu J, Yao Y, Dai Q, Ma G, Zhang S, Cao L, Ren L, Liu N (2012) Erythropoietin attenuates cardiac dysfunction by increasing myocardial angiogenesis and inhibiting interstitial fibrosis in diabetic rats. Cardiovasc Diabetol 11:105. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2840-11-105
Luo H (2019) Prevention and treatment of chronic kidney disease. Sichuan Labor Security 64
Masoud GN, Li W (2015) HIF-1α pathway: role, regulation and intervention for cancer therapy. Acta Pharm Sin B 5:378–389. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsb.2015.05.007
Nakagawa N, Duffield JS (2013) Myofibroblasts in fibrotic kidneys. Curr Pathobiol Rep 1. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40139-013-0025-8.
Park SY, Lee JY, Tak WY, Kweon YO, Lee MS (2012) Erythropoietin decreases carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatic fibrosis by inhibiting transforming growth factor-beta. Chin Med J (engl) 125:3098–3103
Qi M, Wang X, Xu H, Yang Z, Cheng Y, Zhou B (2020) Protective effect of ferulic acid on STZ-induced diabetic nephropathy in rats. Food Funct 11:3706–3718. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9FO02398D
Qu J, Chen C, Hao J (2021) Clinical study on Shenyuan Capsules combined with piperazine ferulate in treatment of chronic nephritis. Drugs & Clinic 36:1935–1939
Rehman SU, Ali T, Alam SI, Ullah R, Zeb A, Lee KW, Rutten BPF, Kim MO (2019) Ferulic acid rescues LPS-induced neurotoxicity via modulation of the TLR4 receptor in the mouse hippocampus. Mol Neurobiol 56:2774–2790. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-018-1280-9
Rjiba-Touati K, Ayed-Boussema I, Bouaziz C, Belarbia A, Azzabi A, Achour A, Hassen W, Bacha H (2012) Protective effect of erythropoietin against cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats: antigenotoxic and antiapoptotic effect. Drug Chem Toxicol 35:89–95. https://doi.org/10.3109/01480545.2011.589440
Semenza GL (2023) Regulation of erythropoiesis by the hypoxia-inducible factor pathway: effects of genetic and pharmacological perturbations. Annu Rev Med 74:307–319. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-med-042921-102602
Sundström J, Bodegard J, Bollmann A, Vervloet MG, Mark PB, Karasik A, Taveira-Gomes T, Botana M, Birkeland KI, Thuresson M, Jäger L, Sood MM, VanPottelbergh G, Tangri N (2022) Prevalence, outcomes, and cost of chronic kidney disease in a contemporary population of 2·4 million patients from 11 countries: the CaReMe CKD study. Lancet Reg Health Eur 20:100438. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lanepe.2022.100438
Tian Q, Lu M (2010) Analysis of the efficacy of irbesartan combined with piperazine ferulate in the treatment of chronic renal failure. Chin J Misdiagnostics 10:6618
Tögel FE, Ahlstrom JD, Yang Y, Hu Z, Zhang P, Westenfelder C (2016) Carbamylated erythropoietin outperforms erythropoietin in the treatment of AKI-on-CKD and other AKI models. J Am Soc Nephrol 27:3394–3404. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2015091059
Tziastoudi M, Theoharides TC, Nikolaou E, Efthymiadi M, Eleftheriadis T, Stefanidis I (2022) Key genetic components of fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Mol Sci 23:15331. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232315331
Voit RA, Sankaran VG (2020) Stabilizing HIF to ameliorate anemia. Cell 180:6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2019.12.010
Wang J, Liu B (2013) Advances in the role of pericytes in the formation of renal fibrosis. J Southeast Univ (medical Science Edition) 32:506–510
Wang B, Li Z-L, Zhang Y-L, Wen Y, Gao Y-M, Liu B-C (2022) Hypoxia and chronic kidney disease. Ebiomedicine 77:103942. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2022.103942
Webster AC, Nagler EV, Morton RL, Masson P (2017) Chronic kidney disease. Lancet 389:1238–1252. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(16)32064-5
Yan M-T, Chao C-T, Lin S-H (2021) Chronic kidney disease: strategies to retard progression. Int J Mol Sci 22:10084. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms221810084
Zhang Y, Zhu X, Huang X, Wei X, Zhao D, Jiang L, Zhao X, Du Y (2020) Advances in understanding the effects of erythropoietin on renal fibrosis. Front Med (lausanne) 7:47. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2020.00047
Funding
This work was supported by the Xinglin Scholar Research Promotion Project of Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine (Grant No. QJRC2022031).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The authors declare that all data were generated in-house and that no paper mill was used. X.Z.: conception/design of the work, methodology, validation, formal analysis, investigation, data curation, visualization, writing and editing. X.M.: methodology, validation, editing. D.L.: investigation, acquisition of data. B.L.: curation, supervision. Yixin Rui: acquisition of data. H.X.: acquisition of data. R.L.: conception/design of the work, writing—review and editing, supervision, project administration, funding acquisition. N.Z.: conceptualization, writing—review and editing, supervision, project administration.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
The feeding and experimental operation of all animals meet the requirements of Experimental Animal Ethics Committee of Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, approval number TCM-2022–26.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, XM., Min, XR., Li, D. et al. The protective effect and mechanism of piperazine ferulate in rats with 5/6 nephrectomy-caused chronic kidney disease. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-024-02976-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-024-02976-1