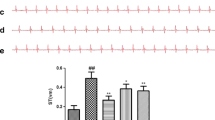
Abstract
Myocardial ischemia–reperfusion injury (MI/R) has been found to be one of the important risk factors for global cardiac mortality and morbidity. The study was conducted to inquire into the protective effect of 4-methylumbilliferon (4-MU) against MI/R in rats and clarify its potential underlying mechanism. Animals were divided into four groups (n = 15) including sham, MI/R, MI/R + vehicle, and MI/R + 4-MU. MI/R was established in Wistar rats by occluding the left anterior descending (LAD) coronary artery for 30 min. 4-MU (25 mg/kg) was injected intraperitoneally before the induction of reperfusion. Cardiac function, fibrosis, oxidant/antioxidant markers, and inflammatory cytokines were evaluated using echocardiography, ELISA, and Western blot assay. As a result of MI/R induction, a decrease in left ventricular contractile function occurred along with increased cardiac fibrosis and tissue damage. The serum levels of TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-18 increased, while IL-10 decreased. Oxidant/antioxidant changes were evident with increased MDA levels and decreased GSH, SOD, and CAT in the MI/R group. Furthermore, the protein levels of TLR4, NF-κB, and NLRP3 were significantly increased in the heart tissue of MI/R group. Treatment with 4-MU significantly prevented the reduction of cardiac contractile function and its pathological changes as a result of MI/R by inhibiting the increase of serum inflammatory factors and improving the oxidant/antioxidant balance probably through the TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3 axis. The results of a current study showed that 4-MU had a potential ability to attenuate the cardiac injury by reducing oxidative stress and inflammation in a TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3-dependent mechanism.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Algoet M, Janssens S, Himmelreich U, Gsell W, Pusovnik M, Van den Eynde J, Oosterlinck W (2022) Myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury and the influence of inflammation. Trends in cardiovascular medicine 33(6):357–366
Al-Majedy YK, Al-Amiery AA, Kadhum AAH, Mohamad AB (2016) Antioxidant activities of 4-methylumbelliferone derivatives. PLoS ONE 11:e0156625
Amani H, Habibey R, Hajmiresmail S, Latifi S, Pazoki-Toroudi H, Akhavan O (2017) Antioxidant nanomaterials in advanced diagnoses and treatments of ischemia reperfusion injuries. Journal of Materials Chemistry B 5:9452–9476
Avesta L, Doustkami H, Zamani B, Nejati A, Mousavy S, Aslani MR (2022) Association of plasma visfatin with epicardial fat thickness and severity of coronary artery diseases in patients with acute myocardial infarction and stable angina pectoris. ARYA Atherosclerosis 18:1
Babapour B, Doustkami H, Avesta L, Moradi A, Saadat S, Piralaei K, Aslani MR (2021) Correlation of serum adipolin with epicardial fat thickness and severity of coronary artery diseases in acute myocardial infarction and stable angina pectoris patients. Med Princ Pract 30:52–61
Bai Y, Li Z, Liu W, Gao D, Zhang P, Liu M (2019) Effects of IL-1β and IL-18 induced by NLRP3 inflammasome activation on myocardial reperfusion injury after PCI. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 23:10101–10106
Benjamin EJ, Virani SS, Callaway CW, Chamberlain AM, Chang AR, Cheng S, Chiuve SE, Cushman M, Delling FN, Deo R (2018) Heart disease and stroke statistics—2018 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 137:e67–e492
Bistoletti M, Bosi A, Caon I, Chiaravalli AM, Moretto P, Genoni A, Moro E, Karousou E, Viola M, Crema F (2020) Involvement of hyaluronan in the adaptive changes of the rat small intestine neuromuscular function after ischemia/reperfusion injury. Sci Rep 10:11521
Chen Y, Peng L, Shi S, Guo G, Wen H (2021) Boeravinone B alleviates gut dysbiosis during myocardial infarction-induced cardiotoxicity in rats. J Cell Mol Med 25:6403–6416
Chouchani ET, Pell VR, Gaude E, Aksentijević D, Sundier SY, Robb EL, Logan A, Nadtochiy SM, Ord EN, Smith AC (2014) Ischaemic accumulation of succinate controls reperfusion injury through mitochondrial ROS. Nature 515:431–435
Del Re DP, Amgalan D, Linkermann A, Liu Q, Kitsis RN (2019) Fundamental mechanisms of regulated cell death and implications for heart disease. Physiol Rev 99:1765–1817
Dong G, Chen T, Ren X, Zhang Z, Huang W, Liu L, Luo P, Zhou H (2016) Rg1 prevents myocardial hypoxia/reoxygenation injury by regulating mitochondrial dynamics imbalance via modulation of glutamate dehydrogenase and mitofusin 2. Mitochondrion 26:7–18
Essa ML, Elashkar AA, Hanafy NA, Saied EM, El-Kemary M (2022) Dual targeting nanoparticles based on hyaluronic and folic acids as a promising delivery system of the encapsulated 4-methylumbelliferone (4-MU) against invasiveness of lung cancer in vivo and in vitro. Int J Biol Macromol 206:467–480
Ezraty B, Gennaris A, Barras F, Collet J-F (2017) Oxidative stress, protein damage and repair in bacteria. Nat Rev Microbiol 15:385–396
Fröhlich GM, Meier P, White SK, Yellon DM, Hausenloy DJ (2013) Myocardial reperfusion injury: looking beyond primary PCI. Eur Heart J 34:1714–1722
Galkina SI, Fedorova NV, Ksenofontov AL, Golenkina EA, Serebryakova MV, Stadnichuk VI, BaratovaSud’ina LAGF (2022) Inhibitor of hyaluronic acid synthesis 4-methylumbelliferone suppresses the secretory processes that ensure the invasion of neutrophils into tissues and induce inflammation. Biomedicines 10:314
Govindasami S, Uddandrao VV, Raveendran N, Sasikumar V (2020) Therapeutic potential of biochanin-A against isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction in rats. Cardiovascular & Hematological Agents in Medicinal Chemistry (Formerly Current Medicinal Chemistry-Cardiovascular & Hematological Agents) 18(6):31–36
Groß CJ, Mishra R, Schneider KS, Médard G, Wettmarshausen J, Dittlein DC, Shi H, Gorka O, Koenig P-A, Fromm S (2016) K+ efflux-independent NLRP3 inflammasome activation by small molecules targeting mitochondria. Immunity 45:761–773
Guo X, Jiang H, Yang J, Chen J, Yang J, Ding J-W, Li S, Wu H, Ding H-S (2016) Radioprotective 105 kDa protein attenuates ischemia/reperfusion-induced myocardial apoptosis and autophagy by inhibiting the activation of the TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway in rats. Int J Mol Med 38:885–893
Hackert K, Homann S, Mir S, Beran A, Gorreßen S, Funk F, Fischer JW, Grandoch M, Schmitt JP (2021) 4-methylumbelliferone attenuates macrophage invasion and myocardial remodeling in pressure-overloaded mouse hearts. Hypertension 77:1918–1927
Heusch G (2020) Myocardial ischaemia–reperfusion injury and cardioprotection in perspective. Nat Rev Cardiol 17:773–789
Heusch G, Gersh BJ (2017) The pathophysiology of acute myocardial infarction and strategies of protection beyond reperfusion: a continual challenge. Eur Heart J 38:774–784
Lee KS, Marwick TH, Cook SA, Go RT, Fix JS, James KB, Sapp SK, MacIntyre WJ, Thomas JD (1994) Prognosis of patients with left ventricular dysfunction, with and without viable myocardium after myocardial infarction. Relative efficacy of medical therapy and revascularization. Circulation 90:2687–2694
Li T, Yu J, Chen R, Wu J, Fei J, Bo Q, Xue L, Li D (2014) Mycophenolate mofetil attenuates myocardial ischemia–reperfusion injury via regulation of the TLR4/NF-B signaling pathway. Die Pharmazie-an International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 69:850–855
Liu J, Wang H, Li J (2016a) Inflammation and inflammatory cells in myocardial infarction and reperfusion injury: a double-edged sword. Clinical Medicine Insights: Cardiology vol 10, 2016 © 2016 SAGE Publications., Article Reuse Guidelines. https://doi.org/10.4137/CMC.S33164
Liu X, Zhang Z, Ruan J, Pan Y, Magupalli VG, Wu H, Lieberman J (2016b) Inflammasome-activated gasdermin D causes pyroptosis by forming membrane pores. Nature 535:153–158
Madungwe NB, Zilberstein NF, Feng Y, Bopassa JC (2016) Critical role of mitochondrial ROS is dependent on their site of production on the electron transport chain in ischemic heart. American Journal of Cardiovascular Disease 6:93
Minutoli L, Puzzolo D, Rinaldi M, Irrera N, Marini H, Arcoraci V, Bitto A, Crea G, Pisani A, Squadrito F (2016) ROS-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome activation in brain, heart, kidney, and testis ischemia/reperfusion injury. Oxidative medicine and cellular longevity 2016:2183026. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/2183026
Mokhtari B, Azizi Y, Rostami Abookheili A, Aboutaleb N, Nazarinia D, Naderi N (2020) Human amniotic membrane mesenchymal stem cells-conditioned medium attenuates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats by targeting oxidative stress. Iran J Basic Med Sci 23:1453–1461
Nagy N, Kuipers HF, Frymoyer AR, Ishak HD, Bollyky JB, Wight TN, Bollyky PL (2015) 4-methylumbelliferone treatment and hyaluronan inhibition as a therapeutic strategy in inflammation, autoimmunity, and cancer. Front Immunol 6:123
Naseroleslami M, Mousavi Niri N, Hosseinian SB, Aboutaleb N (2023) DNAzyme loaded nano-niosomes attenuate myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by targeting apoptosis, inflammation in a NF-κB dependent mechanism. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 396:2127–2136. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-023-02467-9
North BJ, Sinclair DA (2012) The intersection between aging and cardiovascular disease. Circ Res 110:1097–1108
Panda VS, Naik SR (2008) Cardioprotective activity of Ginkgo biloba phytosomes in isoproterenol-induced myocardial necrosis in rats: a biochemical and histoarchitectural evaluation. Exp Toxicol Pathol 60:397–404
Park H, Park H, Mun D, Kang J, Kim H, Kim M, Cui S, Lee S-H, Joung B (2018) Extracellular vesicles derived from hypoxic human mesenchymal stem cells attenuate GSK3β expression via miRNA-26a in an ischemia-reperfusion injury model. Yonsei Med J 59:736–745
Pavillard LE, Marín-Aguilar F, Bullon P, Cordero MD (2018) Cardiovascular diseases, NLRP3 inflammasome, and western dietary patterns. Pharmacol Res 131:44–50
Pluijmert NJ, Atsma DE, Quax PH (2021) Post-ischemic myocardial inflammatory response: a complex and dynamic process susceptible to immunomodulatory therapies. Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine 8:647785
Pomerantz BJ, Reznikov LL, Harken AH, Dinarello CA (2001) Inhibition of caspase 1 reduces human myocardial ischemic dysfunction via inhibition of IL-18 and IL-1β. Proc Natl Acad Sci 98:2871–2876
Reidar Woldbaek P, Tønnessen T, Lie Henriksen U, Florholmen G, Kristian Lunde P, Lyberg T, Christensen G (2003) Increased cardiac IL-18 mRNA, pro-IL-18 and plasma IL-18 after myocardial infarction in the mouse; a potential role in cardiac dysfunction. Cardiovasc Res 59:122–131
Sandanger Ø, Ranheim T, Vinge LE, Bliksøen M, Alfsnes K, Finsen AV, Dahl CP, Askevold ET, Florholmen G, Christensen G (2013) The NLRP3 inflammasome is up-regulated in cardiac fibroblasts and mediates myocardial ischaemia–reperfusion injury. Cardiovasc Res 99:164–174
Saxena A, Russo I, Frangogiannis NG (2016) Inflammation as a therapeutic target in myocardial infarction: learning from past failures to meet future challenges. Transl Res 167:152–166
Schilling D, Thomas K, Nixdorff K, Vogel SN, Fenton MJ (2002) Toll-like receptor 4 and Toll-IL-1 receptor domain-containing adapter protein (TIRAP)/myeloid differentiation protein 88 adapter-like (Mal) contribute to maximal IL-6 expression in macrophages. J Immunol 169:5874–5880
Sharma A, Tate M, Mathew G, Vince JE, Ritchie RH, de Haan JB (2018a) Oxidative stress and NLRP3-inflammasome activity as significant drivers of diabetic cardiovascular complications: therapeutic implications. Front Physiol 9:114
Shen S, He F, Cheng C, Xu B, Sheng J (2021) Uric acid aggravates myocardial ischemia–reperfusion injury via ROS/NLRP3 pyroptosis pathway. Biomed Pharmacother 133:110990
Sim M-O, Ham JR, Lee H-I, Seo K-I, Lee M-K (2014) Long-term supplementation of umbelliferone and 4-methylumbelliferone alleviates high-fat diet induced hypertriglyceridemia and hyperglycemia in mice. Chem Biol Interact 216:9–16
Smit M, Coetzee A, Lochner A (2020) The pathophysiology of myocardial ischemia and perioperative myocardial infarction. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth 34:2501–2512
Somasuntharam I, Yehl K, Carroll SL, Maxwell JT, Martinez MD, Che P-L, Brown ME, Salaita K, Davis ME (2016) Knockdown of TNF-α by DNAzyme gold nanoparticles as an anti-inflammatory therapy for myocardial infarction. Biomaterials 83:12–22
Sun M, Chen M, Dawood F, Zurawska U, Li JY, Parker T, Kassiri Z, Kirshenbaum LA, Arnold M, Khokha R (2007) Tumor necrosis factor-α mediates cardiac remodeling and ventricular dysfunction after pressure overload state. Circulation 115:1398–1407
Takahashi M (2014) NLRP3 inflammasome as a novel player in myocardial infarction. Int Heart J 55:101–105
Thygesen K, Alpert JS, Jaffe AS, Simoons ML, Chaitman B, Vasileva EY (2012) Task Force for the universal definition of myocardial infarction. Third universal definition of myocardial infarction. Nat Rev Cardiol 9:620–633
Toldo S, Mezzaroma E, McGeough MD, Pena CA, Marchetti C, Sonnino C, Van Tassell BW, Salloum FN, Voelkel NF, Hoffman HM (2015) Independent roles of the priming and the triggering of the NLRP3 inflammasome in the heart. Cardiovasc Res 105:203–212
Townsend N, Kazakiewicz D, Lucy Wright F, Timmis A, Huculeci R, Torbica A, Gale CP, Achenbach S, Weidinger F, Vardas P (2022) Epidemiology of cardiovascular disease in Europe. Nat Rev Cardiol 19:133–143
Venkatachalam K, Prabhu SD, Reddy VS, Boylston WH, Valente AJ, Chandrasekar B (2009) Neutralization of interleukin-18 ameliorates ischemia/reperfusion-induced myocardial injury. J Biol Chem 284:7853–7865
Verma VK, Malik S, Narayanan SP, Mutneja E, Sahu AK, Bhatia J, Arya DS (2019) Role of MAPK/NF-κB pathway in cardioprotective effect of Morin in isoproterenol induced myocardial injury in rats. Mol Biol Rep 46:1139–1148
Wittmann N, Mishra N, Gramenz J, Kuthning D, Behrendt A-K, Bossaller L, Meyer-Bahlburg A (2023) Inflammasome activation and formation of ASC specks in patients with juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Front Med 10:1063772
Xu J, Zhang C, Khanna A (2009) Wideband high-frequency echocardiography to evaluate myocardial infarct size. J Ultrasound Med 28:1527–1534
Yang J, Yang J, Ding J-w, Chen L-h, Wang Y-l, Li S, Wu H (2008) Sequential expression of TLR4 and its effects on the myocardium of rats with myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Inflammation 31:304–312
Zhao Z-Q (2004) Oxidative stress-elicited myocardial apoptosis during reperfusion. Curr Opin Pharmacol 4:159–165
Acknowledgements
The research and publication of this article were supported by Iran University of Medical Sciences. This article is a part of a PhD’s degree dissertation by Alireza Moradi.
Funding
This work was funded by Iran University of Medical Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
N.A participated in the design and interpretation of the study, data analysis, and the review of the manuscript. A.M, H.M, N.N, and MR.A conducted the experiment and collected the tissue and were responsible for the data analysis. A.M performed histopathological analyses. A.M wrote the manuscript, and all authors reviewed, read, and approved the article. The authors declare that all data were generated in-house and that no paper mill was used.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All the protocols were approved by the Ethical Committee of Iran University of Medical Sciences (IR.IUMS.FMD.REC.1401.014).
Consent for publication
All the authors agree to publish the article in the present form.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Moradi, A., Aslani, M.R., Mirshekari Jahangiri, H. et al. Protective effects of 4-methylumbelliferone on myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats through inhibition of oxidative stress and downregulation of TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3 signaling pathway. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-023-02934-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-023-02934-3