Abstract
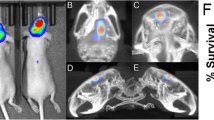
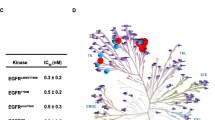
In our previous work, PC-9-Br, a PC-9 brain seeking line established via a preclinical animal model of lung cancer brain metastasis (LCBM), exhibited not only resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitor (EGFR-TKI) gefitinib in vitro, but also chemotherapy regimens of cisplatin plus etoposide in vivo. Using this cell line, we investigated novel potential targeted therapeutics for treating LCBM in vitro and in vivo to combat drug resistance. Significant increases in mRNA and protein expression levels of Bcl-2 were found in PC-9-Br compared with parental PC-9 (PC-9-P), but no significant changes of Bcl-XL were observed. A remarkable synergistic effect between EGFR-TKI gefitinib and Bcl-2 inhibitors ABT-263 (0.17 ± 0.010 µM at 48 h and 0.02 ± 0.004 µM at 72 h), or ABT-199 (0.22 ± 0.008 µM at 48 h and 0.02 ± 0.001 µM at 72 h) to overcome acquired resistance to gefitinib (> 0.5 µM at 48 h and 0.10 ± 0.007 µM at 72 h) in PC-9-Br was observed in MTT assays. AZD9291 was also shown to overcome acquired resistance to gefitinib in PC-9-Br in MTT assays (0.23 ± 0.031 µM at 48 h and 0.03 ± 0.008 µM at 72 h). Western blot showed significantly decreased phospho-Erk1/2 and increased cleaved-caspase-3 expressions were potential synergistic mechanisms for gefitinib + ABT263/ABT199 in PC-9-Br. Significantly decreased protein expressions of phospho-EGFR, phospho-Akt, p21, and survivin were specific synergistic mechanism for gefitinib + ABT199 in PC-9-Br. In vivo studies demonstrated afatinib (30 mg/kg) and AZD9291 (25 mg/kg) could significantly reduce the LCBM in vivo and increase survival percentages of treated mice compared with mice treated with vehicle and gefitinib (6.25 mg/kg). In conclusion, our study demonstrated gefitinib + ABT263/ABT199, afatinib, and AZD9291 have clinical potential to treat LCBM.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akiyama T, Dass CR, Choong PF (2009) Bim-targeted cancer therapy: a link between drug action and underlying molecular changes. Mol Cancer Ther 8(12):3173–3180
Alander JT, Kaartinen I, Laakso A et al (2012) A review of indocyanine green fluorescent imaging in surgery. Int J Biomed Imaging 2012:940585. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/940585
Areeb Z, Stuart SF, West AJ et al (2020) Reduced EGFR and increased miR-221 is associated with increased resistance to temozolomide and radiotherapy in glioblastoma. Sci Rep 10(1):1–12
Bai H, Xiong L, Han B (2017) The effectiveness of EGFR-TKIs against brain metastases in EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer. Onco Targets Ther 10:2335–2340. https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S129809
Baik CS, Chamberlain MC, Chow LQ (2015) Targeted therapy for brain metastases in EGFR-mutated and ALK-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol 10(9):1268–1278. https://doi.org/10.1097/JTO.0000000000000615
Ballard P, Yates JW, Yang Z et al (2016) Preclinical comparison of osimertinib with other EGFR-TKIs in EGFR-mutant NSCLC brain metastases models, and early evidence of clinical brain metastases activity. Clin Cancer Res 22(20):5130–5140. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-0399
Berger LA, Riesenberg H, Bokemeyer C, Atanackovic D (2013) CNS metastases in non-small-cell lung cancer: current role of EGFR-TKI therapy and future perspectives. Lung Cancer 80(3):242–248
Bohn KA, Adkins CE, Nounou MI, Lockman PR (2017) Inhibition of VEGF and angiopoietin-2 to reduce brain metastases of breast cancer burden. Front Pharmacol 8:193. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2017.00193
Burel-Vandenbos F, Ambrosetti D, Coutts M, Pedeutour F (2013) EGFR mutation status in brain metastases of non-small cell lung carcinoma. J Neurooncol 111(1):1–10
Elmeliegy MA, Carcaboso AM, Tagen M, Bai F, Stewart CF (2011) Role of ATP-binding cassette and solute carrier transporters in erlotinib CNS penetration and intracellular accumulation. Clin Cancer Res 17(1):89–99
Erickson AW, Brastianos PK, Das S (2020) Assessment of effectiveness and safety of osimertinib for patients with intracranial metastatic disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Netw Open 3(3):e201617–e201617
Gao W (2020) Two-dimensional difference gel electrophoresis: a gel-based proteomic approach for protein analysis molecular toxicology protocols. Springer, pp 163–176
García-Aranda M, Pérez-Ruiz E, Redondo M (2018) Bcl-2 inhibition to overcome resistance to chemo-and immunotherapy. Int J Mol Sci 19(12):3950
Guikema JE, Amiot M, Eldering E (2017) Exploiting the pro-apoptotic function of NOXA as a therapeutic modality in cancer. Expert Opin Ther Targets 21(8):767–779
Hamamoto J, Yasuda H, Aizawa K et al (2017) Non-small cell lung cancer PC-9 cells exhibit increased sensitivity to gemcitabine and vinorelbine upon acquiring resistance to EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Oncol Lett 14(3):3559–3565. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2017.6591
Harada H, Grant S (2012) Targeting the regulatory machinery of BIM for cancer therapy. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr 22(2):117–129
Ishida CT, Bianchetti E, Shu C et al (2017) BH3-mimetics and BET-inhibitors elicit enhanced lethality in malignant glioma. Oncotarget 8(18):29558
Jin J, Xiong Y, Cen B (2017) Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL mediate resistance to receptor tyrosine kinase targeted therapy in lung and gastric cancer. Anticancer Drugs 28(10):1141
Jorgensen TN, McKee A, Wang M et al (2007) Bim and Bcl-2 mutually affect the expression of the other in T cells. J Immunol 179(6):3417–3424
Karpel-Massler G, Bâ M, Shu C et al (2015) TIC10/ONC201 synergizes with Bcl-2/Bcl-xL inhibition in glioblastoma by suppression of Mcl-1 and its binding partners in vitro and in vivo. Oncotarget 6(34):36456
Karpel-Massler G, Ishida CT, Bianchetti E et al (2017) Induction of synthetic lethality in IDH1-mutated gliomas through inhibition of Bcl-xL. Nat Commun 8(1):1–14
Koizumi F, Shimoyama T, Taguchi F, Saijo N, Nishio K (2005) Establishment of a human non-small cell lung cancer cell line resistant to gefitinib. Int J Cancer 116(1):36–44. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.20985
Levesley J, Steele L, Taylor C, Sinha P, Lawler SE (2013) ABT-263 enhances sensitivity to metformin and 2-deoxyglucose in pediatric glioma by promoting apoptotic cell death. PLoS ONE 8(5):e64051
Liu Z, Gao W (2019) Overcoming acquired resistance of gefitinib in lung cancer cells without T790M by AZD9291 or Twist1 knockdown in vitro and in vivo. Arch Toxicol 93(6):1555–1571
Liu Z, Gao W (2020) Synergistic effects of Bcl-2 inhibitors with AZD9291 on overcoming the acquired resistance of AZD9291 in H1975 cells. Arch Toxicol 94(9):3125–3136
Lu C, Shao C, Cobos E, Singh KP, Gao W (2012) Chemotherapeutic sensitization of leptomycin B resistant lung cancer cells by pretreatment with doxorubicin. PLoS ONE 7(3):e32895
Lu Y, Bian D, Zhang X, Zhang H, Zhu Z (2020) Inhibition of Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL overcomes the resistance to the third-generation EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor osimertinib in non-small cell lung cancer. Mol Med Rep 23(1):1–1
Lv T, Wang Q, Cromie M et al (2015) Twist1-mediated 4E-BP1 regulation through mTOR in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget 6(32):33006
Maji S, Panda S, Samal SK et al (2018) Bcl-2 antiapoptotic family proteins and chemoresistance in cancer Advances in cancer research, vol 137. Elsevier, pp 37–75
Meedendorp AD, ter Elst A, t’Hart NA, Groen HJ, Schuuring E, van der Wekken AJ (2018) Response to HER2 inhibition in a patient with brain metastasis With EGFR TKI acquired resistance and an HER2 amplification. Front Oncol 8:176
Mok TS, Wu Y-L, Ahn M-J et al (2017) Osimertinib or platinum–pemetrexed in EGFR T790M–positive lung cancer. N Engl J Med 376(7):629–640
O’Kane GM, Leighl NB (2018) Systemic therapy of lung cancer CNS metastases using molecularly targeted agents and immune checkpoint inhibitors. CNS Drugs 32(6):527–542
Palmer AC, Sorger PK (2017) Combination cancer therapy can confer benefit via patient-to-patient variability without drug additivity or synergy. Cell 171(7):1678-1691.e13
Pareja F, Macleod D, Shu C et al (2014) PI3K and Bcl-2 inhibition primes glioblastoma cells to apoptosis through downregulation of Mcl-1 and Phospho-BAD. Mol Cancer Res 12(7):987–1001
Park MY, Jung MH, Eo EY et al (2017) Generation of lung cancer cell lines harboring EGFR T790M mutation by CRISPR/Cas9-mediated genome editing. Oncotarget 8(22):36331–36338. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.16752
Patil VM, Noronha V, Joshi A et al (2017) Phase III study of gefitinib or pemetrexed with carboplatin in EGFR-mutated advanced lung adenocarcinoma. ESMO Open 2(1):e000168. https://doi.org/10.1136/esmoopen-2017-000168
Reungwetwattana T, Nakagawa K, Cho BC et al (2018) CNS response to osimertinib versus standard epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in patients with untreated EGFR-mutated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 36(33):3290
Santarpia M, Liguori A, Karachaliou N et al (2017) Osimertinib in the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer: design, development and place in therapy. Lung Cancer Targets Ther 8:109
Sartorius UA, Krammer PH (2002) Upregulation of bcl-2 is involved in the mediation of chemotherapy resistance in human small cell lung cancer cell lines. Int J Cancer 97(5):584–592
Savry A, Carre M, Berges R et al (2013) Bcl-2—enhanced efficacy of microtubule-targeting chemotherapy through bim overexpression: implications for cancer treatment. Neoplasia 15(1):49-IN17
Schuler M, Wu Y-L, Hirsh V et al (2016) First-line afatinib versus chemotherapy in patients with non-small cell lung cancer and common epidermal growth factor receptor gene mutations and brain metastases. J Thorac Oncol 11(3):380–390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtho.2015.11.014
Schwab E, Chen JA, Huynh JC et al (2019) Rational strategies for combining Bcl-2 inhibition with targeted drugs for anti-tumor synergy. J Cancer Treat Diagn 3(4):7–13
Shah N, Liu Z, Tallman RM et al (2020) Drug resistance occurred in a newly characterized preclinical model of lung cancer brain metastasis. BMC Cancer 20:292
Shang E, Zhang Y, Shu C et al (2018) Dual Inhibition of Bcl-2/Bcl-xL and XPO1 is synthetically lethal in glioblastoma model systems. Sci Rep 8(1):1–11
Sionov RV, Vlahopoulos SA, Granot Z (2015) Regulation of Bim in health and disease. Oncotarget 6(27):23058
Skoulidis F, Papadimitrakopoulou VA (2017) Targeting the gatekeeper: osimertinib in EGFR T790M mutation–positive non–small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 23(3):618–622
Takeda M, Nakagawa K (2019) First-and second-generation EGFR-TKIs are all replaced to osimertinib in chemo-naive EGFR mutation-positive non-small cell lung cancer? Int J Mol Sci 20(1):146
Tan J, Li M, Zhong W, Hu C, Gu Q, Xie Y (2017) Tyrosine kinase inhibitors show different anti-brain metastases efficacy in NSCLC: a direct comparative analysis of icotinib, gefitinib, and erlotinib in a nude mouse model. Oncotarget 8(58):98771–98781. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.21936
Vansteenkiste J, Reungwetwattana T, Nakagawa K et al (2017) CNS response to osimertinib vs standard of care (SoC) EGFR-TKI as first-line therapy in patients (pts) with EGFR-TKI sensitising mutation (EGFRm)-positive advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): data from the FLAURA study. Ann Oncol 28:189. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdx729.007
Wang S, Cang S, Liu D (2016) Third-generation inhibitors targeting EGFR T790M mutation in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. J Hematol Oncol 9:34. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-016-0268-z
Wang X, Mao W, Wang Z et al (2020) Enhanced anti-brain metastasis from non-small cell lung cancer of osimertinib and doxorubicin co-delivery targeted nanocarrier. Int J Nanomed 15:5491
Watanabe S, Hayashi H, Nakagawa K (2016) Is afatinib a treatment option for brain metastases in patients with EGFR mutation-positive non-small cell lung cancer? Ann Transl Med 4(11):225
Weber B, Winterdahl M, Memon A et al (2011) Erlotinib accumulation in brain metastases from non-small cell lung cancer: visualization by positron emission tomography in a patient harboring a mutation in the epidermal growth factor receptor. J Thorac Oncol 6(7):1287–1289. https://doi.org/10.1097/JTO.0b013e318219ab87
Weis SM, Cheresh DA (2011) Tumor angiogenesis: molecular pathways and therapeutic targets. Nat Med 17(11):1359–1370. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.2537
Wu Y-L, Ahn M-J, Garassino MC et al (2018) CNS efficacy of osimertinib in patients with T790M-positive advanced non–small-cell lung cancer: data from a randomized phase III trial (AURA3). J Clin Oncol 36(26):2702–2709
Xing L, Pan Y, Shi Y et al (2018) P1. 13-25 efficacy and safety of osimertinib in EGFR T790M-positive advanced NSCLC patients with brain metastases (APOLLO study). J Thorac Oncol 13(10):S592
Yang J, Ahn M, Kim D et al (2017) Osimertinib in pretreated T790M-positive advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: AURA study phase II extension component. J Clin Oncol 35:1288–1296
Yoneya S, Saito T, Komatsu Y, Koyama I, Takahashi K, Duvoll-Young J (1998) Binding properties of indocyanine green in human blood. Invest Ophthalmol vis Sci 39(7):1286–1290
Yu X, Dobrikov M, Keir ST et al (2019) Synergistic antitumor effects of 9.2. 27-PE38KDEL and ABT-737 in primary and metastatic brain tumors. PLoS ONE 14(1):e0210608
Zhan Y, Wang Y, Qi M et al (2019) BH3 mimetic ABT-263 enhances the anticancer effects of apigenin in tumor cells with activating EGFR mutation. Cell Biosci 9(1):60
Zhang SR, Zhu LC, Jiang YP et al (2017) Efficacy of afatinib, an irreversible ErbB family blocker, in the treatment of intracerebral metastases of non-small cell lung cancer in mice. Acta Pharmacol Sin 38(2):233–240. https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2016.107
Zhao R, Zhou S, Xia B et al (2016) AT-101 enhances gefitinib sensitivity in non-small cell lung cancer with EGFR T790M mutations. BMC Cancer 16(1):1–8
Zhou L, Zhang Y, Sampath D et al (2018) Flavopiridol enhances ABT-199 sensitivity in unfavourable-risk multiple myeloma cells in vitro and in vivo. Br J Cancer 118(3):388–397
Zou B, Lee VHF, Chen L, Ma L, Wang DD, Yan H (2017) Deciphering mechanisms of acquired T790M mutation after EGFR inhibitors for NSCLC by computational simulations. Sci Rep 7(1):6595. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-06632-y
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the WVU HSC Microscope Imaging and the Animal Modeling Imaging Facilities.
Funding
This research was partially supported by the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences of the National Institutes of Health (R15ES026789), the National Institute of General Medical Sciences (P20GM121322-03), METAvivor (1008553R), and the Mylan Chair Endowment Fund. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization PRL, WG, ZL and NS. Methodology ZL, NS, KLM, SAS, PS, AM, KEB, TAA, and RF. Software ZL and NS. Validation ZL and NS. Formal analysis ZL and NS. Investigation ZL, NS, KLM, SAS, PS, AM, KEB, TAA, and RF. Data curation ZL, NS, KLM, SAS, PS, AM, KEB, TAA, and RF. Writing—original draft preparation ZL and NS. Writing—review and editing ZL, NS, KLM, SAS, PS, AM, KEB, TAA, and RF. Supervision PRL and WG. Project administration PRL and WG. Funding acquisition SAS, WG, and PRL.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Institutional review board statement
All animal experiments were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee at West Virginia University in Morgantown, West Virginia (Protocol No. 16404001894).
Data availability statement
The interpreted and analyzed data from this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Z., Shah, N., Marshall, K.L. et al. Overcoming the acquired resistance to gefitinib in lung cancer brain metastasis in vitro and in vivo. Arch Toxicol 95, 3575–3587 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-021-03147-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-021-03147-4