Abstract
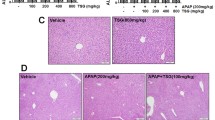
Diosbulbin B (DIOB), a furanoid, is a major constituent of herbal medicine Dioscorea bulbifera L. Exposure to DIOB caused liver injury in humans and experimental animals. The mechanisms of DIOB-induced hepatotoxicities remain unknown. The present study demonstrated that DIOB induced hepatotoxicities in a time- and dose-dependent manner in mice. H&E stained histopathologic image showed the occurrence of necrosis in the liver obtained from the mice treated with DIOB at dose of 200 mg/kg. Pretreatment with KTC protected the animals from hepatotoxicities and hepatic GSH depletion induced by DIOB, increased area under the concentration–time curve of blood DIOB, decreased urinary excretion of GSH conjugates derived from DIOB, and increased urinary excretion of parent drug. Pretreatment with BSO exacerbated DIOB-induced hepatotoxicities. In order to define the role of furan moiety in DIOB-induced liver toxicities, we replaced the furan of DIOB with a tetrahydrofuran group by chemical hydrogenation of the furan ring of DIOB. No liver injury was observed in the animals given the same doses of tetrahydro-DIOB. The furan moiety was essential for DIOB-induced hepatotoxicities. The results implicate the cis-enedial reactive metabolite of DIOB was responsible for the observed toxicities. The observed modest depletion of hepatic GSH in DIOB-treated animals suggests the actions of one or more reactive metabolites, and the hepatic injury observed could be due at least in part to reactions of these metabolites with crucial biomolecules. Cytochrome P450 3A enzymes are implicated in DIOB-induced hepatotoxicities by catalyzing the formation of the reactive metabolite of DIOB.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DIOB:
-
Diosbulbin B
- GSH:
-
Glutathione
- BSO:
-
Buthionine sulfoximine
- DB:
-
Dioscorea bulbifera L.
- ALT:
-
Alanine transaminase
- AST:
-
Aspartate transaminase
- KTC:
-
Ketoconazole
- mBrB:
-
Monobromobimane
- H&E:
-
Hematoxylin and eosin
- C max :
-
Maximum serum concentration
- AUC:
-
Area under the serum concentration–time curve
- T max :
-
Time required to reach maximum serum concentration
- Vz/F :
-
Distribution of apparent solvent
- CLz/F :
-
Clearance rate
- DP:
-
Declustering potential
- CE:
-
Collision energy
- CXP:
-
Collision cell exit potential
- IDA:
-
Information-dependent acquisition
- EPI:
-
Enhanced product ion
- HPLC:
-
High-performance liquid chromatography
- MRM:
-
Multiple reaction monitor
References
Anderson IB, Mullen WH, Meeker J, Khojasteh B, Oishi S, Nelson SD et al (1996) Pennyroyal toxicity: measurement of toxic metabolite levels in two cases and review of the literature. Ann Intern Med 124:726–734
Biswas P, Lin JH, Kang J, Guliants VV (2014) Vapor phase hydrogenation of 2-methylfuran over noble and base metal catalysts. Appl Catal A Gen 475:379–385
Boyd MR, Burka LT, Harris TM, Wilson BJ (1974) Lung-toxic furanoterpenoids produced by sweet potatoes (Ipomoea batatas) following microbial infection. Biochim Biophys Acta 337:184–195
Caldwell TE, Land DP (1997) Desulfurization, deoxygenation and denitrogenation of heterocycles by a palladium surface: a mechanistic study of thiophene, furan and pyrrole on Pd (111) using laser-induced thermal desorption with Fourier-transform mass spectrometry. Polyhedron 16:3197–3211
Cifuente DA, Borkowski EJ, Sosa ME, Gianello JC, Giordano OS, Tonn CE (2002) Clerodane diterpenes from Baccharis sagittalis: insect antifeedant activity. Phytochemistry 61:899–905
Demetzos C, Dimas K, Hatziantoniou S, Anastasaki T, Angelopoulou D (2001) Cytotoxic and anti-inflammatory activity of labdane and cis-clerodane type diterpenes. Planta Med 67:614–618
Fahey RC, Newton GL (1987) Determination of low-molecular-weight thiols using monobromobimane fluorescent labeling and high-performance liquid chromatography. Methods Enzymol 143:85–96
Gao H, Kuroyanaqi M, Wu L, Kawahara N, Yasuno T, Nakamura Y (2002) Antitumor-promoting constituents from Dioscorea bulbifera L. in JB6 mouse epidermal cells. Biol Pharm Bull 25:1241–1243
Grynberg NF, Echevarria A, Lima JE, Pamplona SS, Pinto AC, Maciel MA (1999) Anti-tumour activity of two 19-nor-clerodane diterpenes, trans-dehydrocrotonin and trans-crotonin, from Croton cajucara. Planta Med 65:687–689
Haschek WM, Boyd MR, Hakkinen PJ, Owenby CS, Witschi H (1984) Acute inhalation toxicity of 3-methylfuran in the mouse: pathology, cell kinetics, and respiratory rate effects. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 72:124–133
International Agency for Research on Cancer (1995) Monographs on the evaluation of carcinogenic risks to humans: dry cleaning, some chlorinated solvents and other industrial chemicals, vol 63. IARC, Lyon, France, pp 393–407
Jin H, Li L, Zhong D, Liu J, Chen X, Zheng J (2011) Pulmonary toxicity and metabolic activation of tetrandrine in CD-1 mice. Chem Res Toxicol 24:2142–2152
Jin H, Shen S, Chen X, Zhong D, Zheng J (2012) CYP3A-mediated apoptosis of dauricine in cultured human bronchial epithelial cells and in lungs of CD-1 mice. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 261:248–254
Kawasaki T, Komori T, Setoguchi S (1968) Furanoid norditerpenes from Dioscoreacae plants. I. Diosbulins A, B, and C from Dioscorea bulbifera L. forma spontanea Makino et Nemoto. Chem Pharm Bull 16:2430–2435
Li S, Iliya IA, Deng J, Zhao S (2000) Flavonoids and anthraquinone from Dioscorea bulbifera L. Chin J Chin Mater Med 25:159–160
Lin G, Wang JY, Li N, Li M, Gao H, Ji Y, Zheng J et al (2011) Hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome associated with consumption of Gynura segetum. J Hepatol 54:666–673
Lin D, Li C, Peng Y, Gao H, Zheng J (2014) Cytochrome p450-mediated metabolic activation of Diosbulbin B. Drug Metab Dispos 42:1727–1736
Liu JR (2002) Two cases of toxic hepatitis caused by Dioscorea Bulbifera L. Adverse Drug React 2:129–130 (in Chinese)
Liu H, Chou G, Guo Y, Ji L, Wang J, Wang Z (2010) Norclerodane diterpenoids from the rhizomes of Dioscorea bulbifera. Phytochemistry 71:1174–1180
Ma Y, Niu C, Wang J, Ji L, Wang Z (2013) Diosbulbin B-induced liver injury in mice and its mechanism. Hum Exp Toxicol 33:729–736
Mitchell JR, Potter WZ, Hinson JA, Jollow DJ (1974) Hepatic necrosis caused by furosemide. Nature 251:508–511
Mitchell JR, Nelson WL, Potter WZ, Sasame HA, Jollow DJ (1976) Metabolic activation of furosemide to a chemically reactive, hepatotoxic metabolite. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 199:41–52
Mizutani T, Yoshida K, Murakami M, Shirai M, Kawazoe S (2000) Evidence for the involvement of N-methylthiourea, a ring cleavage metabolite, in the hepatotoxicity of methimazole in glutathione-depleted mice: structure-toxicity and metabolic studies. Chem Res Toxicol 13:170–176
Niu C, Wang J, Ji L, Wang Z (2014) Protection of Angelica sinensis (Oliv) diels against hepatotoxicity induced by Dioscorea bulbifera L. and its mechanism. Biosci Trends 8:253–259
Peterson LA (2013) Reactive metabolites in the biotransformation of molecules containing a furan ring. Chem Res Toxicol 26:6–25
Rasikari HL, Leach DN, Waterman PG, Spooner-Hart RN, Basta AH, Banbury LK et al (2005) Cytotoxic clerodane diterpenes from Glossocarya calcicola. Phytochemistry 66:2844–2850
Rowinsky EK, Noe DA, Ettinger DS, Christian MC, Lubejko BG, Fishman EK et al (1993) Phase I and pharmacological study of the pulmonary cytotoxin 4-ipomeanol on a single dose schedule in lung cancer patients: hepatotoxicity is dose limiting in humans. Cancer Res 53:1794–1801
Shimizu S, Atsumi R, Itokawa K, Iwasaki M, Aoki T, Ono C et al (2009) Metabolism-dependent hepatotoxicity of amodiaquine in glutathione-depleted mice. Arch Toxicol 83:701–707
Sullivan JB Jr, Rumack BH, Thomas H Jr, Peterson RG, Bryson P (1979) Pennyroyal oil poisoning and hepatotoxicity. JAMA 242:2873–2874
Svardal AM, Mansoor MA, Ueland PM (1990) Determination of reduced, oxidized, and protein-bound glutathione in human plasma with precolumn derivatization with monobromobimane and liquid chromatography. Anal Biochem 184:338–346
Tang Y (1995) The research of Dioscoreae bulbifera L. in clinical application. Chin J Chin Mater Med 20:435–438
Teponno RB, Tapondjou AL, Gatsing D, Djoukeng JD, Abou-Mansour E, Tabacchi R et al (2006) Bafoudiosbulbins A, and B, two anti-salmonellal clerodane diterpenoids from Dioscorea bulbifera L. var sativa. Phytochemistry 67:1957–1963
Wang J, Ji L, Liu H, Wang Z (2010a) Study of the hepatotoxicity induced by Dioscorea bulbifera L. rhizome in mice. Biosci Trends 4:79–85
Wang J, Liang Q, Ji L, Liu H, Wang C, Wang Z (2010b) Gender-related difference in liver injury induced by Dioscorea bulbifera L. rhizome in mice. Hum Exp Toxicol 30:1333–1341
Wang J, Cui D, Cui Y (2011) Research progress in chemical components, pharmacological actions and toxicity of diterpene lactones isolated from Dioscorea bulbifera L. rhizome. Chin J Chin Med 26:1319–1321
Williams DP, Antoine DJ, Butler PJ, Jones R, Randle L, Payne A et al (2007) The metabolism and toxicity of furosemide in the Wistar rat and CD-1 mouse: a chemical and biochemical definition of the toxicophore. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 322:1208–1220
Wong SG, Card JW, Racz WJ (2000) The role of mitochondrial injury in bromobenzene and furosemide induced hepatotoxicity. Toxicol Lett 116:171–181
Yang H, Li J, Cui X, Yang C, Li L, Liu J et al (2006) Clinical use and adverse drug reaction of compound prescription of Dioscorea bulbifera L. in clinical trial. Clin Misdiagn Misther 19:85–87 (in Chinese)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 81430086 and 81373471).
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, W., Lin, D., Gao, H. et al. Metabolic activation of furan moiety makes Diosbulbin B hepatotoxic. Arch Toxicol 90, 863–872 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-015-1495-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-015-1495-8