Abstract
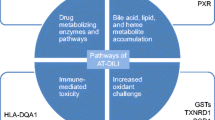
Anti-tuberculosis drug-induced hepatotoxicity (ATDH) is one of the leading adverse drug reactions during the course of tuberculosis treatment and poses a considerable challenge to clinicians and researchers. Previous studies have revealed the important contribution of drug metabolism and transporter enzymes to the complexity of ATDH. The emerging roles of immune response and oxidative stress resulting from reactive metabolite in the development of ATDH have also gained attention recently. Both non-genetic and genetic factors can have a significant impact on the susceptibility to ATDH, consequently altering the risk of hepatotoxicity in susceptible individuals. Non-genetic risk factors associated with ATDH include host factors, environment factors and drug-related factors. Genetic factors contributing to the susceptibility of ATDH involve genetic variations in bioactivation/toxification pathways via the cytochrome P450 enzymes (phase I), detoxification reactions by N-acetyl transferase 2, glutathione S-transferase and uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase (phase II) and hepatic transport (phase III), together with immunological factors and antioxidant response. Better understanding of these factors may help to predict and prevent the occurrence of ATDH and develop more effective treatments. This review focuses on the mechanisms of ATDH and the key factors of susceptibility associated with drug metabolism, hepatic transport, immune response and oxidative stress.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ATDH:
-
Anti-tuberculosis drug-induced hepatotoxicity
- ABC:
-
Adenosine triphosphate binding cassette
- ADRs:
-
Adverse drug reactions
- ALP:
-
Alkaline phosphatase
- ALT:
-
Alanine aminotransferase
- AP:
-
Alkaline phosphatase
- ARE:
-
Antioxidant response element
- ASP:
-
Asparaginic acid
- ATP:
-
Adenosine triphosphate
- AST:
-
Aspartate transaminase
- BACH1:
-
BTB and CNC homology 1
- BCRP (ABCG2):
-
Breast cancer resistance protein
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- CES:
-
Carboxylesterases
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- CYP450:
-
Cytochrome P450
- DIH:
-
Drug-induced hepatotoxicity
- DILI:
-
Drug-induced liver injury
- DMET:
-
Drug metabolism enzymes and transporters
- EMB:
-
Ethambutol
- GSH:
-
Glutathione
- GST:
-
Glutathione S-transferase
- GWAS:
-
Genome-wide association studies
- HBV:
-
Hepatitis B virus
- HCV:
-
Hepatitis C virus
- HIV:
-
Human immunodeficiency virus
- HLA:
-
Human leukocyte antigen
- IL:
-
Interleukin
- INH:
-
Isoniazid
- Keap1:
-
Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1
- MAC:
-
Mid-arm circumference
- MnSOD:
-
Manganese superoxide dismutase
- MRP (ABCC):
-
Multidrug resistance associated proteins
- NAT2:
-
N-acetyl transferase 2
- Nrf2:
-
Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2
- NTCP (SLC10A1):
-
Sodium taurocholate co-transporting polypeptides
- OAT:
-
Organic anion transporter
- OATP (SLCO):
-
Organic anion-transporting polypeptide
- OR:
-
Odds ratio
- P-gp (MDR1, ABCB1):
-
P-glycoprotein
- PZA:
-
Pyrazinamide
- RMP:
-
Rifampicin
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- SLC:
-
Solute carrier
- SM:
-
Streptomycin
- SNP:
-
Single-nucleotide polymorphisms
- TB:
-
Tuberculosis
- TNF-α:
-
Tumor necrosis factor-α
- UGT:
-
Uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase
- ULN:
-
Upper limit of normal
References
Abbas AK, Murphy KM, Sher A (1996) Functional diversity of helper T lymphocytes. Nature 383(6603):787–793. doi:10.1038/383787a0
Adam J, Pichler WJ, Yerly D (2011) Delayed drug hypersensitivity: models of T-cell stimulation. Br J Clin Pharmacol 71(5):701–707. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2125.2010.03764.x
Aithal GP, Ramsay L, Daly AK et al (2004) Hepatic adducts, circulating antibodies, and cytokine polymorphisms in patients with diclofenac hepatotoxicity. Hepatology 39(5):1430–1440. doi:10.1002/hep.20205
An H-r, Wu X-q, Wang Z-y (2012) The relationship between the polymorphism of MnSOD gene and antituberculosis drug-induced liver injury. Chin J Antibiot 37(11):1–4. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1001-8689.2012.11.018
Andrade RJ, Agundez JA, Lucena MI, Martinez C, Cueto R, Garcia-Martin E (2009) Pharmacogenomics in drug induced liver injury. Curr Drug Metab 10(9):956–970
Arbex MA, Varella Mde C, Siqueira HR, Mello FA (2010) Antituberculosis drugs: drug interactions, adverse effects, and use in special situations. Part 1: first-line drugs. Jornal Brasileiro de Pneumologia 36(5):626–640
Baghaei P, Tabarsi P, Chitsaz E et al (2010) Incidence, clinical and epidemiological risk factors, and outcome of drug-induced hepatitis due to antituberculous agents in new tuberculosis cases. Am J Ther 17(1):17–22. doi:10.1097/MJT.0b013e31818f9eae
Bourdi M, Masubuchi Y, Reilly TP et al (2002) Protection against acetaminophen-induced liver injury and lethality by interleukin 10: role of inducible nitric oxide synthase. Hepatology 35(2):289–298. doi:10.1053/jhep.2002.30956
Bozok Cetintas V, Erer OF, Kosova B et al (2008) Determining the relation between N-acetyltransferase-2 acetylator phenotype and antituberculosis drug induced hepatitis by molecular biologic tests. Tuberkuloz ve toraks 56(1):81–86
Cai Y, Yi J, Zhou C, Shen X (2012) Pharmacogenetic study of drug-metabolising enzyme polymorphisms on the risk of anti-tuberculosis drug-induced liver injury: a meta-analysis. PLoS One 7(10):e47769. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0047769
Carr DF, Alfirevic A, Tugwood JD et al (2007) Molecular and genetic association of interleukin-6 in tacrine-induced hepatotoxicity. Pharmacogenet Genomics 17(11):961–972. doi:10.1097/FPC.0b013e3282f00919
Chalasani N, Fontana RJ, Bonkovsky HL et al (2008) Causes, clinical features, and outcomes from a prospective study of drug-induced liver injury in the United States. Gastroenterology 135(6):1924–1934, 1934 e1–4. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2008.09.011
Chalasani NP, Hayashi PH, Bonkovsky HL, Navarro VJ, Lee WM, Fontana RJ (2014) ACG Clinical Guideline: the diagnosis and management of idiosyncratic drug-induced liver injury. Am J Gastroenterol 109(7):950–966; quiz 967. doi:10.1038/ajg.2014.131
Chan ED, Kinney WH, Honda JR et al (2014) Tobacco exposure and susceptibility to tuberculosis: is there a smoking gun? Tuberculosis. doi:10.1016/j.tube.2014.08.010
Chang KC, Leung CC, Yew WW, Lau TY, Tam CM (2008) Hepatotoxicity of pyrazinamide: cohort and case–control analyses. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 177(12):1391–1396. doi:10.1164/rccm.200802-355OC
Chang JC, Liu EH, Lee CN et al (2012) UGT1A1 polymorphisms associated with risk of induced liver disorders by anti-tuberculosis medications. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis 16(3):376–378. doi:10.5588/ijtld.11.0404
Chen R, Zhang Y, Tang S et al (2014) The association between HLA–DQB1 polymorphism and antituberculosis drug-induced liver injury: a case–control study. J Clin Pharm Ther. doi:10.1111/jcpt.12211
Chen R, Wang J, Tang S et al (2015) Association of polymorphisms in drug transporter genes (SLCO1B1 and SLC10A1) and anti-tuberculosis drug-induced hepatotoxicity in a Chinese cohort. Tuberculosis 95(1):68–74. doi:10.1016/j.tube.2014.11.004
Choi JH, Ahn BM, Yi J et al (2007) MRP2 haplotypes confer differential susceptibility to toxic liver injury. Pharmacogenet Genomics 17(6):403–415. doi:10.1097/01.fpc.0000236337.41799.b3
Chowdhury A, Santra A, Kundu S et al (2001) Induction of oxidative stress in antitubercular drug-induced hepatotoxicity. Indian J Gastroenterol 20(3):97–100
Corsini A, Bortolini M (2013) Drug-induced liver injury: the role of drug metabolism and transport. J Clin Pharmacol 53(5):463–474. doi:10.1002/jcph.23
Daly AK, Day CP (2012) Genetic association studies in drug-induced liver injury. Drug Metab Rev 44(1):116–126. doi:10.3109/03602532.2011.605790
Daly AK, Donaldson PT, Bhatnagar P et al (2009) HLA-B*5701 genotype is a major determinant of drug-induced liver injury due to flucloxacillin. Nat Genet 41(7):816–819. doi:10.1038/ng.379
de Castro L, do Brasil PE, Monteiro TP, Rolla VC (2010) Can hepatitis B virus infection predict tuberculosis treatment liver toxicity? Development of a preliminary prediction rule. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis 14(3):332–340
Deeken JF, Cormier T, Price DK et al (2010) A pharmacogenetic study of docetaxel and thalidomide in patients with castration-resistant prostate cancer using the DMET genotyping platform. Pharmacogenomics J 10(3):191–199. doi:10.1038/tpj.2009.57
Deng R, Yang T, Wang Y, Tang N (2012) CYP2E1 RsaI/PstI polymorphism and risk of anti-tuberculosis drug-induced liver injury: a meta-analysis. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis 16(12):1574–1581. doi:10.5588/ijtld.12.0304
Di Martino MT, Arbitrio M, Leone E et al (2011) Single nucleotide polymorphisms of ABCC5 and ABCG1 transporter genes correlate to irinotecan-associated gastrointestinal toxicity in colorectal cancer patients: a DMET microarray profiling study. Cancer Biol Ther 12(9):780–787. doi:10.4161/cbt.12.9.17781
Diehl AM (2000) Cytokine regulation of liver injury and repair. Immunol Rev 174:160–171
Diehl AM, Rai RM (1996) Liver regeneration 3: regulation of signal transduction during liver regeneration. FASEB J 10(2):215–227
Dossing M, Wilcke JT, Askgaard DS, Nybo B (1996) Liver injury during antituberculosis treatment: an 11-year study. Tubercle Lung Dis 77(4):335–340
Du H, Chen X, Fang Y et al (2013) Slow N-acetyltransferase 2 genotype contributes to anti-tuberculosis drug-induced hepatotoxicity: a meta-analysis. Mol Biol Rep 40(5):3591–3596. doi:10.1007/s11033-012-2433-y
Durand F, Bernuau J, Pessayre D et al (1995) Deleterious influence of pyrazinamide on the outcome of patients with fulminant or subfulminant liver failure during antituberculous treatment including isoniazid. Hepatology 21(4):929–932
Elahi MM, Asotra K, Matata BM, Mastana SS (2009) Tumor necrosis factor alpha-308 gene locus promoter polymorphism: an analysis of association with health and disease. Biochim Biophys Acta 1792(3):163–172
Feng FM, Guo M, Chen Y et al (2014) Genetic polymorphisms in metabolic enzymes and susceptibility to anti-tuberculosis drug-induced hepatic injury. Genet Mol Res GMR 13(4):9463–9471. doi:10.4238/2014.November.11.11
Fernandes DC, Santos NP, Moraes MR et al (2014) Association of the CYP2B6 gene with anti-tuberculosis drug-induced hepatotoxicity in a Brazilian Amazon population. Int J Infect Dis IJID. doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2014.04.011
Fountain FF, Tolley EA, Jacobs AR, Self TH (2009) Rifampin hepatotoxicity associated with treatment of latent tuberculosis infection. Am J Med Sci 337(5):317–320. doi:10.1097/MAJ.0b013e31818c0134
Fukuda Y, Schuetz JD (2012) ABC transporters and their role in nucleoside and nucleotide drug resistance. Biochem Pharmacol 83(8):1073–1083. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2011.12.042
Girling DJ (1978) The hepatic toxicity of antituberculosis regimens containing isoniazid, rifampicin and pyrazinamide. Tubercle 59(1):13–32
Halilbasic E, Claudel T, Trauner M (2013) Bile acid transporters and regulatory nuclear receptors in the liver and beyond. J Hepatol 58(1):155–168. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2012.08.002
Hao JQ, Chen Y, Li SM et al (2011) Relationship between the polymorphisms of UGT1A6 genes and anti-tuberculosis drug induced hepatic-injury. Zhonghua gan zang bing za zhi= Zhonghua ganzangbing zazhi= Chin J Hepatol 19(3):201–204. doi:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-3418.2011.03.012
Hein DW, Doll MA, Rustan TD, Ferguson RJ (1995) Metabolic activation of N-hydroxyarylamines and N-hydroxyarylamides by 16 recombinant human NAT2 allozymes: effects of 7 specific NAT2 nucleic acid substitutions. Cancer Res 55(16):3531–3536
Hein DW, Doll MA, Fretland AJ et al (2000) Molecular genetics and epidemiology of the NAT1 and NAT2 acetylation polymorphisms. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev 9(1):29–42
Hilmer SN, Shenfield GM, Le Couteur DG (2005) Clinical implications of changes in hepatic drug metabolism in older people. Ther Clin Risk Manage 1(2):151–156
Hirata K, Takagi H, Yamamoto M et al (2008) Ticlopidine-induced hepatotoxicity is associated with specific human leukocyte antigen genomic subtypes in Japanese patients: a preliminary case–control study. Pharmacogenomics J 8(1):29–33. doi:10.1038/sj.tpj.6500442
Holden AL (2007) The innovative use of a large-scale industry biomedical consortium to research the genetic basis of drug induced serious adverse events. Drug Discov Today Technol 4(2):75–87. doi:10.1016/j.ddtec.2007.11.003
Holt MP, Ju C (2006) Mechanisms of drug-induced liver injury. AAPS J 8(1):E48–E54. doi:10.1208/aapsj080106
Hoofnagle JH (2004) Drug-induced liver injury network (DILIN). Hepatology 40(4):773. doi:10.1002/hep.20445
Horita N, Miyazawa N, Yoshiyama T et al (2013) Decreased activities of daily living is a strong risk factor for liver injury by anti-tuberculosis drugs. Respirology 18(3):474–479. doi:10.1111/resp.12008
Hosokawa M (2008) Structure and catalytic properties of carboxylesterase isozymes involved in metabolic activation of prodrugs. Molecules 13(2):412–431
Huang YS (2007) Genetic polymorphisms of drug-metabolizing enzymes and the susceptibility to antituberculosis drug-induced liver injury. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol 3(1):1–8. doi:10.1517/17425255.3.1.1
Huang YS, Su WJ, Huang YH et al (2007) Genetic polymorphisms of manganese superoxide dismutase, NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase, glutathione S-transferase M1 and T1, and the susceptibility to drug-induced liver injury. J Hepatol 47(1):128–134. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2007.02.009
Kaona FA, Tuba M, Siziya S, Sikaona L (2004) An assessment of factors contributing to treatment adherence and knowledge of TB transmission among patients on TB treatment. BMC Public Health 4:68. doi:10.1186/1471-2458-4-68
Kato H, Horita N, Miyazawa N, Yoshiyama T, Ueda A, Ishigatsubo Y (2013) Risk factors for liver injury with an elevated serum bilirubin concentration caused by antituberculous drugs. Intern Med 52(19):2209–2214
Kim SH, Kim SH, Bahn JW et al (2009) Genetic polymorphisms of drug-metabolizing enzymes and anti-TB drug-induced hepatitis. Pharmacogenomics 10(11):1767–1779. doi:10.2217/pgs.09.100
Kim SH, Kim SH, Lee JH et al (2012a) Polymorphisms in drug transporter genes (ABCB1, SLCO1B1 and ABCC2) and hepatitis induced by antituberculosis drugs. Tuberculosis 92(1):100–104. doi:10.1016/j.tube.2011.09.007
Kim SH, Kim SH, Yoon HJ et al (2012b) TNF-alpha genetic polymorphism -308G/A and antituberculosis drug-induced hepatitis. Liver Int 32(5):809–814. doi:10.1111/j.1478-3231.2011.02697.x
Knolle PA, Uhrig A, Hegenbarth S et al (1998) IL-10 down-regulates T cell activation by antigen-presenting liver sinusoidal endothelial cells through decreased antigen uptake via the mannose receptor and lowered surface expression of accessory molecules. Clin Exp Immunol 114(3):427–433
Lee AM, Mennone JZ, Jones RC, Paul WS (2002) Risk factors for hepatotoxicity associated with rifampin and pyrazinamide for the treatment of latent tuberculosis infection: experience from three public health tuberculosis clinics. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis 6(11):995–1000
Leiro V, Fernandez-Villar A, Valverde D et al (2008) Influence of glutathione S-transferase M1 and T1 homozygous null mutations on the risk of antituberculosis drug-induced hepatotoxicity in a Caucasian population. Liver Int 28(6):835–839. doi:10.1111/j.1478-3231.2008.01700.x
Li LM, Chen L, Deng GH et al (2012) SLCO1B1 *15 haplotype is associated with rifampin-induced liver injury. Mol Med Rep 6(1):75–82. doi:10.3892/mmr.2012.900
Li C, Long J, Hu X, Zhou Y (2013) GSTM1 and GSTT1 genetic polymorphisms and risk of anti-tuberculosis drug-induced hepatotoxicity: an updated meta-analysis. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 32(7):859–868. doi:10.1007/s10096-013-1831-y
Liang X, Zhang J, Zhu Y et al (2013) Specific genetic polymorphisms of IL10-592 AA and IL10-819 TT genotypes lead to the key role for inducing docetaxel-induced liver injury in breast cancer patients. Clin Transl Oncol 15(4):331–334. doi:10.1007/s12094-012-0936-6
Lima Mde F, Melo HR (2012) Hepatotoxicity induced by antituberculosis drugs among patients coinfected with HIV and tuberculosis. Cadernos de Saude Publica 28(4):698–708
Liu W, Ramirez J, Gamazon ER et al (2014) Genetic factors affecting gene transcription and catalytic activity of UDP-glucuronosyltransferases in human liver. Hum Mol Genet 23(20):5558–5569. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddu268
Louis H, Van Laethem JL, Wu W et al (1998) Interleukin-10 controls neutrophilic infiltration, hepatocyte proliferation, and liver fibrosis induced by carbon tetrachloride in mice. Hepatology 28(6):1607–1615. doi:10.1002/hep.510280621
Louis H, Le Moine O, Goldman M, Deviere J (2003) Modulation of liver injury by interleukin-10. Acta Gastro-Enterol Belg 66(1):7–14
Lucena MI, Molokhia M, Shen Y et al (2011) Susceptibility to amoxicillin-clavulanate-induced liver injury is influenced by multiple HLA class I and II alleles. Gastroenterology 141(1):338–347. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2011.04.001
Mahoney FI, Barthel DW (1965) Functional evaluation: the Barthel Index. Md State Med J 14:61–65
Mankhatitham W, Lueangniyomkul A, Manosuthi W (2011) Hepatotoxicity in patients co-infected with tuberculosis and HIV-1 while receiving non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor-based antiretroviral therapy and rifampicin-containing anti-tuberculosis regimen. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health 42(3):651–658
Marra F, Marra CA, Bruchet N et al (2007) Adverse drug reactions associated with first-line anti-tuberculosis drug regimens. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis 11(8):868–875
Marzuki OA, Fauzi AR, Ayoub S, Kamarul Imran M (2008) Prevalence and risk factors of anti-tuberculosis drug-induced hepatitis in Malaysia. Singap Med J 49(9):688–693
Mizzi C, Peters B, Mitropoulou C et al (2014) Personalized pharmacogenomics profiling using whole-genome sequencing. Pharmacogenomics 15(9):1223–1234. doi:10.2217/pgs.14.102
Molokhia M, McKeigue P (2006) EUDRAGENE: european collaboration to establish a case–control DNA collection for studying the genetic basis of adverse drug reactions. Pharmacogenomics 7(4):633–638. doi:10.2217/14622416.7.4.633
Monteiro TP, El-Jaick KB, Jeovanio-Silva AL et al (2012) The roles of GSTM1 and GSTT1 null genotypes and other predictors in anti-tuberculosis drug-induced liver injury. J Clin Pharm Ther 37(6):712–718. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2710.2012.01368.x
Moore KW, de Waal Malefyt R, Coffman RL, O’Garra A (2001) Interleukin-10 and the interleukin-10 receptor. Annu Rev Immunol 19:683–765. doi:10.1146/annurev.immunol.19.1.683
Nader LA, de Mattos AA, Picon PD, Bassanesi SL, De Mattos AZ, Pineiro Rodriguez M (2010) Hepatotoxicity due to rifampicin, isoniazid and pyrazinamide in patients with tuberculosis: is anti-HCV a risk factor? Ann Hepatol 9(1):70–74
Nanashima K, Mawatari T, Tahara N et al (2012) Genetic variants in antioxidant pathway: risk factors for hepatotoxicity in tuberculosis patients. Tuberculosis 92(3):253–259. doi:10.1016/j.tube.2011.12.004
Ohkawa K, Hashiguchi M, Ohno K et al (2002) Risk factors for antituberculous chemotherapy-induced hepatotoxicity in Japanese pediatric patients. Clin Pharmacol Ther 72(2):220–226. doi:10.1067/mcp.2002.126175
Pachkoria K, Lucena MI, Crespo E et al (2008) Analysis of IL-10, IL-4 and TNF-alpha polymorphisms in drug-induced liver injury (DILI) and its outcome. J Hepatol 49(1):107–114. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2008.03.017
Pande JN, Singh SP, Khilnani GC, Khilnani S, Tandon RK (1996) Risk factors for hepatotoxicity from antituberculosis drugs: a case–control study. Thorax 51(2):132–136
Park WB, Kim W, Lee KL et al (2010) Antituberculosis drug-induced liver injury in chronic hepatitis and cirrhosis. J Infect 61(4):323–329. doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2010.07.009
Pukenyte E, Lescure FX, Rey D et al (2007) Incidence of and risk factors for severe liver toxicity in HIV-infected patients on anti-tuberculosis treatment. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis 11(1):78–84
Rumiato E, Boldrin E, Amadori A, Saggioro D (2013) DMET (drug-metabolizing enzymes and transporters) microarray analysis of colorectal cancer patients with severe 5-fluorouracil-induced toxicity. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 72(2):483–488. doi:10.1007/s00280-013-2210-1
Sarich TC, Adams SP, Petricca G, Wright JM (1999) Inhibition of isoniazid-induced hepatotoxicity in rabbits by pretreatment with an amidase inhibitor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 289(2):695–702
Sarma GR, Immanuel C, Kailasam S, Narayana AS, Venkatesan P (1986) Rifampin-induced release of hydrazine from isoniazid: a possible cause of hepatitis during treatment of tuberculosis with regimens containing isoniazid and rifampin. Am Rev Respir Dis 133(6):1072–1075
Shang P, Xia Y, Liu F et al (2011) Incidence, clinical features and impact on anti-tuberculosis treatment of anti-tuberculosis drug induced liver injury (ATLI) in China. PLoS One 6(7):e21836. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0021836
Sharma SK, Balamurugan A, Saha PK, Pandey RM, Mehra NK (2002) Evaluation of clinical and immunogenetic risk factors for the development of hepatotoxicity during antituberculosis treatment. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 166(7):916–919. doi:10.1164/rccm.2108091
Shen C, Meng Q, Zhang G, Hu W (2008) Rifampicin exacerbates isoniazid-induced toxicity in human but not in rat hepatocytes in tissue-like cultures. Br J Pharmacol 153(4):784–791. doi:10.1038/sj.bjp.0707611
Sheng YJ, Wu G, He HY et al (2014) The association between CYP2E1 polymorphisms and hepatotoxicity due to anti-tuberculosis drugs: a meta-analysis. Infect Genet Evol 24:34–40. doi:10.1016/j.meegid.2014.01.034
Shimoda-Matsubayashi S, Matsumine H, Kobayashi T, Nakagawa-Hattori Y, Shimizu Y, Mizuno Y (1996) Structural dimorphism in the mitochondrial targeting sequence in the human manganese superoxide dismutase gene: a predictive evidence for conformational change to influence mitochondrial transport and a study of allelic association in Parkinson’s disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 226(2):561–565. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1996.1394
Shin SM, Yang JH, Ki SH (2013) Role of the Nrf2-ARE pathway in liver diseases. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2013:763257. doi:10.1155/2013/763257
Shu CC, Lee CH, Lee MC, Wang JY, Yu CJ, Lee LN (2013) Hepatotoxicity due to first-line anti-tuberculosis drugs: a five-year experience in a Taiwan medical centre. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis 17(7):934–939. doi:10.5588/ijtld.12.0782
Singh M, Gupta VH, Amarapurkar DN et al (2014) Association of genetic variants with anti-tuberculosis drug induced hepatotoxicity: a high resolution melting analysis. Infect Genetics Evol 23:42–48. doi:10.1016/j.meegid.2014.01.027
Singla R, Sharma SK, Mohan A et al (2010) Evaluation of risk factors for antituberculosis treatment induced hepatotoxicity. Indian J Med Res 132:81–86
Sodhi CP, Rana S, Mehta S, Vaiphei K, Goel RC, Mehta SK (1997a) Study of oxidative-stress in rifampicin-induced hepatic injury in growing rats with and without protein-energy malnutrition. Hum Exp Toxicol 16(6):315–321
Sodhi CP, Rana SV, Mehta SK, Vaiphei K, Attari S, Mehta S (1997b) Study of oxidative-stress in isoniazid-rifampicin induced hepatic injury in young rats. Drug Chem Toxicol 20(3):255–269. doi:10.3109/01480549709003881
Stine JG, Sateesh P, Lewis JH (2013) Drug-induced liver injury in the elderly. Curr Gastroenterol Rep 15(1):299. doi:10.1007/s11894-012-0299-8
Sun L, Luo C, Long J, Wei D, Liu J (2006) Acrolein is a mitochondrial toxin: effects on respiratory function and enzyme activities in isolated rat liver mitochondria. Mitochondrion 6(3):136–142. doi:10.1016/j.mito.2006.04.003
Sun F, Chen Y, Xiang Y, Zhan S (2008) Drug-metabolising enzyme polymorphisms and predisposition to anti-tuberculosis drug-induced liver injury: a meta-analysis. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis 12(9):994–1002
Tang SW, Lv XZ, Zhang Y et al (2012) CYP2E1, GSTM1 and GSTT1 genetic polymorphisms and susceptibility to antituberculosis drug-induced hepatotoxicity: a nested case-control study. J Clin Pharm Ther 37(5):588–593. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2710.2012.01334.x
Tang N, Deng R, Wang Y et al (2013a) GSTM1 and GSTT1 null polymorphisms and susceptibility to anti-tuberculosis drug-induced liver injury: a meta-analysis. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis 17(1):17–25. doi:10.5588/ijtld.12.0447
Tang SW, Lv XZ, Chen R et al (2013b) Lack of association between genetic polymorphisms of CYP3A4, CYP2C9 and CYP2C19 and antituberculosis drug-induced liver injury in a community-based Chinese population. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 40(5):326–332. doi:10.1111/1440-1681.12074
Teschke R, Frenzel C, Wolff A, Eickhoff A, Schulze J (2014) Drug induced liver injury: accuracy of diagnosis in published reports. Ann Hepatol 13(2):248–255
Tostmann A, Boeree MJ, Aarnoutse RE, de Lange WC, van der Ven AJ, Dekhuijzen R (2008) Antituberculosis drug-induced hepatotoxicity: concise up-to-date review. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 23(2):192–202. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1746.2007.05207.x
Urban TJ, Shen Y, Stolz A et al (2012) Limited contribution of common genetic variants to risk for liver injury due to a variety of drugs. Pharmacogenet Genomics 22(11):784–795. doi:10.1097/FPC.0b013e3283589a76
Vavricka SR, Van Montfoort J, Ha HR, Meier PJ, Fattinger K (2002) Interactions of rifamycin SV and rifampicin with organic anion uptake systems of human liver. Hepatology 36(1):164–172. doi:10.1053/jhep.2002.34133
Walter-Sack I, Klotz U (1996) Influence of diet and nutritional status on drug metabolism. Clin Pharmacokinet 31(1):47–64. doi:10.2165/00003088-199631010-00004
Wang PY, Xie SY, Hao Q, Zhang C, Jiang BF (2012) NAT2 polymorphisms and susceptibility to anti-tuberculosis drug-induced liver injury: a meta-analysis. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis 16(5):589–595. doi:10.5588/ijtld.11.0377
Wang J, Chen R, Tang S et al (2014) Interleukin-4 and interleukin-10 polymorphisms and antituberculosis drug-induced hepatotoxicity in Chinese population. J Clin Pharm Ther. doi:10.1111/jcpt.12223
WHO (2014) WHO Global tuberculosis report 2014. World Health Organization, Geneva
Wong WM, Wu PC, Yuen MF et al (2000) Antituberculosis drug-related liver dysfunction in chronic hepatitis B infection. Hepatology 31(1):201–206. doi:10.1002/hep.510310129
Wu XQ, Zhu DL, Zhang JX et al (2012) The relationship between carboxylesterase 1 gene polymorphisms and susceptibility to antituberculosis drug-induced hepatotoxicity. Zhonghua nei ke za zhi 51(7):524–530
Yamada S, Richardson K, Tang M et al (2010) Genetic variation in carboxylesterase genes and susceptibility to isoniazid-induced hepatotoxicity. Pharmacogenomics J 10(6):524–536. doi:10.1038/tpj.2010.5
Yee D, Valiquette C, Pelletier M, Parisien I, Rocher I, Menzies D (2003) Incidence of serious side effects from first-line antituberculosis drugs among patients treated for active tuberculosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 167(11):1472–1477. doi:10.1164/rccm.200206-626OC
Yimer G, Aderaye G, Amogne W et al (2008) Anti-tuberculosis therapy-induced hepatotoxicity among Ethiopian HIV-positive and negative patients. PLoS One 3(3):e1809. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0001809
Yimer G, Ueda N, Habtewold A et al (2011) Pharmacogenetic and pharmacokinetic biomarker for efavirenz based ARV and rifampicin based anti-TB drug induced liver injury in TB-HIV infected patients. PLoS One 6(12):e27810. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0027810
Yimer G, Gry M, Amogne W et al (2014) Evaluation of patterns of liver toxicity in patients on antiretroviral and anti-tuberculosis drugs: a prospective four arm observational study in ethiopian patients. PLoS One 9(4):e94271. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0094271
Zaverucha-do-Valle C, Monteiro SP, El-Jaick KB et al (2014) The role of cigarette smoking and liver enzymes polymorphisms in anti-tuberculosis drug-induced hepatotoxicity in Brazilian patients. Tuberculosis 94(3):299–305. doi:10.1016/j.tube.2014.03.006
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, R., Wang, J., Zhang, Y. et al. Key factors of susceptibility to anti-tuberculosis drug-induced hepatotoxicity. Arch Toxicol 89, 883–897 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-015-1473-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-015-1473-1