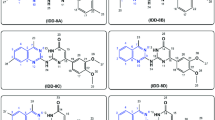
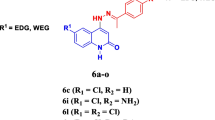
Abstract
To address the growing health threat posed by drug-resistant pathogenic microorganisms, the development of novel antimicrobial medications with multiple mechanisms of action is in urgent demand. With traditional antibacterial drug resources challenging to push forward, developing new antibacterial drugs has become a hot spot in biomedical research. In this study, we tested the antibacterial activity of 119 phenanthridine derivatives via the antibacterial assay and obtained 5 candidates. The cytotoxicity assay showed one phenanthridine derivative, HCK20, was safe for mammalian cells below 125 µM. HCK20 was verified to possess significant antibacterial activity to Streptococcus spp., such as Streptococcus pneumoniae, Streptococcus agalactiae, Streptococcus suis, Streptococcus dysgalactiae, and Streptococcus equi with MICs ranging from 15 to 60 µM. Furthermore, we found that HCK20 probably achieved its bacterial inhibition by influencing the permeability of bacterial cell walls via interacting with Streptococcal penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs). Our results suggest that this phenanthridine derivative, HCK20, has great potential to become a novel antibacterial agent that can be a potent treatment for streptococcal infections.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Adan A, Kiraz Y, Baran Y (2016) Cell proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. Curr Pharm Biotechnol 17:1213–1221. https://doi.org/10.2174/1389201017666160808160513
Antimicrobial Resistance Collaborators (2022) Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in 2019: a systematic analysis. Lancet 399:629–655. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(21)02724-0
Banerjee J, Bhattacharjee A, Biswas A, Chattopadhyay SK (2022) Synthesis, bio-physical and anti-leishmanial studies of some novel indolo[3,2-a]phenanthridine derivatives. Bioorg Chem 123:105766. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioorg.2022.105766
Basu S, Varghese R, Debroy R et al (2022) Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs ketorolac and etodolac can augment the treatment against pneumococcal meningitis by targeting penicillin-binding proteins. Microb Pathog 170:105694. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2022.105694
Cappoen D, Jacobs J, Van Nguyen T et al (2012) Straight forward palladium-mediated synthesis and biological evaluation of benzo[j]phenanthridine-7,12-diones as anti-tuberculosis agents. Eur J Med Chem 48:57–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2011.11.033
CDC (2022) The biggest antibiotic-resistant threats in the U.S. In: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/drugresistance/biggest-threats.html. Accessed 31 Aug 2023
Chen D, Cai J, Yin J et al (2015) Lycorine-derived phenanthridine downregulators of host Hsc70 as potential hepatitis C virus inhibitors. Future Med Chem 7:561–570. https://doi.org/10.4155/fmc.15.14
Chen D-Z, Jing C-X, Cai J-Y et al (2016) Design, synthesis, and structural optimization of lycorine-derived phenanthridine derivatives as Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway agonists. J Nat Prod 79:180–188. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jnatprod.5b00825
Chen D, Zhang H, Jing C et al (2018) Efficient synthesis of new phenanthridine Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway agonists. Eur J Med Chem 157:1491–1499. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2018.08.064
Chen D-Z, Yang B-J, He X-L et al (2019) Design, synthesis and structure-activity relationship optimization of phenanthridine derivatives as new Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway agonists. Bioorg Chem 84:285–294. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioorg.2018.11.020
Chen D-Z, Fan S-R, Yang B-J et al (2021) Phenanthridine derivative host heat shock cognate 70 down-regulators as porcine epidemic diarrhea virus inhibitors. J Nat Prod 84:1175–1184. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jnatprod.0c01252
de Alcântara RI, Ferrari RG, Panzenhagen PHN et al (2020) Antimicrobial resistance genes in bacteria from animal-based foods. Adv Appl Microbiol 112:143–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.aambs.2020.03.001
Deb R, Kumar A, Chakraborty S et al (2013) Trends in diagnosis and control of bovine mastitis: a review. Pak J Biol Sci 16:1653–1661. https://doi.org/10.3923/pjbs.2013.1653.1661
Haas B, Grenier D (2018) Understanding the virulence of Streptococcus suis: a veterinary, medical, and economic challenge. Med Mal Infect 48:159–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.medmal.2017.10.001
Haenni M, Lupo A, Madec J-Y (2018) Antimicrobial resistance in Streptococcus spp. Microbiol Spectr. https://doi.org/10.1128/microbiolspec.ARBA-0008-2017
Hakenbeck R, Brückner R, Denapaite D, Maurer P (2012) Molecular mechanisms of β-lactam resistance in Streptococcus pneumoniae. Future Microbiol 7:395–410. https://doi.org/10.2217/fmb.12.2
Hayes K, O’Halloran F, Cotter L (2020) A review of antibiotic resistance in Group B Streptococcus: the story so far. Crit Rev Microbiol 46:253–269. https://doi.org/10.1080/1040841X.2020.1758626
He N, Wang P, Wang P et al (2018) Antibacterial mechanism of chelerythrine isolated from root of Toddalia asiatica (Linn) Lam. BMC Complement Altern Med 18:261. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12906-018-2317-3
Holmer I, Salomonsen CM, Jorsal SE et al (2019) Antibiotic resistance in porcine pathogenic bacteria and relation to antibiotic usage. BMC Vet Res 15:449. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12917-019-2162-8
Iannello C, Pigni NB, Antognoni F et al (2014) A potent acetylcholinesterase inhibitor from Pancratium illyricum L. Fitoterapia 92:163–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fitote.2013.11.005
Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA), Spellberg B, Blaser M et al (2011) Combating antimicrobial resistance: policy recommendations to save lives. Clin Infect Dis 52(Suppl 5):S397-428. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/cir153
Lasák P, Motyka K, Kryštof V, Stýskala J (2018) Synthesis, bacteriostatic and anticancer activity of novel phenanthridines structurally similar to benzo[c]phenanthridine alkaloids. Molecules 23:2155. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23092155
Liu F, Venter H, Bi F et al (2017) Synthesis and antibacterial activity of 5-methylphenanthridium derivatives as FtsZ inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 27:3399–3402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2017.06.005
Lu C, Zhang N, Kou S et al (2022) Sanguinarine synergistically potentiates aminoglycoside-mediated bacterial killing. Microb Biotechnol 15:2055–2070. https://doi.org/10.1111/1751-7915.14017
Lunha K, Chumpol W, Jiemsup S et al (2023) Relationship between penicillin-binding proteins alterations and β-lactams non-susceptibility of diseased pig-isolated Streptococcus suis. Antibiotics (basel) 12:158. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12010158
Martin MJ, Thottathil SE, Newman TB (2015) Antibiotics overuse in animal agriculture: a call to action for health care providers. Am J Public Health 105:2409–2410. https://doi.org/10.2105/AJPH.2015.302870
Martin JK, Sheehan JP, Bratton BP et al (2020) A dual-mechanism antibiotic kills gram-negative bacteria and avoids drug resistance. Cell 181:1518-1532.e14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2020.05.005
McCauley J, Zivanovic A, Skropeta D (2013) Bioassays for anticancer activities. Methods Mol Biol 1055:191–205. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-62703-577-4_14
Morris GM, Goodsell DS, Halliday RS et al (1998) Automated docking using a Lamarckian genetic algorithm and an empirical binding free energy function. J Comput Chem 19:1639–1662. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1096-987X(19981115)19:14%3c1639::AID-JCC10%3e3.0.CO;2-B
Morris GM, Huey R, Lindstrom W et al (2009) AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: automated docking with selective receptor flexibility. J Comput Chem 30:2785–2791. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcc.21256
Nagendra Prasad HS, Karthik CS, Manukumar HM et al (2019) New approach to address antibiotic resistance: miss loading of functional membrane microdomains (FMM) of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Microb Pathog 127:106–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2018.11.038
Nagendra Prasad HS, Ananda AP, Mukarambi A et al (2023) Design, synthesis, and anti-bacterial activities of piperazine based phthalimide derivatives against superbug-Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Curr Chem Lett 12:65–78. https://doi.org/10.5267/j.ccl.2022.9.005
Naidu KM, Nagesh HN, Singh M et al (2015) Novel amide and sulphonamide derivatives of 6-(piperazin-1-yl)phenanthridine as potent Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv inhibitors. Eur J Med Chem 92:415–426. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2015.01.013
Nakamura M, Aoyama A, Salim MTA et al (2010) Structural development studies of anti-hepatitis C virus agents with a phenanthridinone skeleton. Bioorg Med Chem 18:2402–2411. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2010.02.057
Nandikolla A, Srinivasarao S, Karan Kumar B et al (2021) Novel phenanthridine amide analogs as potential anti-leishmanial agents: in vitro and in silico insights. Bioorg Chem 117:105414. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105414
OneHealthTrust (2023) ResistanceMap: Antibiotic resistance. https://resistancemap.onehealthtrust.org/AntibioticResistance.php. Accessed 31 Aug 2023
Pigni NB, Ríos-Ruiz S, Martínez-Francés V et al (2012) Alkaloids from Narcissus serotinus. J Nat Prod 75:1643–1647. https://doi.org/10.1021/np3003595
Pinzi L, Rastelli G (2019) Molecular docking: shifting paradigms in drug discovery. Int J Mol Sci 20:4331. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20184331
Seaman A, Woodbine M (1954) The antibacterial activity of phenanthridine compounds. Br J Pharmacol Chemother 9:265–270. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1476-5381.1954.tb01679.x
Stanzione F, Giangreco I, Cole JC (2021) Use of molecular docking computational tools in drug discovery. Prog Med Chem 60:273–343. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.pmch.2021.01.004
Trott O, Olson AJ (2010) AutoDock Vina: improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J Comput Chem 31:455–461. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcc.21334
Ulrichová J, Dvorák Z, Vicar J et al (2001) Cytotoxicity of natural compounds in hepatocyte cell culture models. The case of quaternary benzo[c]phenanthridine alkaloids. Toxicol Lett 125:125–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0378-4274(01)00430-1
Wang C-Y, Chen Y-H, Fang C et al (2019) Antibiotic resistance profiles and multidrug resistance patterns of Streptococcus pneumoniae in pediatrics: a multicenter retrospective study in mainland China. Medicine (baltimore) 98:e15942. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000015942
Wang Y-T, Long X-Y, Ding X et al (2022) Novel nucleocapsid protein-targeting phenanthridine inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2. Eur J Med Chem 227:113966. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2021.113966
Xiong W, Sun Y, Zeng Z (2018) Antimicrobial use and antimicrobial resistance in food animals. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 25:18377–18384. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1852-2
Yang B-J, Fan S-R, Zhang X-F et al (2022) Design, synthesis and structure-activity relationship optimization of phenanthridine derivatives as new anti-vitiligo compounds. Bioorg Chem 119:105582. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105582
Zhang Y (2019) Pathogenic mechanism of SecY2/A2 secretion system in streptococcus suis serotype Chz and screening the candidate immunogens. Nanjing Agricultural University, Doctor
Zhang Z (2021) Research advances on tilapia streptococcosis. Pathogens 10:558. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10050558
Zhao C, Yang S, Zhang F et al (2022) Antimicrobial resistance trends of the most common causative pathogens associated with community-acquired respiratory infections in China: 2009–2018. Infect Drug Resist 15:5069–5083. https://doi.org/10.2147/IDR.S374805
Zhu J (2017) Immunoprtection of the inactivated vaccine against streptococcus agalactiae infection for tilapia and characteristics of XtgS gene deletion. Nanjing Agricultural University, Master
Zhu L, Yerramilli P, Pruitt L et al (2021) Functional insights into the high-molecular-mass penicillin-binding proteins of Streptococcus agalactiae revealed by gene deletion and transposon mutagenesis analysis. J Bacteriol 203:e0023421. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.00234-21
Funding
This study was supported by grants from Hainan Province Science and Technology Special Fund (ZDYF2022XDNY236) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (KYTZ2023002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZSD and ZSY performed the experiments, analyzed the data, and drafted the manuscript. WYT and FSR assisted with molecular docking analyses. ZYM and LS gave useful suggestions in writing the manuscript. CDZ provided the phenanthridone derivatives used in the experiments. LGJ guided the study throughout. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Communicated by Yusuf Akhter.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, S., Zhang, S., Wang, Y. et al. Discovery of novel phenanthridone derivatives with anti-streptococcal activity. Arch Microbiol 205, 371 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-023-03705-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-023-03705-7