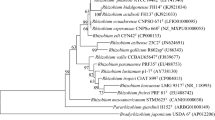
Abstract
The fast-growing Rhizobium sp. strain NGR234, isolated from Papua New Guinea, and 13 strains of Sinorhizobium fredii, isolated from China and Vietnam, were fingerprinted by means of RAPD, REP, ERIC and ARDRA. ERIC, REP and RAPD markers revealed a considerable genetic diversity among fast-growing rhizobia. Chinese isolates showed higher levels of diversity than those strains isolated from Vietnam. ARDRA analysis revealed three different genotypes among fast-growing rhizobia that nodulate soybean, even though all belonged to a subcluster that included Sinorhizobium saheli and Sinorhizobium meliloti. Among S. fredii rhizobia, two strains, SMH13 and HH303, might be representatives of other species of nitrogen-fixing organisms. Although restriction analysis of the nifD–nifK intergenic DNA fragment confirmed the unique nature of Rhizobium sp. strain NGR234, several similarities between Rhizobium sp. strain NGR234 and S. fredii USDA257, the ARDRA analysis and the full sequence of the 16S rDNA confirmed that NGR234 is a S. fredii strain. In addition, ARDRA analysis and the full sequence of the 16S rDNA suggested that two strains of rhizobia might be representatives of other species of rhizobia.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bachem CWB, Kondorosi E, Banfalvi Z, Horvarth B, Kondorosi A, Schell J (1985) Identification and cloning of nodulation genes from the wide host range Rhizobium strain NGR234. Molec Gen Genet 199:271–278
Balatti PA, Pueppke SG (1992) Identification of North American soybean lines that form nitrogen fixing nodules with Rhizobium fredii USDA257. Can J Plant Sci 72:49–55
Balatti PA, Kovacs L, Krishnan HB, Pueppke SG (1995) Rhizobium sp. strain NGR234 contains a functional copy of the soybean cultivar specificity locus, nolXWBTUV. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 8:693–699
Bec-Ferté MP, Krishnan HB, Promé D, Savagnac A, Pueppke SG, Promé JC (1993) Structure of nodulation factors from the nitrogen-fixing soybean symbiont Rhizobium fredii USDA257. Biochem 33:11782–11788
Beringer JE (1974) R factor transfer in Rhizobium leguminosarum. J Gen Microbiol 84:188–198
Broughton WJ, Heycke N, Meyer ZHA, Pankhurst CE (1984). Plasmid linked nif and nod genes in fast-growing rhizobia that nodulate Glycine max, Psophocarpus tetragonolobus and Vigna unguiculata. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81:3093–3097
Buendía-Claveria AM, M Chamber, Ruiz-Sainz JE (1989) A comparative study of the physiological characteristics, plasmid content and symbiotic properties of different Rhizobium fredii strains. Syst Appl Microbiol 12:203–209
Cleyet-Marel JC (1987) Dynamics des populations de Rhizobium et de Bradyrhizobium dans le sol et la rhizosphere. Thesis, Universite Claude Bernard, Lyon, France
Chen WX, Yan GH, Li JL (1988). Numerical taxonomic study of fast-growing soybean rhizobia and a proposal that Rhizobium fredii be assigned to Sinorhizobium gen. Nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol 38:392–397
Dangeard PA (1926) Researches sur les tubercles radicaux des Legumineuses. Botanis (Paris) 16:1–275
De Bruijn FJ (1992) Use of repetitive (Repetitive Extragenic Palindromic and Enterobacterial Repetitive Intergeneric Consensus) sequences and the polymerase chain reaction to fingerprint the genomes of Rhizobium meliloti isolates and other soil bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 58:2180–2187
De Lajudie PA, Willems A, Pot B, Dewettinck D, Maestrojuan G, Neyra M, Collins MD, Dreyfus B, Kersters K, Gillis M (1994) Polyphasic taxonomy of rhizobia: emendation of the genus Sinorhizobium and description of Sinorhizobium meliloti comb. nov., Sinorhizobium saheli sp. nov., and Sinorhizobium terangan sp. nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol 44:715–733
Demezas DH, Reardon TB, Watson JM, Gibson AH (1991) Genetic diversity among Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. trifolii strains revealed by allozyme and restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis. Appl Environ Microbiol 57:3489–3495
Devereux J, Haeberli P, Smithies O (1984) A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res 12:387–395
Dowdle SF, Bohlool BB (1985) Predominance of fast-growing Rhizobium japonicum in a soybean field in the People's Republic of China. Appl Environ Microbiol 50:1171–1176
Eardly BD, Materon LA, Smith NH, Johnson DA, Rumbaugh MD, Selander. RK (1990) Genetic structure of natural populations of the nitrogen-fixing bacterium Rhizobium meliloti. Appl Environ Microbiol 56:187–194
Field GK, Gordon D, Wright T, Rappe M, Urbach E, Vergin K, Giovannoni SJ (1997) Diversity and depth-specific distribution of SAR11 cluster rRNA genes from marine planktonic bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:63–70
Fox GE, Wisotzkey JD, Jurtshuk P (1992) How close is close: 16S rRNA Sequence identity may not be sufficient to guarantee species identity. Int J Syst Bacteriol 42:166–170
Fred EB, Baldwin FL, McCoy E (1932) Root nodule bacteria and leguminous plants. University of Wisconsin Studies in Science no. 5, Madison, Wisconsin, USA
Geniaux E, Laguerre G, Amarguer N (1993) Comparison of geographically distant populations of Rhizobium isolated from root nodules of Phaseolus vulgaris Molec Ecol 2:295–302
Heyndrickx M, Vaurterin L, Vandamme P, Kersters K, De Vos P (1996) Applicability of combined amplified ribosomal DNA restriction analysis (ARDRA) patterns in bacterial phylogeny and taxonomy. J Microbiol Methods 26:247–259
Huber, I, Selenska-Pobell S (1994) Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis-fingerprinting, genome size estimation and loci number of Rhizobium galegae. J Appl Bacteriol 77:528–533
Jamann SM, Fernandez MP, Normand P (1993) Typing method for N2-fixing bacteria based on PCR-RFLP-application to the characterization of Frankia strains. Mol Ecol 2:17–26
Jarvis BDW, Pankhurst CE, Pate l (1982) Rhizobium loti, a new species of legume root nodule bacteria. Int J Syst Bacteriol 32:378–380
Jarvis BDW, Tigue SW (1994) Rapid identification of Rhizobium species based on cellular fatty acid analysis. Plant Soil 161:31–41
Jordan DC, Allen ON (1984) Rhizobiaceae. In: Buchanan RE, Gibbons NE (eds) Bergey's Manual of Determinative Bacteriology. 8th edn. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore
Keyser HH, Bohlool BB, Hu TS, Weber DF (1982) Fast-growing rhizobia isolated from root nodules of soybean. Science 215:1631–1632
Kiss, E, Mergaert P, Olah B, Kereszt A, Staehelin C, Davies AE, Downie AJ, Kondorosi A, Kondorosi E (1998) Conservation of nolR in the Sinorhizobium and Rhizobium genera of the Rhizobiaceae family. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 11:1186–1195
Kondorosi A., Kondorosi E, Horvarth B, Gottfert M, Bachem C, Rodriguez-Quiñones F, Banfalvi Z, Putnoky P, Gyorgypal Z, John M, Schmidt J, Schell J (1986) Common and host specific nodulation genes of Rhizobium meliloti and their conservation in other rhizobia. In: Verma DPS Brisson N (eds) Molecular genetics of plant microbe interactions. Martinus Nijhoff, Dordrecht, pp 217–222
Krishnan HB, Pueppke SG (1991) Sequence analysis of the nodABC region of Rhizobium fredii USDA257, a nitrogen fixing symbiont of soybean and other legumes. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 6:512–520
Krishnan HB, Pueppke SG (1994) Host range, RFLP and antigenic relationship between Rhizobium fredii strains and Rhizobium sp. strain NGR234. Plant Soil 161:21–29
Kuykendall LD, Saxena B, Devine TE, Udell SE (1992) Genetic diversity in Bradyrhizobium japonicum Jordan 1982 and a proposal for Bradyrhizobium elkanii sp. Nov. Can J Microbiol 38:501–505
Laguerre G, Mavingui P, Allard MR, Charnay MP, Louvrier P, Mazurier SI, Rigottier-Gois L, Amarger N. (1996) Typing of rhizobia by PCR DNA fingerprinting and PCR-based restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of chromosomal and symbiotic gene regions: application to Rhizobium leguminosarum and its different biovars. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:2029–2036
Meinhardt LW, Krishnan HB, Balatti PA, Pueppke SG (1993) Molecular clonning and characterization of a sym plasmid locus that regulates cultivar specific nodulation of soybean by Rhizobium fredii USDA257. Molec Microbiol 9:17–29
Nayudu M, Rolfe BG (1987) Analysis of R-primes demonstrates that genes for broad host range nodulation of Rhizobium strain NGR234 are dispersed on the sym plasmid. Molec Gen Genet 206:326–337
Niemann S, Puhler A, Tichy HV, Simon R, Selbitschka. W (1997) Evaluation of the resolving power of three different DNA fingerprint methods to discriminate among isolates of a natural Rhizobium meliloti population. J Appl Microbiol 82:477–484
Nour SM, Cleyet-Marel J-C, Normand P, Fernandez MP (1995) Genomic heterogeneity of strains nodulating chickpeas (Cicer arietinum L.) and description of Rhizobium mediterraneum sp. nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol 45:640–648
Price NPJ, Relic B, Talmont F, Lewin A, Promé D, Pueppke SG, Maillet F, Denarié J, Promé JC, Broughton WJ (1992) Broad-host-range Rhizobium species strain NGR234 secretes a family of carbomylated and fucosylated nodulation signals that are O-acetylated or sulphated. Molec Microbiol 6:3575–3584
Pueppke SG, Broughton WJ (1999) Rhizobium sp. strain NGR234 and R. fredii USDA257 share exceptionally broad, nested host ranges. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 12:293–318
Rehus BL, Geller DP, Kim JS, Fox JE, Kumar Kolli VS, Pueppke SG (1998) Sinorhizobium fredii and Sinorhizobium meliloti produce structurally conserved lipopolysaccharides and strain-specific K antigens. Appl Environ Microbiol 64, 4930–4938
Rehus BL, Stephens SB, Geller DP, Kim JS, Glenn J, Przytycki J, Ojanen-Rehus T (1999) Epitope identification for a panel of anti-Sinorhizobium meliloti monoclonal antibodies and application to the analysis of K antigens and lipopolisaccharides from bacteroids. Appl Environ Microbiol 65, 5186–5191
Relic B, Perret X, Estrada-García MT, Kopcinska J, Golinowski W, Krishnan HB, Pueppke SG, Broughton WJ (1994) Nod factors of Rhizobium are the key to the legume door. Molec Microbiol 13:171–178
Rodriguez-Navarro DN, Ruiz Sainz JE, Buendia-Claveria AM, Santamaria C, Balatti PA, Krishnan HB, Pueppke SG (1996) Characterization of rhizobia from nodulated soybean [Glycine max (L.) Merr] growing in Vietnam. Syst Appl Microbiol 19, 240–248
Rohlf FJ (1990). NTSYS-pc numerical taxonomy and multivariate system. Version 2.01. Exeter Software, Setauket, New York, USA
Sadowsky, MJ, Keyser HH, and Bohlool BB (1983) Biochemical Characterization of fast- and slow-growing rhizobia that nodulate soybeans. Int J Syst Bacteriol 33:716–722
Sadowsky MJ, Bohlool BB, Keyser HH (1987) Serological relatedness of Rhizobium fredii to other rhizobia and to the bradyrhizobia. Appl Environ Microbiol 53:1785–1789
Sanger F, Nicklen S, Coulson AR (1977) DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74:5463–5467
Scholla MH, Elkan GH (1984) Rhizobium fredii sp. Nov., a fast-growing species that effectively nodulates soybeans. Int J Syst Bacteriol 34:484–486
Selenska-Pobell S (1994) How to monitor released rhizobia. Plant Soil 166, 187–191
Sikora S, Redzepovic S, Pejic I, Kozumplik V (1997) Genetic Diversity of Bradyrhizobium japonicum field population revealed by RAPD fingerprinting. J Appl Microbiol 82:527–531
Stowers MD, Eaglesham ARJ (1984) Physiological and symbiotic characteristics of fast-growing Rhizobium japonicum. Plant Soil 77:3–14
Trinick MJ (1980) Relationships amongst the fast-growing rhizobia of Lablad purpureus, Leucaena leucocephala, Mimosa sp., Acacia farnesiana and Sesbania grandiflora and their affinities with other rhizobial groups. J Appl Bacteriol 49:39–53
Van Berkum P, Kotob SI, Abdel Basit H, Salem S, Gewaily EM, Angle JS (1993) Genotypic diversity among strains of Bradyrhizobium japonicum belonging to serogroup 110. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:3130–313
Van Berkum P, Ruihua F, Campbell TA, Eardly BD (1998) Some issues of relevance in the taxonomy of rhizobia.In: Esperanza Martinez, Hernandez G (eds) Highlights of nitrogen fixation research. Kluwer Academic/Plenum
Videira LB, Pastorino GN, Balatti PA (2001) Incompatibility may not be the rule for Sinorhizobium fredii-soybean interactions. Soil Biol Biochem 33:837–840
Videira LB, Pastorino GN, Martinez-Alcántara V, Balatti PA (2002) Sinorhizobium fredii isolates can be specifically identified by a 260 bp fragment from the nolXWBTUV locus. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 59:265–269
Vincent JM (1970) A manual for the practical study of root nodule bacteria. Blackwell Scientific, Oxford
Vinuesa P, Rademaker JLW, de Bruijn FJ, Werner D (1998) Genotypic characterization of Bradyrhizobium strains nodulating endemic woody legumes of the Canary Islands by PCR-restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of genes encoding 16S rRNA (16S rDNA) and 16S-23S rDNA intergenic spacers repetitive extragenic palindromic PCR genomic fingerprinting and partial 16S rDNA sequencing. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:2096–2104
Wong FYK, Stackebrandt E, Ladha JK, Fleishman DE, Date RA, Fuerst JA (1994) Phylogenetic analysis of Bradyrhizobium japonicum and photosynthetic stem-nodulating bacteria from Aeschynomene species grown in separated geographical regions Appl Environ Microbiol 60:940–946
Young CC, Chang JY, Chao CC (1988) Physiological and symbiotic characteristics of Rhizobium fredii isolated from subtropical-tropical soils. Biol Fert Soils 5:350–354
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dr. S.G. Pueppke for critically reviewing the manuscrip. Gustavo Saldaña was supported by a scholarship funded by the Universidad Nacional de La Plata. Pedro Alberto Balatti and Virginia Martinez Alcántara were supported by CICBA and Universidad Nacional de La Plata. This work was supported by grant PICT97 00679 FONCYT SCyT de la Nación, PIA no. CONICET no. 6809/96, Resolución no. 1015/96, by CICBA Resolución 1104/96 and by the CiCYT grant BIO99-0614-C03 of the Spanish Ministry of Science and Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saldaña, G., Martinez-Alcántara, V., Vinardell, J.M. et al. Genetic diversity of fast-growing rhizobia that nodulate soybean (Glycine max L. Merr). Arch Microbiol 180, 45–52 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-003-0559-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-003-0559-y