Abstract:
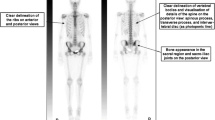
The aim of this study was to evaluate FDG-PET findings in patients with osteoporosis or preclinical osteoporosis and acute vertebral compression fractures in order to determine whether FDG-PET has a value for distinction of pathological from osteoporotic vertebral fractures. 17 patients with a spontaneous compression fracture of the spine were evaluated by bone scanning with Tc-99m HDP, positron emission tomography with fluorine-18 deoxyglucose (FDG-PET) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Osteoporosis had been established in all cases by X-ray and osteodensitometry. PET and bone scan images were scored independently from 0 (no pathological uptake) to 4 (definitive pathological uptake) by two blinded nuclear medicine physicians. The results of the blinded scoring were compared to MRI findings which served as gold standard. In 13 out of 17 patients, MRI demonstrated a vertebral fracture generating from osteoporosis. In 12 of these 13 cases, PET scans were scored with 0 or 1 and categorized as true negative. Standard uptake values (SUV) ranged between 1.1 and 2.4. In one of the 13 patients, PET was interpreted false positive with an uptake score of 3 (SUV = 2.9). Of the 17 patients, MRI revealed a pathological fracture caused by spondylodiscitis in three patients and by plasmacytoma in one patient. In these patients, all PET scans were highly positive with a score of 3 and 4 and SUV values between 3.8 to 9.8. The bone scans of all 17 patients were positive with scores of 3 or 4 but a differentiation between osteoporotic and pathological fractures was not possible. Our preliminary results indicate that acute vertebral fractures that originated from osteoporosis or preclinical osteoporosis tend to have no pathologically increased FDG uptake. Since a high FDG uptake is characteristic for malignant and inflammatory processes, use of FDG-PET may have potential value for differentiation between osteoporotic and pathological vertebral fractures.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 18 October 2001 / Accepted: 25 April 2002
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schmitz, A., Risse, J., Textor, J. et al. FDG-PET Findings of Vertebral Compression Fractures in Osteoporosis: Preliminary Results . Osteoporos Int 13, 755–761 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s001980200103
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s001980200103