Abstract
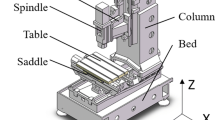
In order to improve machining efficiency and quality of aero-engine blisks, a novel multi-spindle 5-axis machine tool is developed under the inspiration of the blisk structure. The proposed machine contains 8 spindles, which are arranged radially along the blisk and simultaneously participate in machining. The actuator of the machine contains three rotation axes and two translation axes, which can realize 5-axis CNC machining. Based on the unified kinematics model, the mechanism is analyzed in terms of forward and inverse kinematics, singularity, and flexible workspace. Meanwhile, the structural parameters of the machine are optimized according to the flexibility index to improve the kinematic performance of the mechanism. Theoretical and experimental results show that the machine tool has a more compact structure, fewer moving axes, and better kinematics performance, compared with the traditional multi-spindle modular machine tool. Therefore, the machine has significant advantages in processing efficiency and has great application potential in large batch machining of the blisk.
















Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
All data and materials generated or analyzed during this study are included in this manuscript.
References
González-Barrio H, Calleja-Ochoa A, Lamikiz A, Lacalle LNLD (2020) Manufacturing processes of integral blade rotors for turbomachinery, processes and new approaches. Appl Sci 10(9):3063
Fan H, Xi G, Wang W, Cao Y (2016) An efficient five-axis machining method of centrifugal impeller based on regional milling. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 87(1–4):789–799
Fan C, Xue C, Zhang L, Wang K, Wang Q, Gao Y, Lu L (2021) Design and control of the belt-polishing tool system for the blisk finishing process. Mech Sci 12(1):237–248
Ji Y, Wang X, Liu Z, Wang H, Wang K, Wang D (2019) Stability prediction of five-axis ball-end finishing milling by considering multiple interaction effects between the tool and workpiece. Mech Syst Signal Process 131:261–287
Liu Y, Wan M, Xing W, Zhang W (2018) Identification of position independent geometric errors of rotary axes for five-axis machine tools with structural restrictions. Robot Comput Integr Manuf 53:45–57
Ibaraki S, Okumura R (2021) A machining test to evaluate thermal influence on the kinematics of a five-axis machine tool. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 163:103702
Sun S, Altintas Y (2021) A G(3) continuous tool path smoothing method for 5-axis CNC machining. CIRP J Manuf Sci Technol 32:529–549
Hu Q, Chen Y, Yang J (2020) On-line contour error estimation and control for corner smoothed five-axis tool paths. Int J Mech Sci 171:105377
Xin H, Shi Y, Zhao T (2018) Compound efficient and powerful milling machine tool of blisk. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 98(5–8):1745–1753
Gao S, Chen J, Liu S, Yuan X, Hu P, Yang J (2019) Design and kinematic analysis of a novel machine tool with four rotational axes and one translational axis. J Manuf Sci Eng Trans ASME 141(11):111009
Zhang D, Xu Y, Yao J, Zhao Y (2018) Design of a novel 5-DOF hybrid serial-parallel manipulator and theoretical analysis of its parallel part. Robot Comput Integr Manuf 53:228–239
Lai Y, Liao C, Chao Z (2018) Inverse kinematics for a novel hybrid parallel serial five-axis machine tool. Robot Comput Integr Manuf 50:63–79
Lu S, Li Y, Ding B (2020) Kinematics and dynamics analysis of the 3PUS-PRU parallel mechanism module designed for a novel 6-DOF gantry hybrid machine tool. J Mech Sci Technol 34(1):345–357
Dantam NT (2021) Robust and efficient forward, differential, and inverse kinematics using dual quaternions. Int J Robot Res 40(10–11):1087–1105
My CA, Bohez ELJ (2019) A novel differential kinematics model to compare the kinematic performances of 5-axis CNC machines. Int J Mech Sci 163:105117
Zhong G, Wang C, Yang S, Zheng E, Ge Y (2015) Position geometric error modeling, identification and compensation for large 5-axis machining center prototype. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 89:142–150
Lasemi A, Xue D, Gu P (2016) Accurate identification and compensation of geometric errors of 5-axis CNC machine tools using double ball bar. Meas Sci Technol 27(5):055004
Ding S, Huang X, Yu C, Wang W (2016) Actual inverse kinematics for position-independent and position-dependent geometric error compensation of five-axis machine tools. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 111:55–62
Yang B, Zhang G, Ran Y, Yu H (2019) Kinematic modeling and machining precision analysis of multi-axis CNC machine tools based on screw theory. Mech Mach Theory 140:538–552
Borges DS, Joo V, Simoni R, Carboni AP, Martins D (2020) A new method for type synthesis of parallel mechanisms using screw theory and features of genetic algorithms. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng 42(12):615
Carboni AP, Simas H, Martins D (2020) Actuation scheme enumeration and optimal selection for parallel mechanisms based on matroid theory. Mech Mach Theory 151:103891
Tang T, Fang H, Zhang J (2020) Hierarchical design laboratory prototype fabrication and machining tests of a novel 5-axis hybrid serial-parallel kinematic machine tool. Robot Comput Integr Manuf 64:101944
Zhao Y, Mei J, Jin Y, Niu M (2021) A new hierarchical approach for the optimal design of a 5-dof hybrid serial-parallel kinematic machine. Mech Mach Theory 156:104160
Wu M, Zhang Y, Yue X, Lv D, Chen M, Wang X, Zhang J (2021) Optimal design of an asymmetrical parallel mechanism. Proc Inst Mech Eng C-J Mech Eng Sci 235(23):6922–6939
Xu R, Luo J, Wang M (2020) Kinematic and dynamic manipulability analysis for free-floating space robots with closed chain constraints. Robot Auton Syst 130:103548
González H, Calleja A, Pereira O, Ortega N, López DLL, Barton M (2018) Super abrasive machining of integral rotary components using grinding flank tools. Metals 8(1):24
Funding
This work is supported by the National Science and Technology Major Project of the Ministry of Science and Technology of China [grant number 2018ZX04004001].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Shuai Chen: conceptualization, methodology, software, validation, writing-original draft. Zhi-tong Chen: conceptualization, writing-review and editing, project administration, funding acquisition. Chuan-hui Cui: investigation, validation, resources. Chuan-rui Si: software, programming. Huan Ye: validation, resources.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent ofr publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, S., Chen, Z., Cui, C. et al. Hierarchical design, dimensional synthesis, and prototype validation of a novel multi-spindle 5-axis machine tool for blisk machining. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 126, 4213–4224 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-023-11260-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-023-11260-0