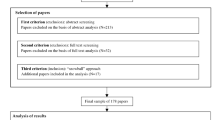
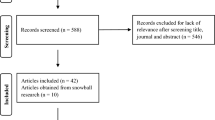
Abstract
This study empirically investigates the effects of sustainable manufacturing practices on sustainable performance, focusing on the moderation effect of companies’ ownership (foreign or local) between sustainable manufacturing practices and sustainable performance. In this study, a survey was conducted among ISO 4001-certified manufacturers in Malaysia, and structural equation modelling was used to examine the moderating effect of a company’s ownership on the relationship between sustainable manufacturing practices and sustainable performance. The findings showed that there was a positive relationship between both sustainable product design and sustainable manufacturing processes and sustainable performance for Malaysian manufacturers. However, the positive relationship between both sustainable product design and sustainable end-of-life practices on sustainable performance was stronger for foreign companies compared with that for local companies. The results showed the strengths of foreign-owned companies were at the implementation of their sustainable product design and sustainable end-of-life management practices of the product manufacturing process. The findings identified in this paper extend previous research and provide empirical evidence that a company’s ownership impacts the relationship between sustainable manufacturing practices and sustainable performance.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Malaysian Department of Statitistics (2020) Compendium of Environment Statistics. Malaysian Department of Statitistics
Hossan Chowdhury MM, Quaddus MA (2021) Supply chain sustainability practices and governance for mitigating sustainability risk and improving market performance: A dynamic capability perspective. J Clean Prod 278:123521
MITI (2020) Dasar Automotif Negara 2020. Ministry of International Trade and Industry: https://www.miti.gov.my/
Huang A, Badurdeen F (2018) Metrics-based approach to evaluate sustainable manufacturing performance at the production line and plant levels. J Clean Prod 192:462–476
Bhanot N, Rao PV, Deshmukh S (2017) An integrated approach for analysing the enablers and barriers of sustainable manufacturing. J Clean Prod 142:4412–4439
Abdul Rashid SH, Evans S, Longhurst P (2008) A comparison of four sustainable manufacturing strategies. Int J Sustain Eng 1(3):214–229
Mangla SK, Govindan K, Luthra S (2017) Prioritizing the barriers to achieve sustainable consumption and production trends in supply chains using fuzzy analytical hierarchy process. J Clean Prod 151:509–525
Rosen MA, Kishawy HA (2012) Sustainable manufacturing and design: concepts, practices and needs. Sustainability 4(2):154–174
Wu Z, Pagell M (2011) Balancing priorities: Decision-making in sustainable supply chain management. J Oper Manag 29(6):577–590
Millar HH, Russell SN (2011) The adoption of sustainable manufacturing practices in the Caribbean. Bus Strateg Environ 20(8):512–526
Shankar KM, Kannan D, Kumar PU (2017) Analyzing sustainable manufacturing practices–a case study in Indian context. J Clean Prod 164:1332–1343
Aboelmaged M (2018) The drivers of sustainable manufacturing practices in Egyptian SMEs and their impact on competitive capabilities: a PLS-SEM model. J Clean Prod 175:207–221
Rusinko C (2007) Green manufacturing: an evaluation of environmentally sustainable manufacturing practices and their impact on competitive outcomes. IEEE Trans Eng Manage 54(3):445–454
Ahmed W, Najmi A (2018) Developing and analyzing framework for understanding the effects of GSCM on green and economic performance: perspective of a developing country. Manag Environ Qua: An Int J
Green KW et al (2012) Green supply chain management practices: impact on performance. Supply Chain Manag: An Int J
Klassen RD, McLaughlin CP (1996) The impact of environmental management on firm performance. Manage Sci 42(8):1199–1214
Montabon F, Sroufe R, Narasimhan R (2007) An examination of corporate reporting, environmental management practices and firm performance. J Oper Manag 25(5):998–1014
Hintošová Aneta B, Kubíková Z (2016) The effect of the degree of foreign ownership on firms' performance. Rev Econ Perspect 16(1):29–44
Gu VC, Cao RQ, Wang J (2019) Foreign ownership and performance: mediating and moderating effects. Rev Int Bus Strat
Balasubramanian S et al (2021) Do firm characteristics affect environmental sustainability? A literature review-based assessment. Bus Strateg Environ 30(2):1389–1416
Luken R, Van Rompaey F, Zigova K (2008) The determinants of EST adoption by manufacturing plants in developing countries. Ecol Econ 66(1):141–152
Ye F et al (2013) The impact of institutional pressures, top managers’ posture and reverse logistics on performance—Evidence from China. Int J Prod Econ 143(1):132–143
KeTTHA(2017) Green Technology Master Plan Malaysia 2017–2030 (GTMP), G.T.a.W.K. Ministry of Energy, Ed.: Putrajaya, Malaysia
Elkington J (1998) Partnerships from cannibals with forks: the triple bottom line of 21st-century business. Environ Qual Manage 8(1):37–51
United States Department of Commerce (2009) Sustainable manufacturing initiative and public‐private dialogue., I.T. Administration, Ed
Siemieniuch C, Sinclair M, Henshaw Md (2015) Global drivers, sustainable manufacturing and systems ergonomics. Appl Ergonom 51:104–119
Jayal A et al (2010) Sustainable manufacturing: modeling and optimization challenges at the product, process and system levels. CIRP J Manuf Sci Technol 2(3):144–152
Kishawy HA, Hegab H, Saad E (2018) Design for sustainable manufacturing: Approach, implementation, and assessment. Sustainability 10(10):3604
Jawahir I, Badurdeen F, Rouch K (2013) Innovation in sustainable manufacturing education. https://doi.org/10.14279/depositonce-3753
Veleva V et al (2001) Indicators of sustainable production. J Clean Prod 9(5):447–452
Duflou JR et al (2012) Towards energy and resource efficient manufacturing: a processes and systems approach. CIRP Ann 61(2):587–609
Ghazilla RAR et al (2015) Design for environment and design for disassembly practices in Malaysia: a practitioner’s perspectives. J Clean Prod 108:331–342
Worrell E, Allwood J, Gutowski T (2016) The role of material efficiency in environmental stewardship. Annu Rev Environ Resour 41:575–598
Pajunen N et al (2012) Drivers and barriers of effective industrial material use. Miner Eng 29:39–46
Sabbaghi M et al (2016) Business outcomes of product repairability: a survey-based study of consumer repair experiences. Resour Conserv Recycl 109:114–122
Desai A, Mital A (2006) Design for maintenance: basic concepts and review of literature. Int J Prod Dev 3(1):77–121
Manzini E, Vezzoli C (2003) A strategic design approach to develop sustainable product service systems: examples taken from the ‘environmentally friendly innovation’Italian prize. J Clean Prod 11(8):851–857
Hirschl B, Konrad W, Scholl G (2003) New concepts in product use for sustainable consumption. J Clean Prod 11(8):873–881
Sakundarini N et al (2013) Optimal multi-material selection for lightweight design of automotive body assembly incorporating recyclability. Mater Des 50:846–857
Vezzoli C (2018) Minimising energy consumption. design for environmental sustainability. Springer, pp 75–91
Ahmad S et al (2018) Sustainable product design and development: a review of tools, applications and research prospects. Resour Conserv Recycl 132:49–61
Le Bourhis F et al (2013) Sustainable manufacturing: evaluation and modeling of environmental impacts in additive manufacturing. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology 69(9–12):1927–1939
Lovins AB, Lovins LH, Hawken P (2007), A road map for natural capitalism. Understand Bus: Environ p. 250–63
Gupta K et al (2016) Recent developments in sustainable manufacturing of gears: a review. J Clean Prod 112:3320–3330
Thiede S, Bogdanski G, Herrmann C (2012) A systematic method for increasing the energy and resource efficiency in manufacturing companies. Procedia CIRP 2:28–33
Gupta S et al (2015) Analytic hierarchy process (AHP) model for evaluating sustainable manufacturing practices in Indian electrical panel industries. Procedia Soc Behav Sci 189:208–216
Singh S, Ramakrishna S, Gupta MK (2017) Towards zero waste manufacturing: a multidisciplinary review. J Clean Prod 168:1230–1243
Bi Z, Wang L (2012) Optimization of machining processes from the perspective of energy consumption: a case study. J Manuf Syst 31(4):420–428
Raman AS et al (2020) Defining near-term to long-term research opportunities to advance metrics, models, and methods for smart and sustainable manufacturing. Smart Sustain Manufact Syst 4(2)
Miller G, Pawloski J, Standridge CR (2010) A case study of lean, sustainable manufacturing. J Indust Eng Manag (JIEM) 3(1):11–32
Ramanathan R et al (2017) Environmental regulations, innovation and firm performance: a revisit of the Porter hypothesis. J Clean Prod 155:79–92
Hamner B (2006) Effects of green purchasing strategies on supplier behaviour. Greening the supply chain. Springer, pp 25–37
Bocken N et al (2019) A review and evaluation of circular business model innovation tools. Sustainability 11(8):2210
Katiyar R et al (2018) Impact of sustainability and manufacturing practices on supply chain performance: findings from an emerging economy. Int J Prod Econ 197:303–316
Seuring S, Müller M (2008) From a literature review to a conceptual framework for sustainable supply chain management. J Clean Prod 16(15):1699–1710
Zailani S et al (2012) Sustainable supply chain management (SSCM) in Malaysia: a survey. Int J Prod Econ 140(1):330–340
Sonneveld K et al (2005) Sustainable packaging: how do we define and measure it. in 22nd IAPRI Symposium
James K et al (2005) Sustainable packaging systems development, in Handbook of sustainability research. RMIT University. p. 371–407
Westkämper E, Alting L, Arndt G (2001) Life cycle management and assessment: approaches and visions towards sustainable manufacturing. Proc Inst Mech EngPart B: J Eng Manuf 215(5):599–626
Çankaya SY, Sezen B (2019) Effects of green supply chain management practices on sustainability performance. J Manufac Technol Manag
Kam BH et al (2006) Strategic business operations, freight transport and eco-efficiency: a conceptual model. Greening the supply chain. Springer, pp 103–115
Sachs W (2006) Transcript of the lecture on: can globalisation become a driver for sustainable development. Wuppertal Institute
Vachon S, Klassen RD (2006) Extending green practices across the supply chain: the impact of upstream and downstream integration. Int J Opera Prod Manag
Walton SV, Handfield RB, Melnyk SA (1998) The green supply chain: integrating suppliers into environmental management processes. Int J Purch Mater Manag 34(1):2–11
Rao P (2002) Greening the supply chain: a new initiative in South East Asia. Int J Opera Prod Manag
Canning L, Hanmer-Lloyd S (2001) Managing the environmental adaptation process in supplier–customer relationships. Bus Strateg Environ 10(4):225–237
Rose CM, Stevels A, Ishii K (2000) A new approach to end-of-life design advisor (ELDA). in Proc 2000 IEEE Int Sympos Electron Environ (Cat. No. 00CH37082)
Jackson T (2013) Material concerns: pollution, profit and quality of life. Routledge
Jackson T (1996) Material concerns: pollution, profit, and quality of life. Psychology Press
De Brito MP, Dekker R (2004) A framework for reverse logistics. Reverse logistics. Springer, pp 3–27
Famiyeh S, Kwarteng A, Asante-Darko D (2018) Service quality, customer satisfaction and loyalty in automobile maintenance services: evidence from a developing country. J Qua Maintenance Eng
Choi D, Hwang T (2015) The impact of green supply chain management practices on firm performance: the role of collaborative capability. Oper Manag Res 8(3):69–83
Kleyner A, Sandborn P (2008) Minimizing life cycle cost by managing product reliability via validation plan and warranty return cost. Int J Prod Econ 112(2):796–807
Lee S-C, Na S-I (2010) E-waste recycling systems and sound circulative economies in East Asia: A comparative analysis of systems in Japan, South Korea China and Taiwan. Sustainability 2(6):1632–1644
Koberg E, Longoni A (2019) A systematic review of sustainable supply chain management in global supply chains. J Clean Prod 207:1084
Abdullah R, Mohamad MN, Thurasamy R (2020) Enhancing sustainable performance through green supply chain management practices: a study of Malaysian manufacturing firms. Religación 5:163–170
Eltayeb TK, Zailani S, Ramayah T (2011) Green supply chain initiatives among certified companies in Malaysia and environmental sustainability: investigating the outcomes. Resour Conserv Recycl 55(5):495–506
Eltayeb TK, Zailani S, Filho WL (2010) Green business among certified companies in Malaysia towards environmental sustainability: benchmarking on the drivers, initiatives and outcomes. Int J Environ Technol Manage 12(1):95–125
Wagner M (2005) How to reconcile environmental and economic performance to improve corporate sustainability: corporate environmental strategies in the European paper industry. J Environ Manage 76(2):105–118
Zaid AA, Jaaron AAM, Talib Bon A (2018) The impact of green human resource management and green supply chain management practices on sustainable performance: an empirical study. J Clean Prod 204:965–979
Malek J, Desai TN (2020) A systematic literature review to map literature focus of sustainable manufacturing. J Clean Prod 256:120345
Zhu Q, Sarkis J, Lai K-H (2008) Confirmation of a measurement model for green supply chain management practices implementation. Int J Prod Econ 111(2):261–273
Zhu Q, Sarkis J (2004) Relationships between operational practices and performance among early adopters of green supply chain management practices in Chinese manufacturing enterprises. J Oper Manag 22(3):265–289
Maxwell D, Sheate W, Van Der Vorst R (2006) Functional and systems aspects of the sustainable product and service development approach for industry. J Clean Prod 14(17):1466–1479
Geyer R, Jackson T (2004) Supply loops and their constraints: the industrial ecology of recycling and reuse. Calif Manage Rev 46(2):55–73
Yawar SA, Seuring S (2017) Management of social issues in supply chains: a literature review exploring social issues, actions and performance outcomes. J Bus Ethics 141(3):621–643
Handfield RB et al (2001) Integrating environmental concerns into the design process: the gap between theory and practice. IEEE Trans Eng Manage 48(2):189–208
Dornfeld DA (2014) Moving towards green and sustainable manufacturing. Int J Precis Eng Manuf-Green Technol 1(1):63–66
Smith L, Ball P (2012) Steps towards sustainable manufacturing through modelling material, energy and waste flows. Int J Prod Econ 140(1):227–238
Yusoff RBM et al (2016) Investigating the relationship of employee empowerment and sustainable manufacturing performance. Int Rev Manag Mark 6(4):284–290
Pigosso DC et al (2010) Ecodesign methods focused on remanufacturing. J Clean Prod 18(1):21–31
Jensen MC, Meckling WH (1976) Theory of the firm: managerial behaviour, agency costs and ownership structure. J Financ Econ 3(4):305–360
Fama EF, Jensen MC (1983) Separation of ownership and control. J Law Econ 26(2):301–325
Yudaeva K et al (2003) Does foreign ownership matter? The Russian experience Economics of transition 11(3):383–409
Shrivastav SM, Kalsie A (2017) The relationship between foreign ownership and firm performance in India: an empirical analysis. Artha Vijnana 59(2):152–162
Jusoh MA (2015) Foreign ownership and firm performance: evidence from Malaysia. Asian J Account Govern 6
Nguyen TXH et al (2020) The impact of foreign ownership and management on firm performance in Vietnam. J Asian Finance Econ Bus 7(9):409–418
Dharwadkar B, George G, Brandes P (2000) Privatization in emerging economies: an agency theory perspective. Acad Manag Rev 25(3):650–669
Rustam A, Wang Y, Zameer H (2019) Does foreign ownership affect corporate sustainability disclosure in Pakistan? A sequential mixed methods approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(30):31178–31197
Omair Alotaibi K, Hussainey K (2016) Determinants of CSR disclosure quantity and quality: evidence from non-financial listed firms in Saudi Arabia. Int J Disclos Govern 13(4):364–393
Khaled R, Ali H, Mohamed EK (2021) The sustainable development goals and corporate sustainability performance: mapping, extent and determinants. J Clean Prod 311:127599
Dries L et al (2014) Supply chain relationships, supplier support programmes and stimulating investment: evidence from the Armenian dairy sector. Supply Chain Manag: An Int J
Li S et al (2006) The impact of supply chain management practices on competitive advantage and organizational performance. Omega 34(2):107–124
Bryman A (2016) Social research methods. Oxford university press
Batista-Foguet JM et al (2009) Effect of response scale on assessment of emotional intelligence competencies. Personality Individ Differ 46(5–6):575–580
Ringle CM, Wende S, Becker J-M (2015) SmartPLS 3. Boenningstedt: SmartPLS GmbH
Hair JF, Jr., Howard MC, Nitzl C (2020) Assessing measurement model quality in PLS-SEM using confirmatory composite analysis. J Bus Res 109:101–110
Kock N, Lynn G (2012) Lateral collinearity and misleading results in variance-based SEM: an illustration and recommendations. J Assoc Inform Syst 13(7)
Kock N (2015) Common method bias in PLS-SEM: a full collinearity assessment approach. Int J e-Collaboration (ijec) 11(4):1–10
Ramayah T et al (2018) Partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM) using smartPLS 3.0. Kuala Lumpur: Pearson
Henseler J, Ringle CM, Sarstedt M (2015) A new criterion for assessing discriminant validity in variance-based structural equation modeling. J Acad Mark Sci 43(1):115–135
Franke G, Sarstedt M (2019) Heuristics versus statistics in discriminant validity testing: a comparison of four procedures. Internet Res
Shmueli G et al (2019) Predictive model assessment in PLS-SEM: guidelines for using PLSpredict. Eur J Market
Ar IM (2012) The impact of green product innovation on firm performance and competitive capability: the moderating role of managerial environmental concern. Procedia Soc Behav Sci 62:854–864
Kushwaha GS, Sharma NK (2016) Green initiatives: a step towards sustainable development and firm’s performance in the automobile industry. J Clean Prod 121:116–129
Camisón C, Villar-López A (2014) Organizational innovation as an enabler of technological innovation capabilities and firm performance. J Bus Res 67(1):2891–2902
Zeng S et al (2010) Impact of cleaner production on business performance. J Clean Prod 18(10–11):975–983
Ghadimi P, Heavey C (2014) Sustainable supplier selection in medical device industry: toward sustainable manufacturing. Procedia Cirp 15:165–170
Tan CL et al (2016) The impact of green supply chain management practices on firm competitiveness. International Journal of Business Innovation and Research 11(4):539–558
Kirchoff JF, Koch C, Nichols BS (2011) Stakeholder perceptions of green marketing: the effect of demand and supply integration. Int J Phys Distribut Logist Manag
Khor KS, Udin ZM (2013) Reverse logistics in Malaysia: investigating the effect of green product design and resource commitment. Resour Conserv Recycl 81:71–80
Ghazilla RAR et al (2015) Drivers and barriers analysis for green manufacturing practices in Malaysian SMEs: a preliminary findings. in Procedia CIRP
Taha Z, Sakundarini N, Ghazila RAR, Gonzales J (2010) Eco design in Malaysian industries: challenges and opportunities. J Appl Sci Res 6(12):2143–2150
Mohamad-Ali N et al (2018) End-of-life vehicle recovery factors: Malaysian stakeholders’ views and future research needs. Sustain Dev 26(6):713–725
Zsidisin GA, Siferd SP (2001) Environmental purchasing: a framework for theory development. Eur J Purchas Supply Manag 7(1):61–73
Kara S, Li W (2011) Unit process energy consumption models for material removal processes. CIRP Ann 60(1):37–40
Zhu Q, Sarkis J, Lai K-H (2007) Green supply chain management: pressures, practices and performance within the Chinese automobile industry. J Clean Prod 15(11–12):1041–1052
Baines TS et al (2007) State-of-the-art in product-service systems. Proc Insti Mech Engi Part B: J Eng Manuf 221(10):1543–1552
Lee S, Lye S, Khoo M (2001) A multi-objective methodology for evaluating product end-of-life options and disassembly. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 18(2):148–156
Despeisse M et al (2012) The emergence of sustainable manufacturing practices. Prod Plan Control 23(5):354–376
Ball PD et al (2009) Zero carbon manufacturing facility—towards integrating material, energy, and waste process flows. Proc Inst Mech Eng, Part B: J Eng Manuf 223(9):1085–1096
Rachuri S, Sriram RD, Sarkar P (2009) Metrics, standards and industry best practices for sustainable manufacturing systems. in 2009 IEEE Int Conf Automat Sci Eng
Masnita Y, Triyowati H, Rasyawal M (2017) Supply chain practices impact on supplier performance: the mediating role of market-based and operational performance. Int J Appl Bus Econ Res 15(8):209–221
Seliger G (2007) Sustainability in manufacturing. Recover Resourc Prod Mater Cycles
Fiksel J (2009) Design for environment: a guide to sustainable product development. McGraw-Hill Education
Frios MM (1999) The real value of by-product exchange. Business and Economics 6(1):7–8
Garetti M, Taisch M (2012) Sustainable manufacturing: trends and research challenges. Produ Plan Control 23(2–3):83–104
Evans S et al (2009) Towards a sustainable industrial system: with recommendations for education, research, industry and policy. University of Cambridge, Institute for Manufacturing
Yang MGM, Hong P, Modi SB (2011) Impact of lean manufacturing and environmental management on business performance: an empirical study of manufacturing firms. Int J Prod Econ 129(2):251–261
Jeswiet J, Kara S (2008) Carbon emissions and CES™ in manufacturing. CIRP Ann 57(1):17–20
Luken R, Van Rompaey F (2008) Drivers for and barriers to environmentally sound technology adoption by manufacturing plants in nine developing countries. J Clean Prod 16(1):S67–S77
Jayaraman V, Singh R, Anandnarayan A (2012) Impact of sustainable manufacturing practices on consumer perception and revenue growth: an emerging economy perspective. Int J Prod Res 50(5):1395–1410
Rao P, Holt D (2005) Do green supply chains lead to competitiveness and economic performance? Int J Opera Prod Manag
Smith AD (2005) Reverse logistics programs: gauging their effects on CRM and online behavior. Vine
Porter ME, Van der Linde C (1995) Toward a new conception of the environment-competitiveness relationship. Journal of economic perspectives 9(4):97–118
Yi-Chan C, Tsai C-H (2007) The effect of green design activities on new product strategies and performance: an empirical study among high-tech companies. Int J Manag 24(2):276
Carter CR, Kale R, Grimm CM (2000) Environmental purchasing and firm performance: an empirical investigation. Transport Res Part E: Logist Transport Rev 36(3):219–228
Funding
This work was supported by the Ministry of Higher Education Malaysia through the Fundamental Research Grant Scheme (FRGS) (grant no.: FRGS/2/2010/TK/UM/03/6).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Salwa Hanim Abdul-Rashid, Novita Sakundarini, Raja Ariffin Raja Ghazilla, Ramayah Thrusamay, and Marini Nurbanum. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Salwa Hanim Abdul-Rashid, Marini Nurbanum, and Ramayah Thurasamy, and the rest of the authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendices
Appendix 1 Constructs and measurement items for SM practices
Constructs | Codes | Measurement items | Sources |
|---|---|---|---|
Sustainable product design (SPDesign) | SPDesign_1 | Elimination of hazardous materials | |
SPDesign_2 | Design for disassembly | ||
SPDesign_3 | Design for repair, rework, and refurbishment | ||
SPDesign_4 | Design to reduce material use | ||
SPDesign_5 | Design to reduce energy consumption | ||
SPDesign_6 | Use environmental-friendly materials | ||
SPDesign_7 | Design to recover obsolete products (e.g. product leasing/PSS) | ||
SPDesign_8 | Design for maintenance | ||
SPDesign_9 | Design to prolong life of materials | ||
Sustainable manufacturing process (SMProcess) | SMProcess_1 | Material recovery | Thiede, Bogdanski [45], Gupta, Dangayach [46], Singh, Ramakrishna [47] |
SMProcess_2 | Waste recovery | ||
SMProcess_3 | Energy savings | Bhanot, Rao [5], Gupta, Laubscher [44], Despeisse, Mbaye [130] | |
SMProcess_4 | Reduce CO2 emissions | Ball, Evans [131] | |
SMProcess_5 | Improve manufacturing processes and machine efficiency | Millar and Russell [10], Bi and Wang [48], Raman, Haapala [49] | |
SMProcess_6 | Adopt lean production systems | ||
SMProcess_7 | Implement and adhere to environmentally conscious programmes, standards, or regulations | ||
SMProcess_8 | Set environmental objectives and targets | Hamner [52] | |
SMProcess_9 | Measure and audit material flows/wastes | ||
Sustainable supply chain management (SSCM) | SSCM_1 | Select green/sustainable suppliers | |
SSCM_2 | Influence suppliers to practise green/sustainable initiatives | ||
SSCM_3 | Collaborate with suppliers | ||
SSCM_4 | Training suppliers on sustainability | ||
SSCM_5 | Influence customers to accept green practices, services, or products | Canning and Hanmer‐Lloyd [66] | |
SSCM_6 | Use less, cleaner, or reusable packaging | Zailani, Jeyaraman [56], Sonneveld, James [57], James, Lewis [58], Westkämper, Alting [59] | |
SSCM_7 | Adopt energy-efficient transportation | Kam, Christopherson [61] | |
SSCM_8 | Adopt energy-efficient logistics | Kam, Christopherson [61] | |
Sustainable end-of-life management (SEOL) | SEOL_1 | Prolong the service life of materials/parts/products by providing maintenance and support services to customers | |
SEOL_2 | Provide hazardous waste treatment in the plant for after-market recovery products/parts | ||
SEOL_3 | Provide and manage product warranty returns | Kleyner and Sandborn [73] | |
SEOL_4 | Provide and manage product recalls | * | |
SEOL_5 | Provide recycling support by using components and material coding standards |
Appendix 2 Constructs and measurement items for SP
Constructs | Codes | Measurement items | Sources |
|---|---|---|---|
Environmental performance (SPEnv) | SPEnv1 | Reduced CO2 emissions | Garetti and Taisch [137] |
SPEnv2 | Reduced wastewater discharge | ||
SPEnv3 | Reduced solid waste generation | Sachs [62] | |
SPEnv4 | Reduced energy consumption | ||
SPEnv5 | Reduced toxic/harmful/hazardous/flammable substances discharges | ||
SPEnv6 | Decrease in material usage | Jeswiet and Kara [140] | |
SPEnv7 | Improved compliance with environmental standards | ||
Economic performance (SPEco) | Economic outcomes | ||
SPEco1 | Improved market share | ||
SPEco2 | Improved company image | ||
SPEco3 | Improved company’s position in the marketplace | ||
SPEpo4 | Increased profitability | Wagner [79] | |
Operational outcomes | |||
SPEco5 | Decreased material purchasing cost | Eltayeb, Zailani [77] | |
SPEco6 | Decreased utility bills | ||
SPEco7 | Decreased waste treatment fees | ||
SPEcop8 | Decreased waste discharge fees | ||
SPEco9 | Reduced environmental accident cases | ||
SPEco10 | Reduced manufacturing costs | ||
SPEcoc11 | Improved product quality | ||
Social performance (SPso) | SPSo1 | Improved relationship with the community and stakeholders | Maxwell, Sheate [84] |
SPSo2 | Improved work safety | Geyer and Jackson [85] | |
SPSo3 | Improved work environment | Kishawy, Hegab [28], Maxwell, Sheate [84], Geyer and Jackson [85] | |
SPSo4 | Improved living quality of the surrounding community | Maxwell, Sheate [84] | |
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Abdul-Rashid, S.H., Mohamad, M.N., Sakundarini, N. et al. Modelling sustainable manufacturing practices effects on sustainable performance: the contingent role of ownership. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 122, 3997–4012 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-022-10140-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-022-10140-3