Abstract
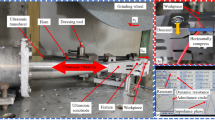
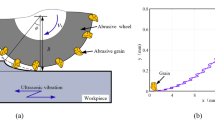
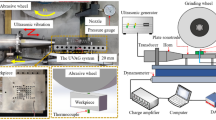
Hardened 12Cr2Ni4A is a kind of high-quality alloy steel material. Due to the comprehensive excellent mechanical properties of high strength, high hardness, good toughness, and good wear resistance, it is widely used to manufacture various mechanical structural parts, such as gears, worm gears, worms, shafts, etc. In order to ameliorate the stress state of the workpiece surface after ordinary grinding (OG) and improve the fatigue life of the workpiece. In view of the effect of grinding heat on surface residual stress, a mathematical model of surface residual stress of hardened 12Cr2Ni4A alloy steel by ultrasonic vibration-assisted ELID grinding (UVAEG) was established and verified by experiments. Ordinary grinding, ultrasonic vibration-assisted grinding (UVAG), and ultrasonic vibration-assisted ELID grinding were used to machine hardened 12Cr2Ni4A alloy steel. The stress state of the machined surface under different grinding methods is explored, and the influence of different parameters on the residual stress on the surface of the workpiece with ultrasonic vibration-assisted ELID grinding is analyzed. The experimental results show that the influence of grinding depth, ultrasonic amplitude, and duty cycle on the residual stress on the surface of the workpiece is basically consistent with the established residual stress model, which confirm the validity of the model. The residual compressive stress on the surface of ultrasonic vibration ELID grinding increases with the increase of ultrasonic amplitude and duty cycle, and shows a decreasing trend with the increase of grinding depth.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Zhang Q, Xu FX, Liu YH (2014) Research on reducing the core hardness of 12Cr2Ni4A after carburizing. Sci Technol Enterp 08:301
Liu WB (2015) Failure analysis and prevention of 12Cr2Ni4A transmission gear. Fail Anal Prev 10(1):31–35
Yu XM, Feng LC, Wang H, He YQ (2015) Fracture failure analysis of 12Cr2Ni4A steel gear. Metal Heat Treat 40(11):191–194
Wang YZ, Wang D (2019) Experimental study on heat treatment process optimization of aviation gears. Mech Des Manuf 338(04):197–199 + 203
Fang SX, Zhao HL, Zhang QJ (2017) The application status and development trend of ultrasonic machining technology. Chinese Journal of. Mech Eng 53(19):22–32
Guan JL, Yang YL, Sun ZJ, Zhao ZQ, Shu XJ (2009) study on ELID grinding of stainless steel. Modern. Manuf Eng 10:17–18
Ning SK, Ke L (2014) Research on ELID grinding process control. Mech Res Appl 000(001):60–61
Yao JG, Ning X, Wang ZK, Su JX (2014) Surface residual stress of nano ZrO2 Ceramics after ultrasonic assisted grinding. Mech Eng Mater 38(02):90–92
He YH, Tang C, Tang JY, Zhou Q (2017) Modeling of surface residual stress in axial ultrasonic vibration assisted grinding. Vibr Shock 36(22):185–191
Zhang J, Pei HJ, Wang GC (2018) Effect of grinding parameters on residual stress in hardened layer of 42CrMo steel. Metal Heat Treat 043(009):238–241
He Y, Xiao GJ, Li W, Huang Y (2018) Residual stress of a TC17 titanium alloy after belt grinding and its impact on the fatigue life. Materials 11(11)
Li YQ, Xiao G, Li T (2019) Surface residual stress of GCr15 bearing steel assisted by ultrasonic vibration grinding. Mater Mech Eng 43(06):50–52
Wang YZ, Chu XM, Huang YZSGY, Liu DW (2019) Surface residual stress distribution for face gear under grinding with a long-radius disk wheel. Int J Mech Sci 159:260–266
Shi XL, Xiu SC, Su HL (2019) Residual stress model of pre-stressed dry grinding considering coupling of thermal, stress, and phase transformation. Adv Manuf 7(4):401–410
Yi J, Jin T, Deng ZH, Zhou W (2019) Estimation of residual stresses in gear form grinding using finite element analysis and experimental study based on grinding force and heat flux distribution models. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 104(1-4):849–866
Florian B, Heiner M, Carsten H, Daniel M, Jeremy E (2020) Development of surface residual stress and surface state of 42CrMo4 in multistage grinding. Procedia CIRP 87(C):198–203
Han JF, Liang JH, Li J, Tang J (2020) Research on the surface residual stress of GH4169 superalloy specimen during forming and grinding. Equip Manuf Technol (03):137–138+142
Xiang DH, Niu XX, Li ZD, Liu ZY, Feng HR, Wu BF, Chen YB (2020) Experimental study on the surface quality of hardened 42CrMo steel with ultrasonic assisted grinding. J Henan Univ Technol (Nat Sci Ed) 39(05):73–79
Huang Y, Liu SA, Xiao GJ, He Y, Dai WT (2020) Prediction of surface residual stress on titanium alloy generated by belt grinding using molecular system dynamics. Procedia CIRP 87(C):480–484
Liu WX (2005) Experimental study on surface residual stress of nano-structured WC/12Co coating material. Hunan University
Zhao B, Liu Z, Zheng YY, Bian PY (2014) Research on grinding force model of ultrasonic ELID compound grinding. Aerospace Mater Technol 44(04):31–35
Li LJ, Fu JC (1979) Research on the mathematical model of grinding force. J Hunan Univ Nat Sci Ed 03:49–60
Shao SJ, Zhao B, Bian PY (2016) Research on the characteristics of oxide film of nano-ceramic ultrasonic ELID composite surface grinding based on workpiece vibration. J Synth Cryst 45(01):217–223
Funding
We are very grateful to the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51975188) and the Open Fund of the State Key Laboratory of High Performance Complex Manufacturing (No. KFKT2017-09) for their strong support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xiaofei Lei: methodology, investigation, formal analysis, writing (review and editing). Daohui Xiang: project administration, formal analysis, writing (review and editing). Peicheng Peng: data curation, investigation. Xiaoxiao Niu: data curation, investigation. Bo Zhao: writing (review and editing). Guofu Gao: writing (review and editing).
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
I would like to declare on behalf of my co-authors that the work described was the application that has not been published previously, and not under consideration for publication elsewhere, in whole or in part.
Consent to participate
All authors know and agree to be co-authors.
Consent to publish
All authors agreed to be publish.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lei, X., Xiang, D., Peng, P. et al. Study on surface residual stress of hardened 12Cr2Ni4A alloy steel by ultrasonic vibration-assisted ELID grinding. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 118, 641–649 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-021-07328-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-021-07328-4