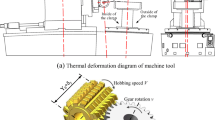
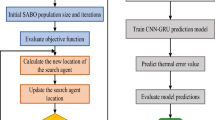
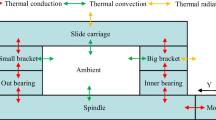
Abstract
It is an increasingly urgent to improve the machining accuracy of the gear hobbing machine. Thermal error is the main source of the machining error of the hobbing machine, and reducing thermal error is necessary to improve the machining accuracy of hobbing machine. In this paper, a novel thermal error prediction model for the hobbing machine was proposed based on the improved gray wolf optimizer (IGWO) and generalized regression neural network (GRNN). The fuzzy cluster grouping and mean impact value (MIV) were firstly combined to select the typical temperature variables and reduce the coupling between temperature variables, so the robustness of the thermal error model can be guaranteed. Then GRNN was used to establish the mapping relationship between temperature variables and thermal error. The IGWO considering the proportion of local optimization and global optimization was applied to optimize the smoothing parameter of GRNN. Finally, the proposed IGWO-GRNN was used to predict the thermal drift of the workpiece shaft of the dry cutting hobbing machine, and its predictive accuracy and generalization performance were compared with four existing algorithms. The results indicate that the prediction accuracy of IGWO-GRNN is at least 5.1% higher than other algorithms and its generalization performance is also promoted.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Okeefe W (1984) Handbook of practical gear design - dudley,dw. Power 128(12):111–111
Sun SL, Wang SL, Wang YW, Lim TC, Yang Y (2018) Prediction and optimization of hobbing gear geometric deviations. Mech Mach Theory 120:288–301
Hsu RH, Su HH (2014) Tooth contact analysis for helical gear pairs generated by a modified hob with variable tooth thickness. Mech Mach Theory 71:40–51
Deng F, Tang Q, Li XG, Yang Y, Zou Z (2018) Study on mapping rules and compensation methods of cutting-force-induced errors and process machining precision in gear hobbing. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 97(9–12):3859–3871
Bouzakis KD, Kombogiannis S, Antoniadis A, Vidakis N (2002) Gear hobbing cutting process simulation and tool wear prediction models. J Manuf Sci Eng-Trans ASME 124(1):42–51
Liu X, Zhao F, Mei XS, Tao T, Shen JG (2019) High-efficiency gear hobbing technics based on fuzzy adaptive control of spindle torque. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part C J Eng Mech Eng Sci 233(10):3331–3345
Jiang J, Fang Z (2015) High-order tooth flank correction for a helical gear on a six-axis CNC hob machine. Mech Mach Theory 91:227–237
BRYAN (1990) International status of thermal error research (1990). CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 39(2):645–656
Ma C, Zhao L, Mei XS, Shi H, Yang J (2017) Thermal error compensation based on genetic algorithm and artificial neural network of the shaft in the high-speed spindle system. Proc Inst Mech Eng B J Eng Manuf 231(5):753–767
Li Y, Zhao J, Ji SJ (2018) Thermal positioning error modeling of machine tools using a bat algorithm-based back propagation neural network. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 97(5–8):2575–2586
Liu JL, Ma C, Wang SL, Wang SB, Yang B, Shi H (2019) Thermal-structure interaction characteristics of a high-speed spindle-bearing system. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 137:42–57
Ma C, Mei XS, Yang J, Zhao L, Shi H (2015) Thermal characteristics analysis and experimental study on the high-speed spindle system. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 79(1–4):469–489
Mian NS, Fletcher S, Longstaff AP, Myers A (2013) Efficient estimation by FEA of machine tool distortion due to environmental temperature perturbations. Precis Eng J Int Soc Precis Eng 37(2):372–379
Li Y, Zhao J, Ji SJ, Liang FS (2019) The selection of temperature-sensitivity points based on K-harmonic means clustering and thermal positioning error modeling of machine tools. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 100(9–12):2333–2348
Liang RJ, Ye WH, Zhang HH, Yang QF (2012) The thermal error optimization models for CNC machine tools. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 63(9–12):1167–1176
Donmez MA, Blomquist DS, Hocken RJ, Liu CR, Barash MM (1986) A general methodology for machine-tool accuracy enhancement by error compensation. Precis Eng J Int Soc Precis Eng 8(4):187–196
Miao EM, Gong YY, Niu PC, Ji CZ, Chen HD (2013) Robustness of thermal error compensation modeling models of CNC machine tools. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 69(9–12):2593–2603
Tan F, Yin M, Wang L, Yin GF (2018) Spindle thermal error robust modeling using LASSO and LS-SVM. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 94(5–8):2861–2874
Xiang ST, Yang JH (2015) Error map construction and compensation of a NC lathe under thermal and load effects. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 79(1–4):645–655
Lei MH, Jiang GD, Yang J, Mei XS, Xia P, Zhao L (2017) Thermal error modeling with dirty and small training sample for the motorized spindle of a precision boring machine. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 93(1–4):571–586
Ma C, Zhao L, Mei XS, Shi H, Yang J (2017) Thermal error compensation of high-speed spindle system based on a modified BP neural network. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 89(9–12):3071–3085
Huang YQ, Zhang J, Li X, Tian LJ (2014) Thermal error modeling by integrating GA and BP algorithms for the high-speed spindle. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 71(9–12):1669–1675
Guo QJ, Yang JG, Wu H (2010) Application of ACO-BPN to thermal error modeling of NC machine tool. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 50(5–8):667–675
Han J, Wang LP, Wang HT, Cheng NB (2012) A new thermal error modeling method for CNC machine tools. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 62(1–4):205–212
Cao WD, Yan CP, Ding L, Ma YF (2016) A continuous optimization decision making of process parameters in high-speed gear hobbing using IBPNN/DE algorithm. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 85(9–12):2657–2667
Cao HJ, Zhu LB, Li XG, Chen P, Chen YP (2016) Thermal error compensation of dry hobbing machine tool considering workpiece thermal deformation. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 86(5–8):1739–1751
Zhang ZL, Yang JG (2016) Narrow density fraction prediction of coarse coal by image analysis and MIV-SVM. Int J Oil Gas Coal Technol 11(3):279–289
Li HZ, Guo S, Li CJ, Sun JQ (2013) A hybrid annual power load forecasting model based on generalized regression neural network with fruit fly optimization algorithm. Knowl Based Syst 37:378–387
Mirjalili S, Mirjalili SM, Lewis A (2014) Grey wolf optimizer. Adv Eng Softw 69:46–61
Muro C, Escobedo R, Spector L, Coppinger RP (2011) Wolf-pack (Canis lupus) hunting strategies emerge from simple rules in computational simulations. Behav Process 88(3):192–197
Long W, Jiao J, Liang X, Tang M (2018) Inspired grey wolf optimizer for solving large-scale function optimization problems. Appl Math Model 60:112–126
Funding
The presented work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation (51635003), National Natural Science Foundation (51905057), the National Key Research and Development Project (2018YFB1701203), and General program of Chongqing Natural Science Foundation (cstc2019jcyj-msxmX0050, cstc2019-jcyj-msxm-0389).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Z., Yang, B., Ma, C. et al. Thermal error modeling of gear hobbing machine based on IGWO-GRNN. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 106, 5001–5016 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-020-04957-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-020-04957-z