Abstract
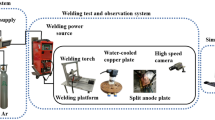
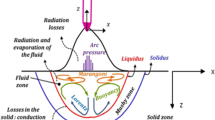
Variable polarity gas tungsten arc welding (VP-GTAW) has been suggested as a feasible method for welding aluminum alloys due to the enhanced surface cleaning of the oxide film. However, the principles governing the correlations between the electrode positive (EP) ratio, weld geometry, and weld microstructure are not well understood. Therefore, experiments with different EP ratios but same welding current were conducted. A three-dimensional heat transfer and fluid flow model of VP-GTAW was developed with validation against experimental results. Solidification parameters such as the temperature gradient, solidification growth rate, and cooling rate were computed from the model. The results indicate that VP-GTAW produces nearly defect-free joints. Both the top weld width and bottom weld width decrease with increasing EP ratio due to the decreased heat input. The bottom weld width is greater than the minimum weld profile width in the middle of the plate, which indicates that the Marangoni stress has a significant effect on the convective heat transfer and weld geometry. Variable grain dimensions are produced by different EP ratios at the same welding current. Weld pool oscillation originated from the alternating arc force plays a dominant role in the grain dimension.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li J, Li H, Wei H, Ni Y (2016) Effect of pulse on pulse frequency on welding process and welding quality of pulse on pulse MIG welding-brazing of aluminum alloys to stainless steel. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 87(1):51–63. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-016-8369-y
Wang LL, Heng GC, Chen H, Xue JX, Lin FL, Huang WJ (2016) Methods and results regarding sinusoid modulated pulse gas metal arc welding. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 86(5):1841–1851. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-015-8267-8
Dragatogiannis DA, Koumoulos EP, Kartsonakis IA, Pantelis DI, Karakizis PN, Charitidis CA (2016) Dissimilar friction stir welding between 5083 and 6082 Al alloys reinforced with TiC nanoparticles. Mater Manuf Process 31(16):2101–2114. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2015.1103856
Li J, Li H, Huang C, Xiang T, Ni Y, Wei H (2017) Welding process characteristics of pulse on pulse MIG arc brazing of aluminum alloy to stainless steel. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 91(1):1057–1067. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-016-9820-9
Pan J, Hu S, Yang L, Li H (2016) Simulation and analysis of heat transfer and fluid flow characteristics of variable polarity GTAW process based on a tungsten–arc-specimen coupled model. Int J Heat Mass Transf 96:346–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2016.01.014
Song G, Wang P, Liu LM (2010) Study on ac-PMIG welding of AZ31B magnesium alloy. Sci Technol Weld Join 15(3):219–225. https://doi.org/10.1179/136217110x12665048207656
Cho J, Lee J-J, Bae S-H (2015) Heat input analysis of variable polarity arc welding of aluminum. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 81(5):1273–1280. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-015-7292-y
Yarmuch MAR, Patchett BM (2007) Variable AC polarity GTAW fusion behavior in 5083 aluminum. Weld J 86(7):196S–200S
Dutra JC, Cirino LM, Gonçalves e Silva RH (2010) AC–GTAW of aluminium—new perspective for evaluation of role of positive polarity time. Sci Technol Weld Join 15(7):632–637. https://doi.org/10.1179/136217110X12813393169570
Pan J, Hu S, Yang L, Wang D (2016) Investigation of molten pool behavior and weld bead formation in VP-GTAW by numerical modelling. Mater Des 111:600–607. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2016.09.022
Babu NK, Cross CE (2012) Grain refinement of AZ31 magnesium alloy weldments by AC pulsing technique. Metall Mater Trans A 43A(11):4145–4154. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-012-1241-2
Wang Y, Qi B, Cong B, Yang M, Liu F (2017) Arc characteristics in double-pulsed VP-GTAW for aluminum alloy. J Mater Process Technol 249:89–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2017.05.027
DebRoy T, David SA (1995) Physical processes in fusion welding. Rev Mod Phys 67(1):85–112. https://doi.org/10.1103/RevModPhys.67.85
Wu C, Li S, Zhang C, Wang X (2016) Microstructural evolution in 316LN austenitic stainless steel during solidification process under different cooling rates. J Mater Sci 51(5):2529–2539. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-015-9565-0
Wang LL, Wei HL, Xue JX, DebRoy T (2017) A pathway to microstructural refinement through double pulsed gas metal arc welding. Scr Mater 134:61–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2017.02.034
David SA, Debroy T (1992) Current issues and problems in welding science. Science 257(5069):497–502. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.257.5069.497
Mishra S, DebRoy T (2005) A heat-transfer and fluid-flow-based model to obtain a specific weld geometry using various combinations of welding variables. J Appl Phys 98(4):article number 044902. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2001153
Roy GG, Elmer JW, DebRoy T (2006) Mathematical modeling of heat transfer, fluid flow, and solidification during linear welding with a pulsed laser beam. J Appl Phys 100(3):article number 034903. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2214392
Voller VR, Prakash C (1987) A fixed grid numerical modelling methodology for convection-diffusion mushy region phase-change problems. Int J Heat Mass Transf 30(8):1709–1719. https://doi.org/10.1016/0017-9310(87)90317-6
Zhang W, Kim C-H, DebRoy T (2004) Heat and fluid flow in complex joints during gas metal arc welding—part I: numerical model of fillet welding. J Appl Phys 95(9):5210–5219. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1699485
Wei HL, Blecher JJ, Palmer TA, Debroy T (2015) Fusion zone microstructure and geometry in complete-joint-penetration laser-arc hybrid welding of low-alloy steel. Weld J 94(4):135S–144S
Ribic B, Rai R, DebRoy T (2008) Numerical simulation of heat transfer and fluid flow in GTA/laser hybrid welding. Sci Technol Weld Join 13(8):683–693. https://doi.org/10.1179/136217108X356782
Cantin GMD, Francis JA (2005) Arc power and efficiency in gas tungsten arc welding of aluminium. Sci Technol Weld Join 10(2):200–210. https://doi.org/10.1179/174329305X37033
Wang LL, Wei HL, Xue JX, DebRoy T (2017) Special features of double pulsed gas metal arc welding. J Mater Process Technol 251:369–375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2017.08.039
Wei HL, Elmer JW, DebRoy T (2016) Origin of grain orientation during solidification of an aluminum alloy. Acta Mater 115:123–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2016.05.057
Wei HL, Mazumder J, DebRoy T (2015) Evolution of solidification texture during additive manufacturing. Sci Rep 5(1):16446. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep16446
Wei HL, Elmer JW, DebRoy T (2017) Crystal growth during keyhole mode laser welding. Acta Mater 133:10–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2017.04.074
Schempp P, Rethmeier M (2015) Understanding grain refinement in aluminium welding. Weld World 59(6):767–784. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40194-015-0251-2
Zhang Z, Wu Q, Grujicic M, Wan ZY (2016) Monte Carlo simulation of grain growth and welding zones in friction stir welding of AA6082-T6. J Mater Sci 51(4):1882–1895. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-015-9495-x
Kumar R, Dilthey U, Dwivedi DK, Ghosh PK (2009) Thin sheet welding of Al 6082 alloy by AC pulse-GMA and AC wave pulse-GMA welding. Mater Des 30(2):306–313. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2008.04.073
Lin ML, Eagar TW (1986) Pressures produced by gas tungsten arcs. Metall Trans B 17(3):601–607. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02670227
Pang J, Hu S, Shen J, Wang P, Liang Y (2016) Arc characteristics and metal transfer behavior of CMT + P welding process. J Mater Process Technol 238:212–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2016.07.033
Rokhlin S, Guu A (1993) A study of arc force, pool depression, and weld penetration during gas tungsten arc welding. Weld J 72(8):381S–390S
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful for the financial support for this research from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51375173) and the Science and Technology Programs of Guangdong Province (Nos. 2014B010104002 and 2016B090927008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, L.L., Wei, J.H. & Wang, Z.M. Numerical and experimental investigations of variable polarity gas tungsten arc welding. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 95, 2421–2428 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-017-1387-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-017-1387-6