Abstract
Purpose
Overstuffing the patellofemoral joint has been associated with poor post-operative outcomes. No study has assessed the effect of over-distracting the tibio-femoral joint in the vertical plane and its effects on function and quality of life. The purpose of this study is to assess the effect of tibio-femoral joint distraction on function and quality of life after total knee arthroplasty.
Methods
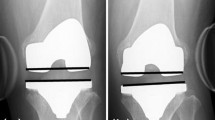
Measurements of knee joint distraction were devised using long-leg alignment radiographs. Seventy-three patients were prospectively recruited and their joint distraction measured post-operatively. A comparison was made between the level of joint distraction and functional outcomes as measured by the International Knee Society score and its components, such as pain and flexion, and the Knee injury and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score and quality of life as measured by the Short-Form 12 score. Twelve-month follow-up was achieved.
Results
Knee joint over-distraction post-arthroplasty correlated significantly with Knee Society score (p = 0.041), flexion (p = 0.005) and pain (p = 0.002). Those knees that were over-distracted post-operatively suffered more pain, less flexion and a lower International Knee Society score compared with their counterparts. No correlation was found between over-distracting the knee joint and quality of life.
Conclusion
Over-distracting the tibio-femoral joint during arthroplasty is a significant predictor of reduction in function and increase in pain in the short to medium term. When between sizes of tibial inserts, the surgeon should consider using the thinner option.
Level of evidence
Prospective cohort study, Level II.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aglietti P, Buzzi R, Gaudenzi A (1988) Patellofemoral functional results and complications with the posterior stabilized total condylar knee prosthesis. J Arthroplasty 3(1):17–25
Andrews G (2002) A brief integer scorer for the SF-12: validity of the brief scorer in Australian community and clinic settings. Aust N Z J Public Health 26(6):508–510
Babazadeh S, Dowsey MM, Bingham RJ, Ek ET, Stoney JD, Choong PF (2012) The long leg radiograph is a reliable method of assessing alignment when compared to computer-assisted navigation and computer tomography. Knee. doi:10.1016/j.knee.2012.07.009
Barrack RL, Burak C (2001) Patella in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 389:62–73
Blackburne JS, Peel TE (1977) A new method of measuring patellar height. J Bone Joint Surg Br 59(2):241–242
Bong MR, Di Cesare PE (2004) Stiffness after total knee arthroplasty. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 12(3):164–171
Classen T, Landgraeber S, Wegner A, Muller RD, von Knoch M (2011) Femoral component rotation in patients with leg axis deviation. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 19(7):1077–1081
Davies AP (2002) Rating systems for total knee replacement. Knee 9(4):261–266
Fern ED, Winson IG, Getty CJ (1992) Anterior knee pain in rheumatoid patients after total knee replacement. Possible selection criteria for patellar resurfacing. J Bone Joint Surg Br 74(5):745–748
Floren M, Davis J, Peterson MG, Laskin RS (2007) A mini-midvastus capsular approach with patellar displacement decreases the prevalence of patella baja. J Arthroplasty 22(6 Suppl 2):51–57
Ghosh KM, Merican AM, Iranpour F, Deehan DJ, Amis AA (2009) The effect of overstuffing the patellofemoral joint on the extensor retinaculum of the knee. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 17(10):1211–1216
Graw BP, Harris AH, Tripuraneni KR, Giori NJ (2010) Rotational references for total knee arthroplasty tibial components change with level of resection. Clin Orthop Relat Res 468:2734–2738
Grelsamer RP, Meadows S (1992) The modified Insall-Salvati ratio for assessment of patellar height. Clin Orthop Relat Res 282:170–176
Hsu HC, Luo ZP, Rand JA, An KN (1996) Influence of patellar thickness on patellar tracking and patellofemoral contact characteristics after total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 11(1):69–80
Insall JN, Dorr LD, Scott RD, Scott WN (1989) Rationale of the Knee Society clinical rating system. Clin Orthop Relat Res 248:13–14
Laskin RS, Beksac B (2004) Stiffness after total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 19(4 Suppl 1):41–46
Meneghini RM, Ritter MA, Pierson JL, Meding JB, Berend ME, Faris PM (2006) The effect of the Insall-Salvati ratio on outcome after total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 21(6 Suppl 2):116–120
Mihalko W, Fishkin Z, Krackow K (2006) Patellofemoral overstuff and its relationship to flexion after total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 449:283–287
Oishi CS, Kaufman KR, Irby SE, Colwell CW Jr (1996) Effects of patellar thickness on compression and shear forces in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 331:283–290
Perruccio AV, Stefan Lohmander L, Canizares M, Tennant A, Hawker GA, Conaghan PG, Roos EM, Jordan JM, Maillefert JF, Dougados M, Davis AM (2008) The development of a short measure of physical function for knee OA KOOS-Physical Function Shortform (KOOS-PS)—an OARSI/OMERACT initiative. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 16(5):542–550
Pierson JL, Ritter MA, Keating EM, Faris PM, Meding JB, Berend ME, Davis KE (2007) The effect of stuffing the patellofemoral compartment on the outcome of total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am 89(10):2195–2203
Reuben JD, McDonald CL, Woodard PL, Hennington LJ (1991) Effect of patella thickness on patella strain following total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 6(3):251–258
Schiavone Panni A, Cerciello S, Vasso M, Tartarone M (2009) Stiffness in total knee arthroplasty. J Orthop Traumatol 10(3):111–118
Scranton PE Jr (2001) Management of knee pain and stiffness after total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 16(4):428–435
Scuderi GR, Insall JN, Scott NW (1994) Patellofemoral pain after total knee arthroplasty. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 2(5):239–246
Star MJ, Kaufman KR, Irby SE, Colwell CW Jr (1996) The effects of patellar thickness on patellofemoral forces after resurfacing. Clin Orthop Relat Res 322:279–284
Su EP, Su SL, Della Valle AG (2010) Stiffness after TKR: how to avoid repeat surgery. Orthopedics 33(9):658
Weale AE, Murray DW, Newman JH, Ackroyd CE (1999) The length of the patellar tendon after unicompartmental and total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br 81(5):790–795
Whiteside LA (2004) Ligament balancing in total knee arthroplasty: an instructional manual. Springer, Berlin, pp 33–90
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Babazadeh, S., Dowsey, M.M., Stoney, J.D. et al. The effect of tibio-femoral over-distraction in primary knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 21, 2810–2816 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-012-2240-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-012-2240-y