Abstract
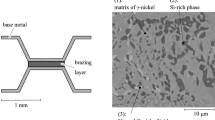
To meet the ever-growing demands for the efficient operation of turbomachinery, a minimum clearance between the rotating and the stationary components is of great importance. A lack of controlling this clearance often leads to interface rubbing. As a result, thermo-mechanical loads arise that can critically damage both components. Maintaining operational reliability and high efficiency requires seal systems that can tolerate rubbing. Honeycomb labyrinth seals can fulfill this task. In this contribution, we present a three-dimensional microstructure-based simulation approach considering the periodic unit cell of a polycrystalline Ni-base superalloy (Hastelloy X) honeycomb structure. Different honeycomb geometries are investigated, and various loading conditions are applied to simulate the thermo-mechanical behavior of the honeycomb structure during rubbing. The problem is solved in a finite element framework, and the deformation behavior is described by a crystal plasticity model accounting for microstructure attributes of the material. To calibrate the material model, numerical simulations on a representative volume element discretized with a realistic three-dimensional periodic mesh are carried out. The overall thermo-mechanical response of the honeycomb structure as well as the development of local field quantities is investigated. The study reveals that large contact areas seem to be very critical for the initiation of premature damage of the honeycomb structure.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abotula, S., Shukla, A., Chona, R.: Dynamic constitutive behavior of Hastelloy X under thermo-mechanical loads. J. Mater. Sci. 46(14), 4971–4979 (2011)
Aghaie-Khafri, M., Golarzi, N.: Dynamic and metadynamic recrystallization of Hastelloy X superalloy. J. Mater. Sci. 43(10), 3717–3724 (2008)
Aghaie-Khafri, M., Golarzi, N.: Forming behavior and workability of Hastelloy X superalloy during hot deformation. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 486, 641–647 (2008)
Barba, D., Alabort, E., Garcia-Gonzalez, D., Moverare, J., Reed, R., Jerusalem, A.: A thermodynamically consistent constitutive model for diffusion-assisted plasticity in Ni-based superalloys. Int. J. Plast. 105, 74–98 (2018)
Böhm, H.: A short introduction to basic aspects of continuum micromechanics. ILSB Report, Vienna University of Technology 206 (1998)
Canistraro, H.A., Jordan, E.H., Shixiang, S., Favrow, L.H., Reed, F.A.: Elastic constants of single crystal Hastelloy X at elevated temperatures. J. Eng. Mater. Technol. 120(3), 242–247 (1998)
Dassault Systèmes: Abaqus 6.13 Analysis User’s Guide (2013)
Dick, T., Cailletaud, G.: Fretting modelling with a crystal plasticity model of Ti6Al4V. Comput. Mater. Sci. 38(1), 113–125 (2006)
Farukh, F., Zhao, L., Jiang, R., Reed, P., Proprentner, D., Shollock, B.: Realistic microstructure-based modelling of cyclic deformation and crack growth using crystal plasticity. Comput. Mater. Sci. 111, 395–405 (2016)
Fillafer, A., Krempaszky, C., Werner, E.: On strain partitioning and micro-damage behavior of dual-phase steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 614, 180–192 (2014)
Frederick, C., Armstrong, P.: A mathematical representation of the multiaxial bauschinger effect. G.E.G.B. Report RD/B/N 731 (1966)
Fritzen, F., Böhlke, T., Schnack, E.: Periodic three-dimensional mesh generation for crystalline aggregates based on Voronoi tessellations. Comput. Mech. 43, 701–713 (2009)
Fromm, B.S., Chang, K., McDowell, D.L., Chen, L.Q., Garmestani, H.: Linking phase-field and finite-element modeling for process-structure-property relations of a Ni-base superalloy. Acta Mater. 60, 5984–5999 (2012)
Ghosh, S., Weber, G., Keshavarz, S.: Multiscale modeling of polycrystalline nickel-based superalloys accounting for subgrain microstructures. Mech. Res. Commun. 78, 34–46 (2016)
Goh, C.H., McDowell, D.L., Neu, R.W.: Characteristics of plastic deformation field in polycrystalline fretting contacts. Int. J. Fatigue 25(9–11), 1047–1058 (2003)
Goh, C.H., McDowell, D.L., Neu, R.W.: Influence of microstructure in partial-slip fretting contacts based upon two-dimensional crystal plasticity simulations. J. Tribol. 128(4), 735–744 (2006)
Goh, C.H., McDowell, D.L., Neu, R.W.: Plasticity in polycrystalline fretting fatigue contacts. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 54(2), 340–367 (2006)
Goh, C.H., Neu, R.W., McDowell, D.L.: Crystallographic plasticity in fretting of Ti–6AL–4V. Int. J. Plast. 19(10), 1627–1650 (2003)
Haynes International, I.: Hastelloy X alloy (UNS N06002). High-temperature alloys (1997)
Hennessey, C., Castelluccio, G.M., McDowell, D.L.: Sensitivity of polycrystal plasticity to slip system kinematic hardening laws for Al 7075–T6. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 687, 241–248 (2017)
Jordan, E.H., Shi, S., Walker, K.P.: The viscoplastic behavior of Hastelloy-X single crystal. Int. J. Plast. 9(1), 119–139 (1993)
Keshavarz, S., Ghosh, S.: Multi-scale crystal plasticity finite element model approach to modeling nickel-based superalloys. Acta Mater. 61, 6549–6561 (2013)
Kouznetsova, V.: Computational homogenization for the multi-scale analysis of multi-phase materials. Ph.D. thesis, TU Eindhoven (2002)
Kumar, R., Wang, A., McDowell, D.L.: Effects of microstructure variability on intrinsic fatigue resistance of nickel-base superalloys - a computational micromechanics approach. Int. J. Fract. 137, 173–210 (2006)
Lin, B., Zhao, L., Tong, J., Christ, H.: Crystal plasticity modeling of cyclic deformation for a polycrystalline nickel-based superalloy at high temperature. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 527(15), 3581–3587 (2010)
Meier, F.: Influence of the aluminum-microstructure on the damage behavior of integrated circuits. Ph.D. thesis, Technical University of Munich (2017)
Meier, F., Schwarz, C., Werner, E.: Crystal-plasticity based thermo-mechanical modeling of Al-components in integrated circuits. Comput. Mater. Sci. 94, 122–131 (2014)
Mohr, D.: Multi-scale finite-strain plasticity model for stable metallic honeycombs incorporating microstructural evolution. Int. J. Plast. 22, 1899–1923 (2006)
Mohr, D., Doyoyo, M.: Deformation-induced folding systems in thin-walled monolithic hexagonal metallic honeycomb. Int. J. Solids Struct. 41, 3353–3377 (2004)
Mohr, D., Doyoyo, M.: Large plastic deformation of metallic honeycomb: orthotropic rate-independent constitutive model. Int. J. Solids Struct. 41, 4435–4456 (2004)
Musinski, W.D., McDowell, D.L.: Microstructure-sensitive probabilistic modeling of HCF crack initiation and early crack growth in Ni-base superalloy IN100 notched components. Int. J. Fatigue 37, 41–53 (2011)
Musinski, W.D., McDowell, D.L.: On the eigenstrain application of shot-peened residual stresses within a crystal plasticity framework: Application to Ni-base superalloy specimens. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 100, 195–208 (2015)
Nygards, M., Gudmundson, P.: Three-dimensional periodic Voronoi grain models and micromechanical FE-simulations of a two-phase steel. Comput. Mater. Sci. 24, 513–519 (2002)
Przybyla, C.P., McDowell, D.L.: Microstructure-sensitive extreme value probabilities for high cycle fatigue of Ni-base superalloy IN100. Int. J. Plast. 26, 372–394 (26)
Quey, R., Dawson, P., Barbe, F.: Large-scale 3D random polycrystals for the finite element method: generation, meshing and remeshing. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 200, 1729–1745 (2011)
Roters, F., Diehl, M., Shanthraj, P., Eisenlohr, P., Reuber, C., L.Wong, S., Ma, D., Jia, N., Kok, P., Fujita, N., Ebrahimi, A., Hochrainer, T., Grilli, N., Janssens, K., Stricker, M., Weygand, D., Meier, F., Werner, E., Fabritius, H.O., Nikolov, S., Friak, M., Raabe, D.: Damask - the Düsseldorf advanced material simulation kit for modelling multi-physics crystal plasticity, damage and thermal phenomena from the single crystal up to the component scale. Comput. Mater. Sci. (in press) (2018)
Roters, F., Eisenlohr, P., Hantcherli, L., Tjahjanto, D., Bieler, T., Raabe, D.: Overview of constitutive laws, kinematics, homogenization and multiscale methods in crystal plasticity finite-element modeling: therory, experiments, applications. Acta Mater. 58(4), 1152–1211 (2010)
Roters, F., Eisenlohr, P., Kords, C., Tjahjanto, D., Diehl, M., Raabe, D.: Damask: The Düsseldorf advanced material simulation kit for studying crystal plasticity using an FE based or a spectral numerical solver. Procedia IUTAM 3, 3–10 (2012)
Rycroft, C.H.: Voro++: a three-dimensional Voronoi cell library in C++. Chaos 19, 041–111 (2009)
Sakthivel, T., Laha, K., Nandagopal, M., Chandravathi, K.S., Parameswaran, P., Selvi, S.P., Mathew, M., Mannan, S.K.: Effect of temperature and strain rate on serrated flow behaviour of Hastelloy X. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 534, 580–587 (2012)
Shahba, A., Ghosh, S.: Crystal plasticity FE modeling of Ti alloys for a range of strain-rates. Part I: a unified constitutive model and flow rule. Int. J. Plast. 87, 48–68 (2016)
Shenoy, M.M., Gordon, A.P., McDowell, D.L., Neu, R.W.: Thermomechanical fatigue behavior of a directionally solidified Ni-base superalloy. J. Eng. Mater. Technol. 127, 325–336 (2005)
Shi, S., Jordan, E.H., Walker, K.P.: Self-consistent constitutive modeling and testing of polycrystalline Hastelloy-X. Int. J. Solids Struct. 29(21), 2623–2638 (1992)
Song, J.E., McDowell, D.L.: Grain scale crystal plasticity model with slip and microtwinning for a third generation Ni-base disk alloy. Superalloys 2012, 159–166 (2012)
Taxer, T., Schwarz, C., Smarsly, W., Werner, E.: A finite element approach to study the influence of cast pores on the mechanical properties of the Ni-base alloy MAR-M247. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 575, 144–151 (2013)
Varshni, Y.P.: Temperature dependence of the elastic constants. Phys. Rev. B 2(10), 3952–3958 (1970)
Wang, A., McDowell, D.L.: Yield surfaces of various periodic metal honeycombs at intermediate relative density. Int. J. Plast. 21(2), 285–320 (2005)
Werner, E., Wesenjak, R., Fillafer, A., Meier, F., Krempaszky, C.: Microstructure-based modelling of multiphase materials and complex structures. Contin. Mech. Thermodyn. 28(5), 1325–1346 (2015)
Ye, C., Chen, J., Xu, M., Wei, X., Lu, H.: Multi-scale simulation of nanoindentation on cast Inconel 718 and NbC precipitate for mechanical properties prediction. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 662, 385–394 (2016)
Zhang, M., McDowell, D.L., Neu, R.W.: Microstructure sensitivity of fretting fatigue based on computational crystal plasticity. Tribol. Int. 42, 1286–1296 (2009)
Zhang, M., Neu, R.W., McDowell, D.L.: Microstructure-sensitive modeling: application to fretting contacts. Int. J. Fatigue 31, 1397–1406 (2009)
Zhang, T., Jiang, J., Britton, B., Shollock, B., Dunne, F.: Crack nucleation using combined crystal plasticity modelling, high-resolution digital image correlation and high-resolution electron backscatter diffraction in a superalloy containing non-metallic inclusions under fatigue. Proc. Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 472, 1–25 (2016)
Zhang, X., Oskay, C.: Polycrystal plasticity modeling of nickel-based superalloy IN 617 subjected to cyclic loading at high temperature. Modell. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 24, 1–27 (2016)
Acknowledgements
This work is part of the research project WE 2351/14–1, funded by the DFG (Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft). We thank the Max Planck Institut für Eisenforschung in Düsseldorf for providing the simulation kit DAMASK.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Andreas Öchsner.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fischer, T., Werner, E., Ulan kyzy, S. et al. Crystal plasticity modeling of polycrystalline Ni-base superalloy honeycombs under combined thermo-mechanical loading. Continuum Mech. Thermodyn. 31, 703–713 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00161-018-0721-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00161-018-0721-z