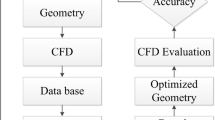
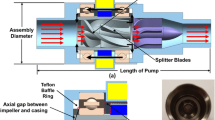
Abstract
The roller pump is a distinctive device that delivers fluid in an analogous manner to the peristaltic movement of a biological organism. The pump with the unique mechanism can isolate the liquid from the pump's mechanical components effectively, thereby preventing contamination of the fluid. Therefore, the pump is widely used in extracorporeal circulation machines as artificial hearts for extracorporeal circulation of blood. However, the roller pump exhibits flow pulsation, and in severe cases, that may potentially harm the human body during extracorporeal circulation surgeries. It is necessary to optimize the structure of the roller pump, reduce the degree of flow pulsation of the roller pump and improve the smoothness of the flow transmission. In order to minimize the extent of flow pulsation, the high fidelity fluid–solid interaction (FSI) model of roller pump is established, the accuracy of the model is verified by experiment. Two methods of optimizing the pump structure are proposed. First, the optimization method based on the flow compensation, a new structure model of Y- shaped is established, that reduce the degree of pulsation by superimposing the flow curves with phase difference for flow compensation. Another one is the rapid and efficient optimization method based on the surrogate model, that the surrogate model combines with the optimization algorithm to optimize the structural parameters. The surrogate model is used to replace the FSI model, and the optimal configuration of the internal structural variables is obtained through the Multi-island genetic algorithm (MIGA). And the accuracy of the surrogate model verified by FSI analysis. The results indicate that the two optimization methods have their own advantages in reducing the pump flow pulsation and the pump flow pulsation performance has been improved significantly.





















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anastasiadis K, Chalvatzoulis O, Antonitsis P et al (2011) Use of minimized extracorporeal circulation system in noncoronary and valve cardiac surgical procedures-A case series. Artif Organs 35:960–963. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1525-1594.2010.01183.x
Bao Y (2023) Modeling of Eddy current NDT simulations by Kriging Surrogate model. Res Nondestruct Eval 34:154–168. https://doi.org/10.1080/09349847.2023.2250281
Ben Salem M, Tomaso L (2018) Automatic selection for general surrogate models. Struct Multidisc Optim 58:719–734. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-018-1925-3
Conlan-Smith C, Andreasen CS (2022) Aeroelastic shape optimization of solid foam core wings subject to large deformations. Struct Multidisc Optim 65:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-022-03246-5
Dalklint A, Wallin M, Tortorelli DA (2021) Structural stability and artificial buckling modes in topology optimization. Struct Multidisc Optim 64:1751–1763. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-021-03012-z
Ding X, Li R, Xu J et al (2022) Study on flow force compensation characteristics and optimization design of jet guiding groove. Flow Meas Instrum 86:102194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.flowmeasinst.2022.102194
Du Y, Pei P, Suo T, Gao G (2023) Large deformation mechanical behavior and constitutive modeling of oriented PMMA. Int J Mech Sci 257:108520. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2023.108520
Elabbasi N, Bergstrom J, Brown S (2011) Fluid-Structure Interaction Analysis of a Peristaltic Pump. Proc 2011 COMSOL Conf 1–4
Embaye M, Al-Dadah RK, Mahmoud S (2015) Thermal performance of hydronic radiator with flow pulsation - Numerical investigation. Appl Therm Eng 80:109–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2014.12.056
Formato G, Romano R, Formato A et al (2019) Fluid-structure interaction modeling applied to peristaltic pump flow simulations. Machines 7:1–12. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines7030050
Genç MS, Demir H, Özden M, Bodur TM (2021) Experimental analysis of fluid-structure interaction in flexible wings at low Reynolds number flows. Aircr Eng Aerosp Technol 93:1060–1075. https://doi.org/10.1108/AEAT-04-2021-0120
He F, Hua L, Guo T (2021) Fluid–structure interaction analysis of hemodynamics in different degrees of stenoses considering microcirculation function. Adv Mech Eng 13:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1177/1687814021989012
Ibanez R, Kelley DH (2022) A bioinspired apparatus for modeling peristaltic pumping in biophysical flows. Bioinspir Biomim. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-3190/ac9c7e
Kant R, Singh H, Nayak M, Bhattacharya S (2013) Optimization of design and characterization of a novel micro-pumping system with peristaltic motion. Microsyst Technol 19:563–575. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-012-1658-y
Kartuzova O, Kassemi M (2023) Computational Fluid Dynamics Analysis of Jet-Ullage Interactions During Microgravity Mixing. J Thermophys Heat Transf. https://doi.org/10.2514/1.t6725
Komeilizadeh K, Kaps A, Duddeck F (2023) Isovolumetric adaptations to space-filling design of experiments. Optim Eng 24:1267–1288. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11081-022-09731-6
Kurtulmuş N, Sahin B (2020) Experimental investigation of pulsating flow structures and heat transfer characteristics in sinusoidal channels. Int J Mech Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2019.105268
Lee JC, Park CY, Choi SW et al (2008a) Comparison of a pulsatile blood pump and a peristaltic roller pump during hemoperfusion treatment in a canine model of paraquat poisoning. Artif Organs 32:541–546. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1525-1594.2008.00582.x
Lee SH, Choi HS, Kwak BM (2008b) Multilevel design of experiments for statistical moment and probability calculation. Struct Multidisc Optim 37:57–70. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-007-0215-2
Li G, Yang J, Wu Z et al (2022) A sequential optimal Latin hypercube design method using an efficient recursive permutation evolution algorithm. Eng Optim. https://doi.org/10.1080/0305215X.2022.2148665
Li K, He X, Lv L et al (2023a) A single-fidelity surrogate modeling method based on nonlinearity integrated multi-fidelity surrogate. J Mech Des 145:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4062665
Li Q, Zong C, Liu F et al (2023b) Numerical and experimental analysis of fluid force for nuclear valve. Int J Mech Sci 241:107939. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2022.107939
Liu H, Hervas JR, Ong YS et al (2018) An adaptive RBF-HDMR modeling approach under limited computational budget. Struct Multidisc Optim 57:1233–1250. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-017-1807-0
Lopes D, Puga H, Teixeira JC, Teixeira SF (2019) Influence of arterial mechanical properties on carotid blood flow: Comparison of CFD and FSI studies. Int J Mech Sci 160:209–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2019.06.029
Manopoulos C, Tsoukalis A, Mathioulakis D (2022) Suppression of flow pulsations and energy consumption of a drug delivery roller pump based on a novel tube design. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part C J Mech Eng Sci 236:7759–7770. https://doi.org/10.1177/09544062221084188
McIntyre MP, van Schoor G, Uren KR, Kloppers CP (2021) Modelling the pulsatile flow rate and pressure response of a roller-type peristaltic pump. Sensors Actuators, A Phys 325:112708. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sna.2021.112708
Najafi Z, Schwartz BF, Chandy AJ, Mahajan AM (2018) A two-dimensional numerical study of peristaltic contractions in obstructed ureter flows. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin 21:22–32. https://doi.org/10.1080/10255842.2017.1415333
Nishinaka T, Nishida H, Endo M et al (1996) Less blood damage in the impeller centrifugal pump: A comparative study with the roller pump in open heart surgery. Artif Organs 20:707–710. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1525-1594.1996.tb04508.x
Niu Y, Xu X, Guo S (2021) Structural optimization design of a typical adhesive bonded honeycomb-core sandwich T-joint in side bending using multi-island genetic algorithm. Appl Compos Mater 28:1039–1066. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10443-021-09882-2
Pang T, Wang Y, Yang JF (2022) Asymptotically optimal maximin distance Latin hypercube designs. Metrika 85:405–418. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00184-021-00833-2
Papathanasiou P, Kissling B, Berberig O et al (2022) Flow disturbance compensation calculated with flow simulations for ultrasonic clamp-on flowmeters with optimized path arrangement. Flow Meas Instrum. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.flowmeasinst.2022.102167
Picelli R, Ranjbarzadeh S, Sivapuram R et al (2020) Topology optimization of binary structures under design-dependent fluid-structure interaction loads. Struct Multidisc Optim 62:2101–2116. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-020-02598-0
Priam SS, Nasrin R (2022) Numerical appraisal of time-dependent peristaltic duct flow using Casson fluid. Int J Mech Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2022.107676
Qian WM, Ahmed B, Khan SU et al (2021) Novel scientific simulations (Finite element method) for peristaltic blood flow in an asymmetric channel: applications of magnetic and inertial forces. J Magn 26:129–140. https://doi.org/10.4283/JMAG.2021.26.1.129
Rossi N, Méndez CG, Huespe AE (2023) Surrogate model for a mechanical metamaterial undergoing microstructure instabilities and phase transformations. Int J Mech Sci 243:107913. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2022.107913
Shukla R, Bhatt SS, Medhavi A et al (2020) Effect of Surface Roughness during Peristaltic Movement in a Nonuniform Channel. Math Probl Eng. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/9643425
Sibilio S, De Gregorio V, Urciuolo F et al (2019) Effect of peristaltic-like movement on bioengineered intestinal tube. Mater Today Bio. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtbio.2019.100027
Sun X, Zhang B, Jiang Y et al (2021) Multi-island genetic-algorithm-based approach to uniquely calibrate polycrystal plasticity models for magnesium alloys. Jom 73:1395–1402. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-021-04614-0
Suzuki K, Nakamura T (2010) Development of a peristaltic pump based on bowel peristalsis using for artificial rubber muscle. IEEE/RSJ 2010 Int Conf Intell Robot Syst IROS 2010 - Conf Proc 3085–3090. https://doi.org/10.1109/IROS.2010.5653006
Tang C, Zhang F, Zhang J et al (2022) Novel reliability evaluation method combining active learning kriging and adaptive weighted importance sampling. Struct Multidisc Optim. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-022-03346-2
Tang T, Lei L, Xiao L et al (2023) Flow characteristic optimization of a multi-stage orifice plate using surrogate-based modeling and Bayesian optimization. Struct Multidisc Optim 66:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-023-03647-0
Walker SW, Shelley MJ (2010) Shape optimization of peristaltic pumping. J Comput Phys 229:1260–1291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcp.2009.10.030
Wang B, Xu N, Yang R (2021a) Flow pulsation reduction of a single-piston piezoelectric pump based on elastic cavity group and unloading valve. Adv Mech Eng 13:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1177/16878140211031023
Wang C, Yang J, Liu MQ (2021b) Construction of space-filling orthogonal designs. J Stat Plan Inference 213:130–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jspi.2020.11.009
Wu K, Hu H, Wang L, Gao Y (2022) Parametric optimization of an aperiodic metastructure based on genetic algorithm. Int J Mech Sci 214:106878. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2021.106878
Wu X, Chen L (2021) 2-D orthogonal polynomial model for concurrent dual-band digital predistortion based on complex Gaussian assumption. AEU - Int J Electron Commun 135:153704. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aeue.2021.153704
Wu X, Cui QZ (2011) Structure Analyses and Flow Rate Model of Peristaltic Pump of Cement Foaming Machine. Adv Eng Forum 2–3:852–855. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/aef.2-3.852
Yamatsuta E, Ping Beh S, Uesugi K et al (2019) A Micro Peristaltic Pump Using an Optically Controllable Bioactuator. Engineering 5:580–585. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eng.2018.11.033
Yang F, Chang P, Yuan Y et al (2021) Analysis of timing effect on flow field and pulsation in vertical axial flow pump. J Mar Sci Eng 9:1–23. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9121429
Yin M, Wang J, Sun Z (2019) An innovative DoE strategy of the kriging model for structural reliability analysis. Struct Multidisc Optim 60:2493–2509. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-019-02337-0
Yuan X, ju, Ling H tao, Chen J jie, et al (2022) A dynamic modelling method for an electro-hydraulic proportional valve combining multi-systems and moving meshes. J Brazilian Soc Mech Sci Eng 44:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-022-03603-x
Zang JL, Yao HY, Zhang FH et al (2022) Dynamic characteristics analysis of pilot valves with different inlet diameters installed on the main steam valve set. Case Stud Therm Eng 34:102004. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csite.2022.102004
Zhang L, Choi SK, Xie T et al (2021) Multi-fidelity surrogate model-assisted fatigue analysis of welded joints. Struct Multidisc Optim 63:2771–2787. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-020-02840-9
Zhao Y, Ye S, Chen X et al (2022) Polynomial Response Surface based on basis function selection by multitask optimization and ensemble modeling. Complex Intell Syst 8:1015–1034. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40747-021-00568-7
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural-Science Foundation of China (No.52075068).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Fuwen Liu proposed the methodology, constructed the model, and wrote the manuscript;Qing ye Li, Zhuang zhuang Gong, and Yanfeng Zhang performed data organization and data visualization; Xueguan Song provided financial support and overall oversight.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Replication of results
In this work, the basic codes for the evidence theory and the numerical results presented are available from the author on reasonable request.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Zhen Hu
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, F., Li, Q., Gong, Z. et al. Structure optimization design of extracorporeal circulation blood transport pump. Struct Multidisc Optim 67, 37 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-024-03762-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-024-03762-6