Abstract
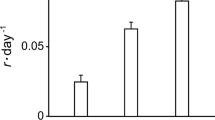
Global warming and pesticide contamination are two stressors of high concern, but their combined effects on freshwater biota are controversial. This study investigated the combined effects of warming and imidacloprid (IMI) on survival (measured as life expectancy at hatching), reproduction (net reproductive rate), population growth (intrinsic rate of population increase) and sexual reproduction (proportion of sexual offspring) of Brachionus calyciflorus using a life table experiment. The results showed that compared with controls, treatments with IMI at 50–100 mg/L significantly decreased survival, reproduction and population growth of the rotifers at 20℃. The inhibiting effect at higher IMI concentrations on survival increased with increasing temperatures, but those on reproduction and population growth increased only when the temperature increased from 25℃ to 30℃. The proportion of sexual offspring decreased with increasing temperatures. When monitoring the ecological effects of pollutants, environmental temperature and the possible adaptation of rotifers to it should be taken into consideration.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agatz A, Cole TA, Preuss TG et al (2013) Feeding inhibition explains effects of imidacloprid on the growth, maturation, reproduction, and survival of Daphnia magna. Environ Sci Technol 47:2909–2917. https://doi.org/10.1021/es304784t
Calabrese EJ (2008) Hormesis: why it is important to toxicology and toxicologists. Environ Toxicol Chem 27(7):1451–1474. https://doi.org/10.1897/07-541.1
Cambronero MC, Marshall H, De Meester L, Davidson TA, Beckerman AP, Orsini L (2018) Predictability of the impact of multiple stressors on the keystone species Daphnia. Sci Rep 8:17572. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-35861-y
Colombo V, Mohr S, Berghahn R, Pettigrove VJ (2013) Structural changes in a macrozoobenthos assemblage after imidacloprid pulses in aquatic field-based microcosms. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 65:683–692. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-013-9940-2
de Beeck LO, Verheyen J, Olsen K, Stoks R (2017) Negative effects of pesticides under global warming can be counteracted by a higher degradation rate and thermal adaptation. J Appl Ecol 54:1847–1855. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2664.12919
Ge LL (2021) Effects of imidacloprid on physiological and ecological characteristics and related gene expression of Brachionus calyciflorus. Master’s thesis, Anhui Normal University
Gharaei A, Karimi M, Mirdar Harijani J, Miri M, Faggio C (2020) Population growth of Brachionus calyciflorus affected by deltamethrin and imidacloprid insecticides. Iran J Fisheries Sci 19(2):588–601. https://doi.org/10.22092/ijfs.2018.117180
Gilbert JJ, Schröder T (2004) Rotifers from diapausing, fertilized eggs: unique features and emergence. Limnol Oceanogr 49:1341–1354. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.2004.49.4_part_2.1341
Holmstrup M, Bindesbøl AM, Oostingh GJ et al (2010) Interactions between effects of environmental chemicals and natural stressors: A review. Sci Total Environ 408:3746–3762. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2009.10.067
Hooper MJ, Ankley GT, Cristol DA, Maryoung LA, Noyes PD, Pinkerton KE (2013) Interactions between chemical and climate stressors: a role for mechanistic toxicology in assessing climate change risks. Environ Toxicol Chem 32:32–48
Huang L, Xi YL, Zha CW, Zhao LL (2007) Effect of aldrin on life history characteristics of rotifer Brachionus calyciforus Pallas. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 79:524–528. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-007-9271-y
IPCC (2019) Summary for Policymakers. World Meteorological Organization, Geneva. https://www.ipcc.ch/site/assets/uploads/sites/4/2019/12/02_Summary-for-Policymakers_SPM.pdf. Accessed 22 March 2022
Jackson MC, Loewen CJ, Vinebrooke RD, Chimimba CT (2016) Net effects of multiple stressors in freshwater ecosystems: a meta-analysis. Glob Chang Biol 22:180–118. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.13028
Krebs CJ (1985) Ecology: the experimental analysis of distribution and abundance. Harper & Row Publishers, New York
Li SH, Zhu H, Xia YZ, Yu MJ, Liu KS, Ye ZY, Chen YX (1959) The mass culture of unicellular green algae. Acta Hydrobiol Sin 4:462–472 (in Chinese)
Metcalfe C, Helm P, Paterson G, Kaltenecker G, Murray C, Nowierski M, Sultana T (2019) Pesticides related to land use in watersheds of the Great Lakes basin. Sci Total Environ 648:681–692. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.08.169
Noyes PD, McElwee MK, Miller HD, Clark BW, Van Tiem LA, Walcott KC, Erwin KN, Levin ED (2009) The toxicology of climate change: environmental contaminants in a warming world. Environ Int 35(6):971–986. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2009.02.006
Peng Y, Fang W, Krauss M, Brack W, Wang Z, Li F, Zhang X (2018) Screening hundreds of emerging organic pollutants (EOPs) in surface water from the Yangtze River Delta (YRD): occurrence, distribution, ecological risk. Environ Pollut 241:484–493. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.05.061
Pestana JLT, Loureiro S, Baird DJ, Soares AMVM (2010) Pesticide exposure and inducible antipredator responses in the zooplankton grazer. Daphnia magna Straus Chemosphere 78:241–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2009. 10.066
Poole RW (1974) An introduction to quantitative ecology. McGraw-Hill, New York
Raby M, Zhao X, Hao C, Poirier DG, Sibley PK (2018) Relative chronic sensitivity of neonicotinoid insecticides to Ceriodaphnia dubia and Daphnia magna. Ecotoxicol Environ Safety 163:238–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.201807.086
Sánchez-Bayo F, Goka K, Hayasaka D (2016) Contamination of the aquatic envi ronment with neonicotinoids and its implication for ecosystems. Front Environ Sci 4:71. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2016.00071
Snell TW, Janssen C (1995) Rotifers in ecotoxicology: a review. Hydrobiologia 313/314:231–247. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-009-1583-1_32
Sumon KA, Ritika AK, Peeters ETHM, Rashid H, Bosma RH, Rahman MS, Fatema MK, Van den Brink PJ (2018) Effects of imidacloprid on the ecology of sub-tropical freshwater microcosms. Environ Pollut 236:432–441. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.01.102
Tomizawa M, Casida JE (2009) Molecular recognition of neonicotinoid insecticides: the determinants of life or death. Acc Chem Res 42(2):260–269. https://doi.org/10.1021/ar800131p
Weber CI (1993) Methods for measuring the acute toxicity of effluents and receiving waters to freshwater and marine organisms. National Service Center for Environmental Publications (NSCEP), Washington, DC
Xiang XL, Chen YY, Xu QL, Zhu LY, Wen XL, Xi YL (2017) Combined effects of temperature and the microcystin MC-LR on the feeding behavior of the rotifer Brachionus calyciflorus. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 99:493–499. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-017-2172-9
Yi X, Zhang C, Liu H, Wu R, Tian D, Ruan J, Zhang T, Huang M, Ying G (2019) Occurrence and distribution of neonicotinoid insecticides in surface water and sediment of the Guangzhou section of the Pearl River, South China. Environ Pollut 251:892–900. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.05.062
Zha CW, Xi YL, Huang L, Zhao LL (2007) Effect of sublethal exposure to chlordecone on life history characteristics of freshwater rotifer Brachionus calyciflorus Pallas. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 78(1):79–83. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-007-9003-3
Zhang Y, Zhou A, Xi YL, Sun Q, Ning LF, Xie P, Wen XL, Xiang XL (2018) Temporal patterns and processes of genetic differentiation of the Brachionus calyciflorus (Rotifera) complex in a subtropical shallow lake. Hydrobiologia 807(1):313–331. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-017-3407-9
Acknowledgements
This study was support by the Natural Science Foundation of China (31971562, 31470015) and the Foundation of Provincial Key Laboratory of Biotic Environment and Ecological Safety in Anhui Province.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wen, Y., Cao, MM., Huang, ZY. et al. Combined Effects of Warming and Imidacloprid on Survival, Reproduction and Population Growth of Brachionus calyciflorus (Rotifera). Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 109, 990–995 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-022-03587-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-022-03587-3