Abstract
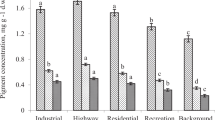
The washed and unwashed current (C) and previous year (C + 1) needles, branches and top soils of Pinus tabulaeformis trees were sampled at five sites Haitai industrial district (HT), Puji River (PJ), Fukang road (FK), Residential area (RA) and Baxian Mountain (BX) in Tianjin along an urban–rural gradient and analyzed for heavy metals (Cu, Mn, Zn, Pb and Cd) concentrations via ICP. C + 1 needles generally had higher Mn, Pb, Cd than C needles while the opposite was for Cu and Zn. Total Cu, Zn, Pb, Cd in soils peaked at HT and decreased at RA and BX. Heavy metals were generally higher in the unwashed needles than the washed needles at all sites. Meanwhile MDA, soluble sugar and free proline concentration in needles were increased with the increasing of heavy metal contents along the urban–rural gradient, further correlated with the heavy metal contents.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Alawi MM, Mandiwana KL (2007) The use of Aleppo pine needles as a bio-monitor of heavy metals in the atmosphere. J Hazard Mater 148:43–46
Al-Khashman OA (2004) Heavy metal distribution in dust and soils from the work place in Korak Industrial Estate, Jordan. Atmos Environ 38:6803–6812
Aznar JC, Richer-Laflèche M, Bégin C, Bégin Y (2009) Lead exclusion and copper translocation in black spruce Needles. Water Air Soil Pollut 203:139–145
Bates LS, Waldren RP, Teare ID (1973) Rapid determination of free proline for water-stress studies. Plant Soil 39:205–207
Beauchamp C, Fridovich I (1971) Superoxide dismutase: improved assays and an assay applicable to acrylamide gels. Anal Biochem 44:276–287
Celik A, Kartal AA, Akdoğan A, Kaska Y (2005) Determining the heavy metal pollution in Denizli (Turkey) by using Robinio pseudo-acacia L. Environ Int 31:105–112
Chen P, Zhang J, Bi X, Feng Y, Wu J (2013) Pollution characteristics and sources of heavy metals in PM10 and PM2.5 in Tianjin City. Acta Sci Nat Univ Nankaiensis 46:1–7 (in Chinese)
Gu J, Bai Z, Li W, Wu L, Liu A, Dong H, Xie Y (2011) Chemical composition of PM2.5 during winter in Tianjin, China. Particuology 9:215–221
Huang D, Xu J, Zhang S (2012) Valuing the health risks of particulate air pollution in the Pearl River Delta, China. Environ Sci Policy 15:38–47
Hwang HJ, Yook SJ, Ahn KH (2011) Experimental investigation of submicron and ultrafine soot particle removal by tree leaves. Atmos Environ 45:6987–6994
Iii FSC, Kedrowski RA (1983) Seasonal changes in nitrogen and phosphorus fractions and autumn retranslocation in evergreen and deciduous taiga trees. Ecology 64:376–391
Kayama M, Sasa K, Koike T (2002) Needle life span, photosynthetic rate and nutrient concentration of Picea glehnii, P. jezoensis and P. abies planted on serpentine soil in northern Japan. Tree Physiol 22:707–716
Kingston HM (1996) Microwave assisted acid digestion of siliceous and or ganically-based matrices, method 3052. United States Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC, USA
Kuang YW, Wen DZ, Zhou GY, Liu SZ (2007) Distribution of elements in needles of Pinus massoniana (Lamb.) was uneven and affected by needle age. Environ Pollut 145:146–153
Liu G (1996) Soil physical and chemical analysis & description of soil profiles. Standards Press of China, Beijing (in Chinese)
Nicola FD, Maisto G, Prati MV, Alfani A (2008) Leaf accumulation of trace elements and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in Quercus ilex L. Environ Pollut 153:376
Nouri J, Khorasani N, Lorestani B, Karami M, Hassani AH, Yousefi N (2009) Accumulation of heavy metals in soil and uptake by plant species with phytoremediation potential. Environ Earth Sci 59:315–323
Pietrzykowski M, Socha J, van Doorn NS (2014) Linking heavy metal bioavailability (Cd, Cu, Zn and Pb) in Scots pine needles to soil properties in reclaimed mine areas. Sci Total Environ 470–471:501–510
Raghunath R, Tripathi RM, Kumar AV, Sathe AP, Khandekar RN, Nambi KS (1999) Assessment of Pb, Cd, Cu, and Zn exposures of 6–10 year-old children in Mumbai. Environ Res 80:215
Rothpfeffer C, Karltun E (2007) Inorganic elements in tree compartments of Picea abies —concentrations versus stem diameter in wood and bark and concentrations in needles and branches. Biomass Bioenerg 31:717–725
Sameckacymerman A, Stankiewicz A, Kolon K, Kempers AJ (2009) Self-organizing feature map (neural networks) as a tool to select the best indicator of road traffic pollution (soil, leaves or bark of Robinia pseudoacacia L.). Environ Pollut 157:2061–2065
Serbula SM, Kalinovic T, Ilic A, Kalinovic J, Steharnik M (2013) Assessment of airborne heavy metal pollution using Pinus spp. and Tilia spp. Aerosol Air Qual Res 13:563–573
Shao L, Xiao H, Daishe WU (2013) Speciation of heavy metals in airborne particles, road dusts, and soils along expressways in China. Acta Geochim 32:420–429
Shi C, Watanabe T, Koike T (2017) Leaf stoichiometry of deciduous tree species in different soils exposed to free-air O3 enrichment over two growing seasons. Environ Exp Bot 138:148–163
Sun F, Wen D, Kuang Y, Li J, Li J, Zuo W (2010) Concentrations of heavy metals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in needles of Masson pine (Pinus massoniana L.) growing nearby different industrial sources. J Environ Sci 22:1006–1013
Tan J, Duan J, He K, Ma Y, Duan F, Chen Y, Fu J (2009) Chemical characteristics of PM2.5 during a typical haze episode in Guangzhou. J Environ Sci 21:774–781
Uddin I, Bano A, Masood S (2015) Chromium toxicity tolerance of Solanum nigrum L. and Parthenium hysterophorus L. plants with reference to ion pattern, antioxidation activity and root exudation. Ecotoxicol Environ Safe 113:271–278
Wang Q et al (2015) Probing the severe haze pollution in three typical regions of China: characteristics, sources and regional impacts. Atmos Environ 120:76–88
Yilmaz S, Zengin M (2004) Monitoring environmental pollution in Erzurum by chemical analysis of Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris L.) needles. Environ Int 29:1041–1047
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by Nankai University, College of Life Sciences, as well as the project of Tianjin Agricultural Environmental Monitoring Station (No. 2017SJ004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, R., Yang, T., Shi, C. et al. Effects of Urban–rural Atmospheric Environment on Heavy Metal Accumulation and Resistance Characteristics of Pinus tabulaeformis in Northern China. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 102, 432–438 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-019-02548-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-019-02548-7