Abstract
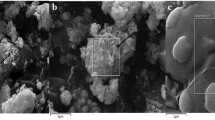
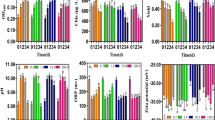
The ecotoxicity of α-Fe2O3 nanoparticles (NPs) and its interaction with a typical natural organic matter (NOM), fulvic acid (FA) on the physiological responses of Synechococcus sp. PCC7942 was studied. α-Fe2O3 NPs inhibited the algae growth at concentration higher than 10 mg L−1 and induced oxidative stress, indicated by enhanced antioxidant enzymes activities, elevated protein and sugar content. FA could efficiently recover cell growth and reduce antioxidant enzyme activities which induced by α-Fe2O3 NPs, indicating the toxicity of NPs was alleviated in the presence of FA. α-Fe2O3 NPs could form large aggregates coating on cell surface and inhibit cell growth. FTIR spectra verified FA interacted with α-Fe2O3 NPs through carboxyl groups, partly replaced the binding sites of α-Fe2O3 NPs on algal cell walls, thus reduced NPs aggregates coating on cell surface. This favors reducing the oxidative stress caused by direct contact and increasing light availability, thus mitigate NPs toxicity.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad NS, Radiman S, Yaacob WZW (2016) Aggregation and stability of Fe2O3: influence of humic acid concentration, Fe2O3 concentration and pH. In: Proceeding of the 4th international conference of fundamental and applied sciences 2016 (ICFAS2016), vol 1787
Auffan M, Flahaut E, Thill A, Mouchet F, Carriere M, Gauthier L, Achouak W, Rose J, Wiesner MR, Bottero J-Y (2011) Ecotoxicology: Nanoparticle reactivity and living organisms. In: Nanoethics and nanotoxicology, Springer, Berlin, pp 325–357
Baalousha M (2009) Aggregation and disaggregation of iron oxide nanoparticles: Influence of particle concentration, pH and natural organic matter. Sci Total Environ 407(6):2093–2101
Berg JM, Romoser A, Banerjee N, Zebda R, Sayes CM (2009) The relationship between pH and zeta potential of ~ 30 nm metal oxide nanoparticle suspensions relevant to in vitro toxicological evaluations. Nanotoxicology 3(4):276–283
Chen J, Xiu Z, Lowry GV, Alvarez PJJ (2011) Effect of natural organic matter on toxicity and reactivity of nano-scale zero-valent iron. Water Res 45(5):1995–2001
D’Souza L, Prabha Devi DS, Naik CG (2008) Use of Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy to study cadmium-induced changes in Padina tetrastromatica (Hauck). Anal Chem Insights 3:135
Demir V, Ates M, Arslan Z, Camas M, Celik F, Bogatu C, Can ŞS (2015) Influence of alpha and gamma-iron oxide nanoparticles on marine microalgae species. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 95(6):752–757
Deng X, Gao K, Sun J (2012) Physiological and biochemical responses of Synechococcus sp. PCC7942 to Irgarol 1051 and diuron. Aquat Toxicol 122–123(0):113–119
Dickson D, Liu G, Li C, Tachiev G, Cai Y (2012) Dispersion and stability of bare hematite nanoparticles: effect of dispersion tools, nanoparticle concentration, humic acid and ionic strength. Sci Total Environ 419:170–177
El Badawy AM, Scheckel KG, Suidan M, Tolaymat T, 2012. The impact of stabilization mechanism on the aggregation kinetics of silver nanoparticles. Sci Total Environ 429(Supplement C):325–331
Fabrega J, Fawcett SR, Renshaw JC, Lead JR (2009) Silver nanoparticle impact on bacterial growth: effect of pH, concentration, and organic matter. Environ Sci Technol 43(19):7285–7290
Farooq W, Lee Y-C, Han J-I, Darpito CH, Choi M, Yang J-W (2013) Efficient microalgae harvesting by organo-building blocks of nanoclays. Green Chem 15(3):749–755
Ji J, Long Z, Lin D (2011) Toxicity of oxide nanoparticles to the green algae Chlorella sp. Chem Eng J 170(2–3):525–530
Kalive M, Zhang W, Chen Y, Capco D (2012) Human intestinal epithelial cells exhibit a cellular response indicating a potential toxicity upon exposure to hematite nanoparticles. Cell Biol Toxicol 28(5):343–368
Kaplan D, Christiaen D, Arad SM (1987) Chelating properties of extracellular polysaccharides from Chlorella spp. Appl Environ Microbiol 53(12):2953–2956
Keller AA, Wang H, Zhou D, Lenihan HS, Cherr G, Cardinale BJ, Miller R, Ji Z (2010) Stability and aggregation of metal oxide nanoparticles in natural aqueous matrices. Environ Sci Technol 44(6):1962–1967
Kim K-T, Jang M-H, Kim J-Y, Xing B, Tanguay RL, Lee B-G, Kim SD (2012) Embryonic toxicity changes of organic nanomaterials in the presence of natural organic matter. Sci Total Environ 426(0):423–429
Lei C, Zhang L, Yang K, Zhu L, Lin D (2016) Toxicity of iron-based nanoparticles to green algae: effects of particle size, crystal phase, oxidation state and environmental aging. Environ Pollut 218:505–512
Li Z, Greden K, Alvarez PJJ, Gregory KB, Lowry GV (2010) Adsorbed polymer and NOM limits adhesion and toxicity of nano scale zerovalent iron to E. coli. Environ Sci Technol 44(9):3462–3467
Lichtenthaler HK, Wellburn AR (1983) Determinations of total carotenoids and chlorophylls a and b of leaf extracts in different solvents. Biochem Soc Trans 11:591–592
Lin M, Tseng YH, Huang C-P (2015) Interactions between nano-TiO2 particles and algal cells at moderate particle concentration. Front Chem Sci Eng 9(2):242–257
Maurer-Jones MA, Gunsolus IL, Murphy CJ, Haynes CL (2013) Toxicity of engineered nanoparticles in the environment. Anal Chem 85(6):3036–3049
Mishra NP, Mishra RK, Singhal GS (1993) Changes in the activities of anti-oxidant enzymes during exposure of intact wheat leaves to strong visible light at different temperatures in the presence of protein synthesis inhibitors. Plant Physiol 102(3):903–910
Mohamed Z (2008) Polysaccharides as a protective response against microcystin-induced oxidative stress in Chlorella vulgaris and Scenedesmus quadricauda and their possible significance in the aquatic ecosystem. Ecotoxicology 17(6):504–516
Mohapatra M, Anand S (2010) Synthesis and applications of nano-structured iron oxide/hydroxides. Int J Eng Sci Technol 2(8):127–146
Nason JA, McDowell SA, Callahan TW (2012) Effects of natural organic matter type and concentration on the aggregation of citrate-stabilized gold nanoparticles. J Environ Monitor 14(7):1885–1892
Palomino D, Stoll S (2013) Fulvic acids concentration and pH influence on the stability of hematite nanoparticles in aquatic systems. J Nanopart Res 15(2):1428
Schwab F, Bucheli TD, Lukhele LP, Magrez A, Nowack B, Sigg L, Knauer K (2011) Are carbon nanotube effects on green algae caused by shading and agglomeration? Environ Sci Technol 45(14):6136–6144
Stumm W, Morgan JJ (2012) Aquatic chemistry: chemical equilibria and rates in natural waters. Wiley, Hoboken
Tran N, Mir A, Mallik D et al (2010) Bactericidal effect of iron oxide nanoparticles on Staphylococcus aureus. Int J Nanomed 5:277–283
Van Hoecke K, De Schamphelaere KAC, Van der Meeren P, Smagghe G, Janssen CR (2011) Aggregation and ecotoxicity of CeO2 nanoparticles in synthetic and natural waters with variable pH, organic matter concentration and ionic strength. Environ Pollut 159(4):970–976
Wang Z, Li J, Zhao J, Xing B (2011) Toxicity and internalization of CuO nanoparticles to prokaryotic alga Microcystis aeruginosa as affected by dissolved organic matter. Environ Sci Technol 45(14):6032–6040
Zhou K, Hu Y, Zhang L, Yang K, Lin D, 2016. The role of exopolymeric substances in the bioaccumulation and toxicity of Ag nanoparticles to algae. Sci Rep 6
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful for the financial support from Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20140713) and China Postdoctoral Science Foundation Funded Project (No. 2015M571764), Jiangsu Collaborative Innovation Center for Solid Organic Waste Resource Utilization and Co-Innovation Center for Jiangsu Marine Bio-Industry Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, M., Chen, Y., Yan, Y. et al. Influence of Interaction Between α-Fe2O3 Nanoparticles and Dissolved Fulvic Acid on the Physiological Responses in Synechococcus sp. PCC7942. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 99, 719–727 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-017-2199-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-017-2199-y