Abstract
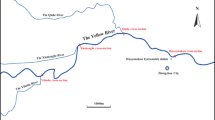
Estrogenic activities and main causative fractions in three representative sections of Yangtze River (Nanjing section) were determined. The results showed that significant vitellogenin (VTG) and 17β-estradiol (E2) induction and gonad atrophy were observed. Estradiol equivalents of actual water samples from Jiangxinzhou section, Sanchahe section and Daqiao section were 0.3651, 0.1301 and 0.5060 ng L−1, respectively. Polar contaminants were responsible for the estrogenic activities in Jiangxinzhou section and Daqiao section while mid-polar and nonpolar contaminants resulted in majority of the estrogenic activity in Sanchahe section. To Jiangxinzhou section, Sanchahe section and Daqiao section, good positive correlations between VTG and E2 (the correlation coefficients were 0.737, 0.690 and 0.817, respectively) and good inverse correlations between VTG and gonado-somatic index (GSI; the correlation coefficients were −0.838, −0.540 and −0.794, respectively) were obtained, whereas the correlations between E2 and GSI were relatively poor (the correlation coefficients were only −0.557, −0.620 and −0.509, respectively).




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Brion F, Tyler CR, Palazzi X, Laillet B, Porcher JM, Garric J, Flammarion P (2004) Impacts of 17β-estradiol, including environmentally relevant concentrations, on reproduction after exposure during embryo-larval-, juvenile- and adult-life stages in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Aquat Toxicol 68:193–217
Coors A, Jones PD, Glesy JP, Ratte HT (2004) Assessing the elimination of estrogenic activity in advanced wastewater treatment with a reporter genebased bioassay. Water Sci Technol 50:181–188
Desbrow C, Routledge EJ, Brighty GC, Sumpter JP, Waldock M (1998) Identification of estrogenic chemicals in STW effluent. 1. Chemical fractionation and in vitro biological screening. Environ Sci Technol 32:1549–1558
Dick Vethaak A, Lahr J, Kuiper RV, Grinwis GCM, Rankouhi TR, Giesy JP, Gerritsen A (2003) Estrogenic effects in fish in The Netherlands: some preliminary results. Toxicology 181–182:147–150
Folmar LC, Hemmer M, Hemmer R, Bowman C, Kroll K, Denslow ND (2000) Comparative estrogenicity of estradiol, ethynyl estradiol and diethylstilbestrol in an in vivo, male sheepshead minnow (Cyprinodon 6ariegatus), vitellogenin bioassay. Aquat Toxicol 49:77–88
Hashimoto S, Bessho H, Hara A, Nakamura M, Iguchi T, Fujita K (2000) Elevated serum vitellogenin levels and gonadal abnormalities in wild male founder (Pleuronectes yokohamae) from Tokyo Bay, Japan. Mar Environ Res 49:37–53
Hu JY, An LH, Sun XH, Zhang HF, Deng BS (2003) Investigation of vitellogenin in wild crucian (Carassius auratus) Tianjin. China Environ Sci 23:281–284
Li ZL, Li YQ, Chen HG, Xu Y, Kong ZM, Liu ZT (2006) Evaluation of genotoxic effects induced by organic pollutants in the Yangtze River in Nanjing section. Res Environ Sci 19:105–108
Ma M, Rao KF, Wang ZJ (2007) Occurrence of estrogenic effects in sewage and industrial wastewaters in Beijing, China. Environ Pollut 147:331–336
Metcalfe CD, Metcalfe TL, Kiparissis Y, Koenig BG, Khan C, Hughes RJ, Croley TR, March RE, Potter T (2001) Estrogenic potency of chemicals detected in sewage treatment plant effluents as determined by in vivo assays with Japanese medaka (Oryzias latipes). Environ Toxicol Chem 20:297–308
Milnes MR, Bermudez DS, Bryan TA, Edwards TM, Gunderson MP, Larkin ILV, Moore BC, Guillette LJ Jr (2006) Contaminant-induced feminization and demasculinization of nonmammalian vertebrate males in aquatic environments. Environ Res 100:3–17
Oh SM, Choung SY, Sheen YY, Chung KH (2000) Quantitative assessment of estrogenic activity in the water environment of Korea by the E-SCREEN assay. Sci Total Environ 263:161–169
Pawlowski S, van Aerle R, Tyler CR, Braunbecka T (2004) Effects of 17α-ethinylestradiol in a fathead minnow (Pimephales promelas) gonadal recrudescence assay. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 57:330–345
Peng G (2006) Present state and protection countermeasure for fishery resources in the Yangtze River in Jiangsu section. Fish Econ Res 23:18–21
Pojana G, Gomiero A, Jonkers N, Marcomini A (2007) Natural and synthetic endocrine disrupting compounds (EDCs) in water, sediment and biota of a coastal lagoon. Environ Int 33:929–936
Rempel MA, Reyes J, Steinert S, Hwang W, Armstrong J, Sakamoto K, Kelley K, Schlenk D (2006) Evaluation of relationships between reproductive metrics, gender and vitellogenin expression in demersal flatfish collected near the municipal wastewater outfall of Orange County, California, USA. Aquat Toxicol 77:241–249
Roy LA, Armstrong JL, Sakamoto K, Steinert S, Perkins E, Lomax DP, Johnson LL, Schlenk D (2003) The relationships of biochemical endpoints to histopathology and population metrics in feral flatfish species collected near the municipal wastewater outfall of Orange County, California, USA. Environ Toxicol Chem 22:1309–1317
Shen JH, Gutendorf B, Vahl HH, Shen L, Westendorf J (2001) Toxicological profile of pollutants in surface water from an area in Taihu Lake, Yangtze Delta. Toxicology 166:71–78
Solé M, Raldua D, Piferrer F, Barceló D, Porte C (2003) Feminization of wild carp, Cyprinus carpio, in a polluted environment: plasma steroid hormones, gonadal morphology and xenobiotic metabolizing system. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 136:145–156
Sun QF, Deng SB, Huang J, Shen G, Yu G (2008) Contributors to estrogenic activity in wastewater from a large wastewater treatment plant in Beijing, China. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 25:20–26
Sun LW, Zha JM, Wang ZJ (2009) Interactions between estrogenic chemicals in binary mixtures investigated using vitellogenin induction and factorial analysis. Chemosphere 75:410–415
Thompson S, Tilton F, Schlenk D, Benson WH (2000) Comparative vitellogenic responses in three teleost species: extrapolation to in situ field studies. Mar Environ Res 51:185–189
Tilton F, Benson WH, Schlenk D (2002) Evaluation of estrogenic activity from a municipal wastewater treatment plant with predominantly domestic input. Aquat Toxicol 61:211–224
Todorov JR, Elskus AA, Schlenk D, Lee Ferguson P, Brownawell BJ, McElroy AE (2002) Estrogenic responses of larval sunshine bass (Morone saxatilis × M. Chrysops) exposed to New York city sewage effluent. Mar Environ Res 54:691–695
Acknowledgments
This research was financially supported by the Key Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China (50830304), China’s National Basic Research Program (2008CB418203) and the Key Project of Chinese Ministry of Education (109076).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, W.T., Lu, G.H., Wang, C. et al. Study on Environmental Estrogen Pollution in Yangtze River (Nanjing Section) by an In Vivo Bioassay. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 84, 406–412 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-010-9944-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-010-9944-9