Abstract
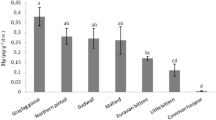
Persian Gulf supports diverse ecosystems and biota in need of remediation and protection, and metal data from this region is needed. Mercury (Hg) in tissues of three waders (Black-winged Stilt Himantopus himantous, Red-wattled Plover Hoplopterus indicus, and White-tailed Plover Vanellus leucurus) from Shadegan Wetlands is reported. Black-winged Stilt had higher Hg in feather (6.6 ± 0.6 μg/g dry weight), liver (3.5 ± 1 μg/g dry weight), kidney (4.5 ± 0.8 μg/g dry weight) and muscle (1.2 ± 0.2 μg/g dry weight) (not statistically significant). Differences in Hg among waders could have resulted from diverse feeding habitats and dissimilar foraging sites.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Majid NB, Preston MR (2000) Factors influencing the total mercury and methyl mercury in the hair of the fishermen of Kuwait. Environ Pollut 109:239–250
Burger J (1993) Metals in avian feathers: bioindicators of environmental pollution. Rev Environ Toxicol 5:203–311
Burger J, Gochfeld M (1991) Lead, mercury, and cadmium in feathers of tropical terns in Puerto Rico and Australia. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 21:311–315
Burger J, Gochfeld M (1993) Heavy metal and selenium levels in feathers of young egrets and herons from Hong kong and Szechan, China. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 25:322–327
Dam M, Hoydal K, Jensen JK (2004) Mercury in liver, eggs and feather of black guillemot Cepphus grylle faeroeensis in the Fareo Islands. Frooskaparrit 52:73–84
Eagles-Smith CA, Ackerman JT, Adelsbach TL, Takekawa JY, Miles AK, Keister RA (2008) Mercury correlations among six tissues for four waterbird species breeding in San Francisco Bay, California, USA. Environ Toxicol Chem 10:2136–2153
Eisler R (1987) Mercury hazards to fish, wildlife, and invertebrates: a synoptic review. US Fish Wildl Serv Biol Rep 85(1.10):85
Evans MI (1994) Important bird areas in the Middle East. BirdLife International, Cambridge, UK
Evans PR, Moon SJ (1981) Heavy metals in shore birds and their prey, in northeast England. In: Say PJ, Whitton BA (eds) Heavy metals in Northern England: environmental and biological aspects. University of Durham, Durham, pp 181–190
Evers DC, Burgess NM, Champoux L, Hoskins B, Major A, Goodale WM, Taylor RJ, Poppenga R, Daigle T (2005) Patterns and interpretation of mercury exposure in freshwater avian communities in Northeastern North America. Ecotoxicology 14:193–221
Furness RW (1993) Birds as monitors of pollutants. In: Furness RW, Greenwood JJD (eds) Birds as monitors of environmental change. Chapman & Hall, London, UK, p 103
Furness RW, Thompson DR, Walsh PM (1990) Evidence from biological samples for historical changes in global metal pollution. In: Furness RW, Rainbow PS (eds) Heavy metal in the marine environment. CRC Press, New York, pp 219–225
Gochfeld M, Burger J (1987) Heavy metal concentrations in the liver of three duck species: influence of species and sex. Environ Pollut Ser A 45:1–15
Holm S (1979) A simple sequentially rejective multiple test procedure. Scan J Stat 6:65–70
Honda K, Min BY, Tatsukawa R (1986) Distribution of heavy metals and their age-related changes in the Eastern Great White Egret, Egretta alba modesta, in Korea. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 15:185–197
Hui CA, Takekawa JY, Warnock SE (2001) Contaminant profiles of two species of shorebirds foraging together at two neighboring sites in South San Francisco Bay, California. Environ Monitor Assess 71:107–121
Hutton M (1981) Accumulation of heavy metals and selenium in three seabird species from the United Kingdom. Environ Pollut 26:129–145
Lee DP, Honda K, Tatsukawa R, Won PO (1989) Distribution and residue level of mercury, cadmium and lead in Korean birds. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 43:550–555
Sterry P, Cleave A, Clements A, Goodfellow P (2001) Birds of Britain and Europe. Norfolk House, London
Zamani-Ahmadmahmoodi R, Esmaili-Sari A, Ghasempoury SM, Savabieasfahani M (2008) Mercury levels in selected tissues of three kingfisher species; Ceryle rudis, Alcedo atthis, and Halcyon smyrnensi, from Shadegan Marshes of Iran. Ecotoxicology 18:319–324
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Bahram Hassanzade Kiabi for insightful comments; and Morteza Davodi, Alireza Nikvarz, Mohamad-mehdi Hosseini and Mostafa Alahverdi for field assistance. This work was funded by Tarbiat Modares University of Iran.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zamani-Ahmadmahmoodi, R., Esmaili-Sari, A., Savabieasfahani, M. et al. Mercury Pollution in Three Species of Waders from Shadegan Wetlands at the Head of the Persian Gulf. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 84, 326–330 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-010-9933-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-010-9933-z