Abstract
Purpose
This study aimed to assess the evolution of imaging patterns over time in patients with neurological complications caused by reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome.
Methods
A total of 24 consecutive patients with reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome presenting between 2009 and 2016 were included, whose disease course was complicated by intracranial hemorrhage and/or ischemic events. In total 55 angiographic studies were carried out. The nature of the intracranial complication and location of vasoconstriction on the angiograms in relation to the time interval since symptom-onset were assessed.
Results
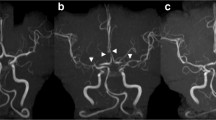
Complications included subarachnoid hemorrhage (n = 19, 79%), intracerebral hemorrhage (n = 7, 29%), ischemic stroke (n = 6, 25%), and transient ischemic attack (n = 4, 17%). Hemorrhagic complications mainly occurred within 7 days after symptom onset (18/19 patients, 95%), whereas ischemic events only occurred after the first week (10/10 patients, 100%, p < 0.00001). Distal vasospasm was predominantly observed within 7 days (26/28 angiograms, 93%) and proximal vasospasm ≥7 days (23/27 angiograms, 85%, p < 0.00001).
Conclusion
In reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome causing neurological complications, an early hemorrhagic phase with distal vasospasm and a delayed ischemic phase with proximal vasospasm can be discriminated.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ducros A. Reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome. Lancet Neurol. 2012;11:906–17.
Ducros A, Fiedler U, Porcher R, Boukobza M, Stapf C, Bousser MG. Hemorrhagic manifestations of reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome: frequency, features, and risk factors. Stroke. 2010;41:2505–11.
Miller TR, Shivashankar R, Mossa-Basha M, Gandhi D. Reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome, part 1: epidemiology, pathogenesis, and clinical course. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2015;36:1392–9.
Miller TR, Shivashankar R, Mossa-Basha M, Gandhi D. Reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome, part 2: diagnostic work-up, imaging evaluation, and differential diagnosis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2015;36:1580–8.
Chen SP, Fuh JL, Wang SJ, Chang FC, Lirng JF, Fang YC, Shia BC, Wu JC. Magnetic resonance angiography in reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndromes. Ann Neurol. 2010;67:648–56.
Ducros A, Boukobza M, Porcher R, Sarov M, Valade D, Bousser MG. The clinical and radiological spectrum of reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome. A prospective series of 67 patients. Brain. 2007;130:3091–101.
Calabrese LH, Dodick DW, Schwedt TJ, Singhal AB. Narrative review: reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndromes. Ann Intern Med. 2007;146:34–44.
Marder CP, Donohue MM, Weinstein JR, Fink KR. Multimodal imaging of reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome: a series of 6 cases. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2012;33:1403–10.
Topcuoglu MA, Singhal AB. Hemorrhagic reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome. Features and mechanisms. Stroke. 2016;47:1742–7.
Singhal AB, Hajj-Ali RA, Topcuoglu MA, Fok J, Bena J, Yang D, Calabrese LH. Reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndromes: analysis of 139 cases. Arch Neurol. 2011;68:1005–12.
Singhal AB. Postpartum angiopathy with reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy. Arch Neurol. 2004;61:411–6.
Mandell DM, Matouk CC, Farb RI, Krings T, Agid R, terBrugge K, Willinsky RA, Swartz RH, Silver FL, Mikulis DJ. Vessel wall MRI to differentiate between reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome and central nervous system vasculitis: preliminary results. Stroke. 2012;43:860–2.
Obusez EC, Hui F, Hajj-Ali RA, Cerejo R, Calabrese LH, Hammad T, Jones SE. High-resolution MRI vessel wall imaging: spatial and temporal patterns of reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome and central nervous system vasculitis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2014;35:1527–32.
Shimoda M, Oda S, Shigematsu H, Hoskikawa K, Imai M, Komatsu F, Hirayama A, Osada T. Clinical significance of centripetal propagation of vasoconstriction in patients with reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome. Cephalalgia. 2018;38:1864–75. https://doi.org/10.1177/0333102418762471
Singhal AB, Topcuoglu MA. Glucocorticoid-associated worsening in reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome. Neurology. 2017;88:228–36.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
B. Xing, S. Lenck, T. Krings, J. Hengwei, C.S. Jaigobin and J.D. Schaafsma declare that they have no competing interests.
Caption Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xing, B., Lenck, S., Krings, T. et al. Angiographic Characteristics of Hemorrhagic and Ischemic Phases of Reversible Cerebral Vasoconstriction Syndrome. Clin Neuroradiol 30, 85–89 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00062-018-0736-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00062-018-0736-7