Abstract
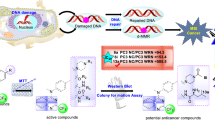
The lysine-specific demethylase enzyme (LSD1) is a potential therapeutic target in cancer, which has a significant role in oncogenic processes such as cellular plasticity, cell motility and metabolic reprogramming. LSD1 is overexpressed in many cancer types such as, non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), estrogen receptor (ER)-negative breast cancer, prostate cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma, acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and others. The down regulation of LSD1 increases the apoptotic activity of cancer cells, thus its inhibition using small molecules could result in cancer cell death and tumour regression. In a previous study, a series of compounds with amino-carboxamide benzothiazole scaffold has been designed, synthesized, and tested against LSD1 enzyme resulting in the identification of the hit inhibitor 1 with IC50 value of 18.4 µM. In this study, hit-to-lead optimization process of the hit inhibitor 1 was implemented through the synthesis and in vitro evaluation of twenty-four analogues aiming to enhance hit inhibitor 1 potency and to explore the structure-activity relationship map of amino-carboxamide benzothiazole series as LSD1 inhibitors. Inhibitors 26 and 30 showed the best inhibitory activity with IC50 values equal to 4.64 and 4.35 µM, respectively. The results from this study helped in understanding the structural requirements of amino-carboxamide benzothiazole as LSD1 inhibitors, which would pave the way towards identifying novel drug candidates with potential anticancer activity.
Graphical Abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen Y, Yang Y, Wang F, Wan K, Yamane K, Zhang Y, et al. Crystal structure of human histone lysine-specific demethylase 1 (LSD1). Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2006;103:13956–61.
Hosseini A, Minucci S. A comprehensive review of lysine-specific demethylase 1 and its roles in cancer. Epigenomics. 2017;9:1123–42.
Hino S, Kohrogi K, Nakao M. Histone demethylase LSD1 controls the phenotypic plasticity of cancer cells. Cancer Sci. 2016;107:1187–92.
Lynch JT, Harris WJ, Somervaille TC. LSD1 inhibition: a therapeutic strategy in cancer?. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2012;16:1239–49.
Song Y, Zhang H, Yang X, Shi Y, Yu B. Annual review of lysine-specific demethylase 1 (LSD1/KDM1A) inhibitors in 2021. Eur J Med Chem. 2022;228:114042.
Fang Y, Yang C, Teng D, Su S, Luo X, Liu Z, et al. Discovery of higenamine as a potent, selective and cellular active natural LSD1 inhibitor for MLL-rearranged leukemia therapy. Bioorganic Chem. 2021;109:104723.
Agboyibor C, Dong J, Effah CY, Drokow EK, Pervaiz W, Liu HM. LSD1 as a Biomarker and the Outcome of Its Inhibitors in the Clinical Trial: The Therapy Opportunity in Tumor. J Oncol. 2021;2021:5512524.
Dai X-J, Liu Y, Xue LP, Xiong XP, Zhou Y, Zheng YC, et al. Reversible Lysine Specific Demethylase 1 (LSD1) Inhibitors: A Promising Wrench to Impair LSD1. J Med Chem. 2021;64:2466–88.
Li C, Su M, Zhu W, Kan W, Ge T, Xu G, et al. Structure–Activity Relationship Study of Indolin-5-yl-cyclopropanamine Derivatives as Selective Lysine Specific Demethylase 1 (LSD1) Inhibitors. J Med Chem. 2022;65:4335–49.
Zhang X, Wang X, Wu T, Yin W, Yan J, Sun Y, et al. Therapeutic potential of targeting LSD1/ KDM1A in cancers. Pharmacol Res. 2022;175:105958.
Kanouni T, Severin C, Cho RW, Yuen NYY, Xu J, Shi L, et al. Discovery of CC-90011: A Potent and Selective Reversible Inhibitor of Lysine Specific Demethylase 1 (LSD1). J Med Chem. 2020;63:14522–9.
Sartori L, Mercurio C, Amigoni F, Cappa A, Faga G, Fattori R, et al. Thieno[3,2-b]pyrrole-5-carboxamides as New Reversible Inhibitors of Histone Lysine Demethylase KDM1A/LSD1. Part 1: High-Throughput Screening and Preliminary Exploration. J Med Chem. 2017;60:1673–92.
Vianello P, Sartori L, Amigoni F, Cappa A, Faga G, Fattori R, et al. Thieno[3,2-b]pyrrole-5-carboxamides as New Reversible Inhibitors of Histone Lysine Demethylase KDM1A/LSD1. Part 2: Structure-Based Drug Design and Structure–Activity Relationship. J Med Chem. 2017;60:1693–715.
Chen Y, Jie W, Yan W, Zhou K, Xiao Y. Lysine-specific histone demethylase 1 (LSD1): A potential molecular target for tumor therapy. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2012;22:53–9.
Maiques-Diaz A, Somervaille TC. LSD1: biologic roles and therapeutic targeting. Epigenomics. 2016;8:1103–16.
Yang GJ, Lei PM, Wong SY, Ma DL, Leung CH, Pharmacological Inhibition of LSD1 for Cancer Treatment. Molecules, 2018. 23.
Fang Y, Liao G, Yu B. LSD1/KDM1A inhibitors in clinical trials: advances and prospects. J Hematol Oncol. 2019;12:129.
Fang Y, Liao G, Yu B. LSD1/KDM1A inhibitors in clinical trials: advances and prospects. J Hematol Oncol. 2019;12:129.
Ishikawa Y, Gamo K, Yabuki M, Takagi S, Toyoshima K, Nakayama K, et al. A Novel LSD1 Inhibitor T-3775440 Disrupts GFI1B-Containing Complex Leading to Transdifferentiation and Impaired Growth of AML Cells. Mol Cancer Ther. 2017;16:273–84.
Ueda R, Suzuki T, Mino K, Tsumoto H, Nakagawa H, Hasegawa M, et al. Identification of Cell-Active Lysine Specific Demethylase 1-Selective Inhibitors. J American Chem Society. 2009;131:17536–7.
Hayward D, Cole PA. LSD1 Histone Demethylase Assays and Inhibition. Methods Enzymol. 2016;573:261–78.
Johnson DS, Weerapana E, Cravatt BF. Strategies for discovering and derisking covalent, irreversible enzyme inhibitors. Future Med Chem. 2010;2:949–64.
Hitchin JR, Blagg J, Burke R, Burns S, Cockerill MJ, Fairweather EE, et al. Development and evaluation of selective, reversible LSD1 inhibitors derived from fragments. MedChemComm. 2013;4:1513–22.
Zheng Y-C, Duan YC, Ma JL, Xu RM, Zi X, Lv WL, et al. Triazole–Dithiocarbamate Based Selective Lysine Specific Demethylase 1 (LSD1) Inactivators Inhibit Gastric Cancer Cell Growth, Invasion, and Migration. J Med Chem. 2013;56:8543–60.
Ma L-Y, Zheng YC, Wang SQ, Wang B, Wang ZR, Pang LP, et al. Design, Synthesis, and Structure–Activity Relationship of Novel LSD1 Inhibitors Based on Pyrimidine–Thiourea Hybrids As Potent, Orally Active Antitumor Agents. J Med Chem. 2015;58:1705–16.
Wu F, Zhou C, Yao Y, Wei L, Feng Z, Deng L, et al. 3-(Piperidin-4-ylmethoxy)pyridine Containing Compounds Are Potent Inhibitors of Lysine Specific Demethylase 1. J Med Chem. 2016;59:253–63.
Yu B, Qi PP, Shi XJ, Huang R, Guo H, Zheng YC, et al. Efficient synthesis of new antiproliferative steroidal hybrids using the molecular hybridization approach. Eur J Med Chem. 2016;117:241–55.
Wang J, Lu F, Ren Q, Sun H, Xu Z, Lan R, et al. Novel histone demethylase LSD1 inhibitors selectively target cancer cells with pluripotent stem cell properties. Cancer Res. 2011;71:7238–49.
Hazeldine S, Pachaiyappan B, Steinbergs N, Nowotarski S, Hanson AS, Casero RA Jr, et al. Low molecular weight amidoximes that act as potent inhibitors of lysine-specific demethylase 1. J Med Chem. 2012;55:7378–91.
Dulla B, Kirla KT, Rathore V, Deora GS, Kavela S, Maddika S, et al. Synthesis and evaluation of 3-amino/guanidine substituted phenyl oxazoles as a novel class of LSD1 inhibitors with anti-proliferative properties. Org Biomol Chem. 2013;11:3103–7.
Li L, Li R, Wang Y. Identification of selective and reversible LSD1 inhibitors with anti-metastasis activity by high-throughput docking. Bioorganic Med Chem Lett. 2019;29:544–8.
Reed DR, Chawla SP, Setty B, Mascarenhas L, Meyers PA, Metts J, et al. Phase 1 trial of seclidemstat (SP-2577) in patients with relapsed/refractory Ewing sarcoma. J Clinical Oncol. 2021;39:11514–11514.
Alnabulsi S, Al-Hurani EA, Al-shar'i NA, El-Elimat T. Amino-carboxamide benzothiazoles as potential LSD1 hit inhibitors. Part I: Computational fragment-based drug design. J Mol Graph Model. 2019;93:107440.
Duan YC, Guan YY, Zhai XY, Ding LN, Qin WP, Shen DD, et al. Discovery of resveratrol derivatives as novel LSD1 inhibitors: Design, synthesis and their biological evaluation. Eur J Med Chem. 2017;126:246–58.
Rezki N. A Green Ultrasound Synthesis, Characterization and Antibacterial Evaluation of 1,4-Disubstituted 1,2,3-Triazoles Tethering Bioactive Benzothiazole Nucleus. Molecules. 2016;21:505.
Ali R, Siddiqui N. New benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl-aminoacetamides as potential anticonvulsants: synthesis, activity and prediction of molecular properties. Arch Pharm. 2015;348:254–65.
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank the Deanship of Scientific Research at Jordan University of Science and Technology, Jordan for financial support (Grant ID 20190241).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Al bustanji, D., Alnabulsi, S. & Al-Hurani, E.A. Hit-to-lead optimization of amino-carboxamide benzothiazoles as LSD1 inhibitors. Med Chem Res 32, 910–929 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-023-03046-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-023-03046-6