Abstract
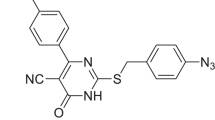
SecA, a key component of the bacterial Sec-dependent secretion pathway, is an attractive target for the development of new antimicrobial agents. We have previously reported pyrimidine analogs as SecA inhibitors. Herein, we report an extension of the earlier work in the synthesis and evaluation of a series of 15 5-cyanothiouracil derivatives as SecA inhibitors. All the compounds have been evaluated for their inhibition of SecA ATPase (EcSecAN68) and for their antimicrobial activity against Escherichia coli NR698 (a leaky mutant) and Bacillus anthracis Sterne. Twelve compounds showed IC50 of less than 6.3 μM when tested against EcSecAN68. In antimicrobial studies against E. coli NR698, six compounds showed MIC of <12.5 μM with three being less than 6.3 μM. Against B. anthracis Sterne, three compounds showed MIC of <6.3 μM.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Levy SB, Marshall B. Antibacterial resistance worldwide: causes, challenges and responses. Nat Med. 2004;10:S122–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm1145.
Smets D, Loos MS, Karamanou S, Economou A. Protein transport across the bacterial plasma membrane by the Sec pathway. Protein J. 2019;38:262–73. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10930-019-09841-8.
Catipovic MA, Bauer BW, Loparo JJ, Rapoport TA. Protein translocation by the SecA ATPase occurs by a power-stroke mechanism. Embo J. 2019;38. https://doi.org/10.15252/embj.2018101140.
Chaudhary AS, Chen W, Jin J, Tai PC, Wang B. SecA: a potential antimicrobial target. Future Med Chem. 2015;7:989–1007. https://doi.org/10.4155/fmc.15.42.
Kusters I, Driessen AJ. SecA, a remarkable nanomachine. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2011;68:2053–66. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-011-0681-y.
Hsieh YH, Zhang H, Lin BR, Cui N, Na B, Yang H, et al. SecA alone can promote protein translocation and ion channel activity: SecYEG increases efficiency and signal peptide specificity. J Biol Chem. 2011;286:44702–9. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M111.300111.
Banerjee T, Zheng Z, Abolafia J, Harper S, Oliver D. The SecA protein deeply penetrates into the SecYEG channel during insertion, contacting most channel transmembrane helices and periplasmic regions. J Biol Chem. 2017;292:19693–707. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA117.000130.
Findik BT, Smith VF, Randall LL. Penetration into membrane of amino-terminal region of SecA when associated with SecYEG in active complexes. Protein Sci. 2018;27:681–91. https://doi.org/10.1002/pro.3362.
Cranford-Smith T, Huber D. The way is the goal: how SecA transports proteins across the cytoplasmic membrane in bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2018;365. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsle/fny093.
Ma C, Wu X, Sun D, Park E, Catipovic MA, Rapoport TA, et al. Structure of the substrate-engaged SecA-SecY protein translocation machine. Nat Commun. 2019;10:2872 https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-10918-2.
Gupta R, Toptygin D, Kaiser CM. The SecA motor generates mechanical force during protein translocation. Nat Commun. 2020;11:3802 https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-17561-2.
Cui J, Jin J, Hsieh YH, Yang H, Ke B, Damera K, et al. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of rose bengal analogues as SecA inhibitors. ChemMedChem. 2013;8:1384–93. https://doi.org/10.1002/cmdc.201300216.
Chen W, Huang YJ, Gundala SR, Yang H, Li M, Tai PC, et al. The first low microM SecA inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem. 2010;18:1617–25.
Li M, Huang YJ, Tai PC, Wang B. Discovery of the first SecA inhibitors using structure-based virtual screening. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008;368:839–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2008.01.135.
Chaudhary AS, Jin J, Chen W, Tai PC, Wang B. Design, syntheses and evaluation of 4-oxo-5-cyano thiouracils as SecA inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem. 2015;23:105–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2014.11.017.
Jang MY, De Jonghe S, Segers K, Anné J, Herdewijn P. Synthesis of novel 5-amino-thiazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidines as E. coli and S. aureus SecA inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem. 2011;19:702–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2010.10.027.
Akula N, Trivedi P, Han FQ, Wang N. Identification of small molecule inhibitors against SecA of Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus by structure based design. Eur J Med Chem. 2012;54:919–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2012.05.035.
Akula N, Zheng H, Han FQ, Wang N. Discovery of novel SecA inhibitors of Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus by structure based design. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2011;21:4183–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2011.05.086.
Bamba F, Jinn J, Tai PC, Wang B. Synthesis and biological evaluation of novel 4-oxo-5-cyano thiouracil derivatives as SecA inhibitors. Heterocyc Commun. 2020;26. https://doi.org/10.1515/hc-2020-0100.
Kondoh A, Yorimitsu H, Oshima K. Nucleophilic aromatic substitution reaction of nitroarenes with alkyl- or arylthio groups in dimethyl sulfoxide by means of cesium carbonate. Tetrahedron. 2006;62:2357–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tet.2005.11.073.
Rao PJ, Gopal MV, Shaheen SM, Chakrathi B. Synthesis characterization and biological activity of some pyrimidine derivatives. World J Pham Pharm Sci. 2015;4:896.
Wang W, Yang Q, Zhou R, Fu H-Y, Li R-X, Chen H, et al. Palladium nanoparticles generated from allylpalladium chloride in situ: a simple and highly efficient catalytic system for Mizoroki–Heck reactions. J Organomet Chem. 2012;697:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jorganchem.2011.10.002.
Yi T, Mo M, Fu H-Y, Li R-X, Chen H, Li X-J. Highly efficient Pd/tetraphosphine catalytic system for copper-free sonogashira reactions of aryl bromides with terminal alkynes. Catal Lett. 2012;142:594–600. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-012-0796-2.
Arienti KL, Brunmark A, Axe FU, McClure K, Lee A, Blevitt J, et al. Checkpoint kinase inhibitors: SAR and radioprotective properties of a series of 2-arylbenzimidazoles. J Med Chem. 2005;48:1873–85. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm0495935.
Ruiz N, Falcone B, Kahne D, Silhavy TJ. Chemical conditionality: a genetic strategy to probe organelle assembly. Cell. 2005;121:307–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2005.02.014.
Hanaki H, Labischinski H, Sasaki K, Kuwahara-Arai K, Inaba Y, Hiramatsu K. Mechanism of vancomycin resistance in MRSA strain Mu50. Jpn J Antibiot. 1998;51:237–47.
Acknowledgements
FB was a visiting scholar at GSU when conducting the lab research with partial financial support from the Islamic Development Bank (IDB) under a merit scholarship program. We also acknowledge the partial financial support to PCT and BW (AI104168) by the National Institutes of Health. JJ and ASC were supported by the Molecular Basis of Diseases Fellowship of Georgia State University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bamba, F., Jin, J., Chaudhary, A.S. et al. Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of pyrimidine analogs as SecA inhibitors. Med Chem Res 30, 1334–1340 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-021-02717-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-021-02717-6