Abstract
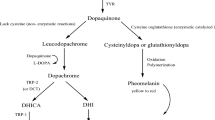
Modeling inhibition data for a series of most potent tyrosinase inhibitors for hyper-pigmentation treatment was done with quantitative structure–activity relationship (QSAR). In this report, multiple linear regression (MLR) methodology coupled with feature selection method, genetic algorithm (GA), was applied to derive QSAR models. A model with seven selected descriptors was obtained by the database that consisted of 49 compounds. The power of the model for prediction was verified with the leave-one-out and leave-group-out cross-validation test, which have values of 0.766 and 0.795, respectively. Moreover, the statistical parameters provided by the GA–MLR model (\( R_{\text{train}}^{ 2} \) = 0.85, \( R_{\text{test}}^{ 2} \) = 0.84, and \( F_{\text{train}}^{ 2} \) = 24.498) lead to a better understanding of the structural requirements of designing novel potent tyrosinase inhibitors. The study showed that the number of six-membered rings, the branching of a molecule, the van der Waals volume of atoms, the lopping centric index, the global charge transfer in a molecule and atomic masses are the main criteria in the inhibitory activity of compounds.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrawal VK, Khadikar PV (2001) QSAR prediction of toxicity of nitrobenzenes. Bioorg Med Chem 9:3035–3040
Ahmad S, Gromiha MM (2003) Design and training of a neural network for predicting the solvent accessibility of proteins. J Comput Chem 24:1313–1320
Aires-de-Sousa J, Hemmer MC, Gasteiger J (2002) Prediction of 1H NMR chemical shifts using neural networks. Anal Chem 74:80–90
Alijanianzadeh M, Saboury AA (2007) Temperature dependence of activation and inhibition of mushroom tyrosinase by ethyl xanthate. Bull Korean Chem Soc 28:758–762
Alijanianzadeh M, Saboury AA, Mansuri-Torshizi H, Haghbeen K, Moosavi-Movahedi AA (2007) The inhibitory effect of some n-alkyl xanthates on the cresolase and catecholase activities of mushroom tyrosinase. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem 22:239–246
Baek YS, Ryu YB, CurtisLong MJ, Ha TJ, Rengasamy R, Yang MS, Park KH (2008) Tyrosinase inhibitory effects of 1,3-diphenylpropanes from Broussonetia kazinoki. Bioorg Med Chem 17:35–41
Bao K, Dai Y, Zhu ZB, Tu FJ, Zhang WG, Yao XS (2010) Design and synthesis of biphenyl derivatives as mushroom tyrosinase inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem 18:6708–6714
Bonchev D (1983) Information theoretic indices for characterization of chemical structures. RSP/Wiley, Chichetser
Casañola-Martin GM, Hassan Khan MT, Marrero-Ponce Y, Ather A, Sultankhodzhaev MN, Torrens F (2006) New tyrosinase inhibitors selected by atomic linear indices-based classification models. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 16:324–330
Chase MR, Raina K, Bruno J, Sugumaran M (2000) Purification, characterization and molecular cloning of prophenoloxidases from Sarcophaga bullata insect. Biochem Mol Biol 30:953–967
Cho SJ, Seop RJ, Suck WS, Han KS, Park KD (2006) N-benzylbenzamides: a new class of potent tyrosinase inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 16:2682–2684
Decker H, Tuczek F (2000) Phenoloxidase activity of hemocyanins: activation, substrate orientation and molecular mechanism. Trends Biochem Soc 25:392–397
Depczynski U, Frost VJ, Molt K (2000) Genetic algorithms applied to the selection of factors in principal component regression. Anal Chimica Acta 420:217–227
Di Marzio W, Galassi S, Todeschini R, Consolaro F (2001) Traditional versus WHIM molecular descriptors in QSAR approaches applied to fish toxicity studies. Chemosphere 44:401–406
Duck SW, Bae RY, Curtis-Long MJ, Lee CW, Won RH, Chang JK, Hun Park K (2010) Evaluation of anti-pigmentary effect of synthetic sulfonylamino chalcone. Eur J Med Chem 45:2010–2017
Friedman M (1996) Food browning and its prevention: an overview. J Agric Food Chem 44:631–653
Ghani U, Ullah N (2010) New potent inhibitors of tyrosinase: novel clues to binding of 1,3,4-thiadiazole-2(3H)-thiones, 1,3,4-oxadiazole-2(3H)-thiones, 4-amino-1,2,4-triazole-5(4H)-thiones, and substituted hydrazides to the dicopper active site. Bioorg Med Chem 18:4042–4048
Gheibi N, Saboury AA, Mansuri-Torshizi H, Haghbeen K, Moosavi-Movahedi AA (2005) The inhibition effect of some n-alkyl dithiocarbamates on Mushroom tyrosinase. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem 20:393–399
Gheibi N, Saboury AA, Haghbeen K, Rajabi F, Pahlavani AA (2009) Dual effects of aliphatic carboxylic acids on cresolase and catecholase reactions of mushroom tyrosinase. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem 24:1076–1081
Golbraikh A, Tropsha A (2002) Beware of q2! J Mol Graph Model 20:269–276
Gupta S, Singh M, Madan AKJ (1999) A novel topological descriptor for predicting biological activity. J Chem Inf Comput Sci 39:272–277
Habibi-Yangjeh A, Pourbasheer E, Danandeh-Jenagharad M (2008) Prediction of melting point for drug-like compounds using principal component–genetic algorithm–artificial neural network. Bull Korean Chem Soc 29:833–841
Habibi-Yangjeh A, Pourbasheer E, Danandeh-Jenagharad M (2009) Application of principal component-genetic algorithm-artificial neural network for prediction acidity constant of various nitrogen-containing compounds in water. Monatshefte für Chemie Chem Monthly 140:15–27
Hemmateenejad B, Javidnia K, Nematollahi M, Elyasi M (2009) QSAR studies on the antiviral compounds of natural origin. J Iran Chem Soc 6:420–435
Hunger J, Huttner G (1999) Optimization and analysis of force field parameters by combination of genetic algorithms and neural networks. J Comput Chem 20:455–471
Hyper Chem. (2002) Release 7.03 for Windows, molecular modeling system. Hypercube, Inc., Gainesville, FL. http://www.hyper.com/. Accessed 10 Mar 2009
Jaiswal M, Khadikar PV, Scozzafava A, Supuran CT (2004) Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors: the first QSAR study on inhibition of tumor-associated isoenzyme IX with aromatic and heterocyclic sulfonamides. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 14:3283–3290
Jun N, Hong G, Jun K (2007) Synthesis and evaluation of 2,4,6-trihydroxychalcones as a new class of tyrosinase inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem 15:2396–2402
Kapetanovic IM (2008) Computer-aided drug discovery and development (CADDD): in silico-chemico-biological approach. Chemico-Biol Interac 171:165–176
Karbassi F, Saboury AA, Hassan Khan MT, Iqbal Choudhary M, Saifi ZS (2004) Mushroom tyrosinase inhibition by two potent uncompetitive inhibitors. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem 19:349–353
Khajehsharifi H, Pourbasheer E (2008) Genetic-algorithm-based wavelength selection in multicomponent spectrophotometric determination by PLS: application on ascorbic acid and uric acid. J Chin Chem Soc 55:163–170
Khan MTH, Choudhary MI, Ather A, Rahman AU (2006) Modelling of the mushroom tyrosinase and its molecular dynamic (MD) simulations experiments in room and elevated temperatures and the docking interactions with nucleotides. Minerva Biotech 18:181–184
Knaggs MH, McGuigan C, Harris SA, Heshmati P, Cahard D, Gilbert IH, Balzarini J (2000) A QSAR study investigating the effect of l-alanine ester variation on the anti-HIV activity of some phosphoramidate derivatives of d4T. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 10:2075–2078
Kubo WLI (2004) QSAR and kinetics of the inhibition of benzaldehyde derivatives against Sacrophaga neobelliaria phenoloxidase. Bioorg Med Chem 12:701–713
Likhitwitayawuid K, Sornsute A, Sritularaka B, Ploypradith P (2006) Chemical transformations of oxyresveratrol (trans-2,4,3′,5′-tetrahydroxystilbene) into a potent tyrosinase inhibitor and a strong cytotoxic agent. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 16:5650–5653
Mahmood Janlou ML, Abdolmaleki P, Tajbakhsh M, Amanlou P, Eidi A (2012) Quantitative structure–activity relationships study of tyrosinase inhibitors using logistic regression and artificial neural networks. J Iran Chem Soc 9:643–653
Marrero PY (2003) Total and local quadratic indices of the molecular pseudograph’s atom adjacency matrix: applications to the prediction of physical properties of organic compounds. Molecules 8:687–726
Marrero-Ponce Y, Hassan Khan MT, Casañola-Martín GM, Ather A, Sultankhodzhaev MN, Torrens F, Rotondo R (2007a) Prediction of tyrosinase inhibition activity using atom-based bilinear indices. Chem Med Chem 2:449–478
Marrero-Ponce Y, Hassan Khan MT, Casañola-Martín GM, Ather A, Sultankhodzhaev MN, Torrens F (2007b) Bond-based 2D TOMOCOMD-CARDD approach for drug discovery: aiding decision-making in ‘in silico’ selection of new lead tyrosinase inhibitors. J Comput-Aided Mol Des 21:167–188
Moosavi-Movahedi AA, Safarian S, Hakimelahi GH, Ataei G, Ajloo D, Panjehpour S, Riahi S, Mousavi MF, Mardanyan S, Soltani N, Khalafi-Nezhad A, Sharghi H, Moghadamnia H, Saboury AA (2004) QSAR analysis for ADA upon interaction with a series of adenine derivatives as inhibitors. Nucleos Nucleot Nucleic Acids 23:613–624
Murumkar PR, Giridhar R, Yadav MR (2008) 3D-quantitative structure–activity relationship studies on benzothiadiazepine hydroxamates as inhibitors of tumor necrosis factor-alpha converting enzyme. Chem Biol Drug Des 71:363–373
Noh JM, Kwak SY, Seo HS, Seo JH, Kim BG, Lee YS (2009) Kojic acid-amino acid conjugates as tyrosinase inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 19:5586–5589
Pasha FA, Neaz MM, Cho SJ, Kang SB (2007) Quantitative structure–activity relationship (QSAR) study of estrogen derivatives based on descriptors of energy and softness. Chem Biol Drug Des 70:520–529
Saboury AA (2009) Enzyme inhibition and activation: a general theory. J Iran Chem Soc 6:219–229
Saboury AA, Zolghadri S, Haghbeen K, Moosavi-Movahedi AA (2006) The inhibitory effect of benzenethiol on the cresolase and catecholase activities of mushroom tyrosinase. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem 21:711–717
Shapiro S, Guggenheim B (1998) Inhibition of oral bacteria by phenolic compounds. Part 1. QSAR analysis using molecular connectivity. Quant Struct Act Relat 17:327–337
Sharma BK, Pilania P, Singh P, Sharma S, Prabhakar YS (2009) CP-MLR directed QSAR study of carbonic anhydrase inhibitors: sulfonamide and sulfamate inhibitors. Central Eur J Chem 7:909–922
Takahashi S, Kamiya T, Saeki K, Nezu T, Takeuchi S, Takasawa R, Sunaga S, Yoshimori A, Ebizuka S, Abe T, Tanuma S (2010) Structural insights into the hot spot amino acid residues of mushroom tyrosinase for the bindings of thujaplicins. Bioorg Med Chem 18:8112–8118
Taylor SL, Bush RK (1998) Sulfites as food ingredients. Food Tech 40:47–52
Todeschini R, Consonni V (2000) Handbook of molecular descriptors. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim
Todeschini R, Consonni V, Mauri A, Pavan M (2005) DRAGON, version 5.3 for Windows, software for the calculation of molecular descriptors. Talete srl, Milan, Italy. http://www.talete.mi.it/products/dragon_description.htm.. Accessed 10 Apr 2009
Toropov AA, Benfenati E (2006a) QSAR models for daphnia toxicity of pesticides based on combinations of topological parameters of molecular structures. Bioorg Med Chem 14:2779–2788
Toropov AA, Benfenati E (2006b) QSAR models of quail dietary toxicity based on the graph of atomic orbitals. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 16:1941–1943
Tropsha A, Gramatica P, Gombar VK (2003) The importance of being earnest: validation is the absolute essential for successful application and interpretation of QSAR models. QSAR Comb Sci 22(1):69–77
Waller CL, Bradley MP (1999) Development and validation of a novel variable selection technique with application to multidimensional quantitative structure–activity relationship studies. J Chem Inf Comput Sci 39:345–355
Wang Y, Wang XW, Cheng YY (2006) A computational approach to botanical drug design by modeling quantitative composition–activity relationship. Chem Biol Drug Des 68:166–172
Xu J, Hagler A (2002) Chemoinformatics drug discovery. Molecules 7:566–600
Acknowledgments
The support of the Research Councils of the University of Tehran, and Tehran University of Medical Sciences are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bazl, R., Ganjali, M.R., Derakhshankhah, H. et al. Prediction of tyrosinase inhibition for drug design using the genetic algorithm–multiple linear regressions. Med Chem Res 22, 5453–5465 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-012-0440-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-012-0440-0