Abstract
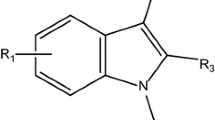
The k nearest neighbor-molecular field analysis (kNN-MFA) is used to study the correlation between the molecular properties and biological activities of the recently reported 2,5-disubstituted imidazo[4,5-c]pyridines as anti-HCV agents. The most predictive kNN-MFA model derived from the superposition of docked conformations, has good cross-validated q 2 (0.96) and satisfied predictive ability \( r_{\text{pred}}^{2} \) (0.88). It could rationalize the HCV inhibitory activity profile of many compounds used in the present study as well as the important structural features responsible for activity. Furthermore, the effects of various structural modifications on biological activity are investigated, and biological activities of novel structures are estimated using the developed 3D QSAR model.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ajmani S, Jadav K, Kulkarni SA (2006) Three dimensional QSAR using k-nearest neighbor method and its interpretation. J Chem Inf Model 46:24–31
Beaulieu PL, Tsantrizos YS (2004) Inhibitors of the HCV NS5B polymerase: new hope for the treatment of hepatitis C infections. Curr Opin Invest Drugs 5:838–850
Choo QL, Kuo G, Weiner AJ, Overbv LR, Bradley DW, Houghton M (1989) Isolation of a cDNA clone derived from a blood-borne non-A, non-B viral hepatitis genome. Science 244:359–362
Cramer RD III, Bunce JD, Patterson DE (1988a) Cross-validation, bootstrapping, and partial least squares compared with multiple regression in conventional QSAR studies. Quant Struct Act Relat 7:18–25
Cramer RD, Patteerson DE, Bunce JD (1988b) Comparative molecular field analysis (CoMFA). 1. Effect of shape on binding of steroids to carrier proteins. J Am Chem Soc 110:5959–5967
Davis GL, Wong JB, McHutchison JG, Manns MP, Harvey J, Albrecht JJ (2003) Early virologic response to treatment with peginterferon alfa-2b plus ribavirin in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology 38:645–652
Fried MW, Shiffman ML, Reddy KR, Smith C, Marinos G, Goncales FL, Haussinger D, Diago M, Carosi G, Dhumeaux D, Craxi A, Lin A, Hoffman J, Yu J (2002) N Engl J Med 347:975–982
Gasteiger J, Marsili M (1980) Iterative partial equalization of orbital electronegativity—a rapid access to atomic charges. Tetrahedron 36:3219–3228
Gordon CP, Keller PA (2005) Control of hepatitis C: a medicinal chemistry perspective. J Med Chem 48:1–20
Halgren TA, Nachbar R (1996) Merck molecular force field. IV. Conformational energies and geometries for MMFF94. J Comput Chem 17:587–615
Hoffmann D, Kramer B, Washio T, Steinmetzer T, Rarey M, Lengauer T (1999) Two-stage method for protein–ligand docking. J Med Chem 42:4422–4433
Manns MP, McHutchison JG, Gordon SC, Rustgi VK, Shiffman M, Reindollar R, Goodman ZD, Koury K, Ling MH, Albrecht JK (2001) International Hepatitis Interventional Therapy Group. Peginterferon alfa-2b plus ribavirin compared with interferon alfa-2b plus ribavirin for initial treatment of chronic hepatitis C: a randomised trial. Lancet 358:958–965
Michael WF (2002) Side effects of therapy of hepatitis C and their management. Hepatology 36:S237–S244
Patil VM, Gupta SP, Samanta S, Masand N (2011) 3D QSAR kNN MFA studies on thiouracil derivatives as hepatitis C virus inhibitors. Med Chem Res 20:1614–1621
Poynard T, Macrellin P, Lee SS, Niederau C, Minuk GS, Ideo G, Bain V, Heathcote J, Zeuzem S, Trepo C, Albrecht J (1998) Randomized trial of interferon alpha2b plus ribavirin for 48 weeks or for 24 weeks versus interferon alpha2b plus placebo for 48 weeks for treatment of chronic infection with hepatitis C virus. International Hepatitis Interventional Therapy Group (IHIT). Lancet 352:1426–1432
Poynard T, Yuen MF, Ratziu V, Lai CL (2003) Viral hepatitis C. Lancet 362:2095–2100
Puerstinger G, Paeshuyse J, Clercq ED, Neyts J (2007a) Antiviral 2,5-disubstituted imidazo[4,5-c]pyridines: from anti-pestiirus to hepatitis C virus activity. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 17:390–393
Puerstinger G, Paeshuyse J, Heinrich S, Mohr J, Schraff N, Clercq ED, Neyts J (2007b) Antiviral 2,5-disubstituted imidazo[4,5-c]pyridines: further optimization of anti-hepatitis C virus activity. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 17:5111–5114
Rarey M, Kramer B, Lengauer T, Klebe G (1996) A fast flexible docking method using an incremental construction algorithm. J Mol Biol 261(3):470–489
Scott LJ, Perry CM (2002) Interferon-alpha-2b plus ribavirin: a review of its use in the management of chronic hepatitis C. Drugs 62:507–556
Sharaf MA, Illman DL, Kowalski BR (1986) Chemometrics. Wiley, New York
Shen M, Tiran AL, Xiao Y, Golbraikh A, Kohn H, Tropsha A (2002) Quantitative structure-activity relationships analysis of funcionalized amino acid anticonvulsant agents using k nearest neighbor and simulated annealing PLS methods. J Med Chem 45:2811–2823
Shepard CW, Alter MJ (2005) Global epidemiology of hepatitis C virus infection. Lancet Infect Dis 5:524–531
Tan SL, Pause A, Shi Y, Sonenberg N (2002) Hepatitis C therapeutics: current status and emerging strategies. Nat Rev Drug Disc 1:867–881
VLife Sciences Private Limited (2002) VLife QSAR Plus, Version 1.0, Pune
Wold S (1978) Cross-validatory estimation of the number of components in factor and principal components models. Technometrics 4:397–405
Zheng W, Tropsha A (2000) Novel variable selection quantitative structure property relationship approach based on k-nearest neighbor principle. J Chem Inf Comput Sci 40:185–194
Acknowledgments
Support in the form of resources from Bharat Institute of Technology and Meerut Institute of Engineering & Technology, Meerut UP (India) is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gupta, S.P., Samanta, S., Masand, N. et al. k nearest neighbor-molecular field analysis on human HCV NS5B polymerase inhibitors: 2,5-disubstituted imidazo[4,5-c]pyridines. Med Chem Res 22, 330–339 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-012-0033-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-012-0033-y