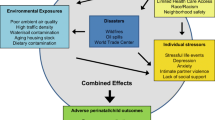
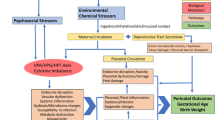
Abstract
Objectives
The aim of this study was to determine the health effects of prenatal exposure to disaster, based on a systematic review of existing research.
Methods
A literature search of scientific databases was conducted in February 2015 for articles on prenatal exposure to a natural or man-made disaster. Data was extracted from all articles that met the inclusion criteria, and we systematically analyzed contents based on type of disaster, health outcome, target group and time after birth.
Results
Prenatal exposure to famine or war was found to be associated with mental health, cardiovascular or metabolic outcomes, with varying degrees of significance. The majority of the studies showed limited or weak associations between exposures and outcomes.
Conclusions
Due to the lack of variety in type of events studied, as well as large methodological variation, it is difficult to draw firm conclusions from existing literature. However, our systematic review highlights the potential of evaluating secondary data, both to accentuate research gaps in the field and to increase the understanding of what effects various types of disasters potentially have on the unborn child.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agay-Shay K, Friger M, Linn S, Peled A, Amitai Y, Peretz C (2013) Ambient temperature and congenital heart defects. Hum Reprod 28(8):2289–2297
Armony-Sivan R, Aviner S, Cojocaru L, Fytlovitch S, Ben-Alon D, Eliassy A, Babkoff H, Lozoff B, Anteby E (2013) Prenatal maternal stress predicts cord-blood ferritin concentration. J Perinat Med 41(3):259–265
Bercovich E, Keinan-Boker L, Shasha SM (2014) Long-term health effects in adults born during the Holocaust. Isr Med Assoc J 16(4):203–207
Brown A, Susser E (1997) Sex differences in prevalence of congenital neural defects after periconceptual famine exposure. Epidemiology 8(1):55–59
Brown AS, Susser ES, Lin SP, Neugebauer R, Gorman JM (1995) Increased risk of affective disorders in males after 2nd trimester prenatal exposure to the Dutch Hunger Winter of 1944–45. Br J Psychiatry 166:601–606
Brown AS, van Os J, Driessens C, Hoek HW, Susser ES (2000) Further evidence of relation between prenatal famine and major affective disorder. Am J Psychiatry 157(2):190–195
Dancause KN, Laplante DP, Fraser S, Brunet A, Ciampi A, Schmitz N, King S (2012) Prenatal exposure to a natural disaster increases risk for obesity in 51/2-year-old children. Pediatr Res 71(1):126–131
Dancause KN, Veru F, Andersen RE, Laplante DP, King S (2013) Prenatal stress due to a natural disaster predicts insulin secretion in adolescence. Early Hum Dev 89(9):773–776
de Rooij SR, Painter RC, Holleman F, Bossuyt PM, Roseboom TJ (2007) The metabolic syndrome in adults prenatally exposed to the Dutch famine. Am J Clin Nutr 86(4):1219–1224
de Rooij SR, Painter RC, Phillips DI, Raikkonen K, Schene AH, Roseboom TJ (2011) Self-reported depression and anxiety after prenatal famine exposure: mediation by cardio-metabolic pathology? J Dev Orig Health Dis 2(3):136–143
Doocy S, Daniels A, Dick A, Kirsch TD (2013a) The Human impact of tsunamis: a historical review of events 1900–2009 and systematic literature review. PLoS Curr. 5. (pii: ecurrents.dis.40f3c5cf61110a0fef2f9a25908cd795)
Doocy S, Daniels A, Dooling S, Gorokhovich Y (2013b) The human impact of volcanoes: a historical review of events 1900–2009 and systematic literature review. PLoS Curr. 5. (pii: ecurrents.dis.841859091a706efebf8a30f4ed7a1901)
Doocy S, Daniels A, Murray S, Kirsch TD (2013c) The human impact of floods: a historical review of events 1980–2009 and systematic literature review. PLoS Curr. 5. (pii: ecurrents.dis.f4deb457904936b07c09daa98ee8171a)
Doocy S, Daniels A, Packer C, Dick A, Kirsch TD (2013d) The human impact of earthquakes: a historical review of events 1980–2009 and systematic literature review. PLoS Curr. 5. (pii: ecurrents.dis.67bd14fe457f1db0b5433a8ee20fb833)
Doocy S, Dick A, Daniels A, Kirsch TD (2013e) The human impact of tropical cyclones: a historical review of events 1980–2009 and systematic literature review. PLoS Curr. 5. (pii: ecurrents.dis.2664354a5571512063ed29d25ffbce74)
Ekamper P, van Poppel F, Stein AD, Lumey LH (2014) Independent and additive association of prenatal famine exposure and intermediary life conditions with adult mortality between age 18–63 years. Soc Sci Med 119:232–239
Ekamper P, van Poppel F, Stein AD, Bijwaard GE, Lumey LH (2015) Prenatal famine exposure and adult mortality from cancer, cardiovascular disease, and other causes through age 63 years. Am J Epidemiol 181(4):271–279
Eskenazi B, Mocarelli P, Warner M, Chee WY, Gerthoux PM, Samuels S, Needham LL, Patterson DG Jr (2003) Maternal serum dioxin levels and birth outcomes in women of Seveso, Italy. Environ Health Perspect 111(7):947–953
Goldhaber MK, Staub SL, Tokuhata GK (1983) Spontaneous abortions after the Three Mile Island nuclear accident: a life table analysis. Am J Public Health 73(7):752–759
Guha-Sapir D, Below R, Hoyois P (2015) EM-DAT: the International Disaster Database Brussels. Belgium: Université Catholique de Louvain. http://www.emdat.be/. Accessed 9 Mar 2015
Harville EW, Xiong X, Buekens P (2010) Disasters and perinatal health: a systematic review. Obstet Gynecol Surv 65(11):713–728
Hernandez-Julian R, Mansour H, Peters C (2014) The effects of intrauterine malnutrition on birth and fertility outcomes: evidence from the 1974 Bangladesh famine. Demography 51(5):1775–1796
Hoek HW, Susser E, Buck KA, Lumey LH, Lin SP, Gorman JM (1996) Schizoid personality disorder after prenatal exposure to famine. Am J Psychiatry 153(12):1637–1639
Hult M, Tornhammar P, Ueda P, Chima C, Bonamy AKE, Ozumba B, Norman M (2010) Hypertension, diabetes and overweight: looming legacies of the Biafran famine. PLoS ONE 5(10):8
King S, Dancause K, Turcotte-Tremblay AM, Veru F, Laplante DP (2012) Using natural disasters to study the effects of prenatal maternal stress on child health and development. Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today 96(4):273–288
Kinney DK, Miller AM, Crowley DJ, Huang E, Gerber E (2008) Autism prevalence following prenatal exposure to hurricanes and tropical storms in Louisiana. J Autism Dev Disord 38(3):481–488
Kleinhaus K, Harlap S, Perrin M, Manor O, Margalit-Calderon R, Opler M, Friedlander Y, Malaspina D (2013) Prenatal stress and affective disorders in a population birth cohort. Bipolar Disord 15(1):92–99
Klooker TK, Braak B, Painter RC, de Rooij SR, van Elburg RM, van den Wijngaard RM, Roseboom TJ, Boeckxstaens GE (2009) Exposure to severe wartime conditions in early life is associated with an increased risk of irritable bowel syndrome: a population-based cohort study. Am J Gastroenterol 104(9):2250–2256
Louphaä CE, Roseboom TJ, Osmond C, Barker DJ, Ravelli AC, Bleker OP, van der Zee JS, van der Meulen JH (2000) Atopy, lung function, and obstructive airway disease after prenatal exposure to famine. Thorax 55(7):555–561
Lumey LH, Martini LH, Myerson M, Stein AD, Prineas RJ (2012) No relation between coronary artery disease or electrocardiographic markers of disease in middle age and prenatal exposure to the Dutch famine of 1944–5. Heart 98(22):1653–1659
Malaspina D, Corcoran C, Kleinhaus KR, Perrin MC, Fennig S, Nahon D, Friedlander Y, Harlap S (2008) Acute maternal stress in pregnancy and schizophrenia in offspring: a cohort prospective study. BMC Psychiatry 8:71
Neugebauer R, Hoek HW, Susser E (1999) Prenatal exposure to wartime famine and development of antisocial personality disorder in early adulthood. JAMA 282(5):455–462
Nour NN (2011) Maternal health considerations during disaster relief. Rev Obstet Gynecol 4(1):22–27
Painter RC, De Rooij SR, Bossuyt PM, Osmond C, Barker DJ, Bleker OP, Roseboom TJ (2006a) A possible link between prenatal exposure to famine and breast cancer: a preliminary study. Am J Hum Biol 18(6):853–856
Painter RC, de Rooij SR, Bossuyt PM, Simmers TA, Osmond C, Barker DJ, Bleker OP, Roseboom TJ (2006b) Early onset of coronary artery disease after prenatal exposure to the Dutch famine. Am J Clin Nutr 84(2):322–327
Peterka M, Peterkova R, Likovsky Z (2004) Chernobyl: prenatal loss of four hundred male fetuses in the Czech Republic. Reprod Toxicol 18(1):75–79
Ravelli ACJ, van der Meulen JHP, Osmond C, Barker DJP, Bleker OP (1999) Obesity at the age of 50 y in men and women exposed to famine prenatally. Am J Clin Nutr 70(5):811–816
Roseboom TJ, van der Meulen JH, Ravelli AC, van Montfrans GA, Osmond C, Barker DJ, Bleker OP (1999) Blood pressure in adults after prenatal exposure to famine. J Hypertens 17(3):325–330
Roseboom TJ, van der Meulen JH, Osmond C, Barker DJ, Ravelli AC, Schroeder-Tanka JM, van Montfrans GA, Michels RP, Bleker OP (2000) Coronary heart disease after prenatal exposure to the Dutch famine, 1944–45. Heart 84(6):595–598
Roseboom TJ, van der Meulen JHP, Osmond C, Barker DJP, Ravelli ACJ, Bleker OP (2001) Adult survival after prenatal exposure to the Dutch famine 1944–5. Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol 15(3):220–225
Schreier NK, Moltchanova EV, Blomstedt PA, Kajantie E, Eriksson JG (2011) Prenatal exposure to wartime stress: long-term effect on coronary heart disease in later life. Ann Med 43(7):555–561
Selten JP, van der Graaf Y, van Duursen R, Gispen-de Wied CC, Kahn RS (1999) Psychotic illness after prenatal exposure to the 1953 Dutch flood disaster. Schizophr Res 35(3):243–245
Selten JP, Cantor-Graae E, Nahon D, Levav I, Aleman A, Kahn RS (2003) No relationship between risk of schizophrenia and prenatal exposure to stress during the Six-Day War or Yom Kippur War in Israel. Schizophr Res 63(1–2):131–135
Skokic F, Muratovic S, Radoja G (2006) Perinatal and maternal outcomes in Tuzla Canton during 1992–1995 war in Bosnia and Herzegovina. Croat Med J 47(5):714–721
Sotomayor O (2013) Fetal and infant origins of diabetes and ill health: evidence from Puerto Rico’s 1928 and 1932 hurricanes. Econ Hum Biol 11(3):281–293
Stein AD, Zybert PA, Lumey LH (2004) Acute undernutrition is not associated with excess of females at birth in humans: the Dutch Hunger Winter. Proc Biol Sci 271(Suppl 4):S138–S141
Stein AD, Zybert PA, van der Pal-de Bruin K, Lumey LH (2006) Exposure to famine during gestation, size at birth, and blood pressure at age 59 years: evidence from the Dutch famine. Eur J Epidemiol 21(10):759–765
Stein AD, Pierik FH, Verrips GHW, Susses ES, Lurney LH (2009) Maternal exposure to the Dutch famine before conception and during pregnancy: quality of life and depressive symptoms in adult offspring. Epidemiology 20(6):909–915
Susser ES, Lin SP (1992) Schizophrenia after prenatal exposure to the Dutch Hunger Winter of 1944–1945. Arch Gen Psychiatry 49(12):983–988
Susser E, Neugebauer R, Hoek HW, Brown AS, Lin S, Labovitz D, Gorman JM (1996) Schizophrenia after prenatal famine: further evidence. Arch Gen Psychiatry 53(1):25–31
Turcotte-Tremblay AM, Lim R (2014) Prenatal maternal stress predicts childhood asthma in girls: project ice storm. Biomed Res Int 2014:201717
United Nations International Strategy for Disaster Reduction (2009) UNISDR terminology on disaster risk reduction [press release]. UNISDR, Geneva
van Abeelen AF, Veenendaal MV, Painter RC, de Rooij SR, Dijkgraaf MG, Bossuyt PM, Elias SG, Grobee DE, Uiterwaal CS, Roseboom TJ (2012) Survival effects of prenatal famine exposure. Am J Clin Nutr 95(1):179–183
Walder DJ, Laplante DP, Sousa-Pires A, Veru F, Brunet A, King S (2014) Prenatal maternal stress predicts autism traits in 6½ year-old children: Project Ice Storm. Psychiatry Res 219(2):353–360
Wilcox AJ, Skjaerven R, Irgens LM (1994) Harsh social conditions and perinatal survival: an age–period–cohort analysis of the World War II occupation of Norway. Am J Public Health 84(9):1463–1467
Yarde F, Broekmans FJ, van der Pal-de Bruin KM, Schonbeck Y, te Velde ER, Stein AD, Lumey LH (2013) Prenatal famine, birthweight, reproductive performance and age at menopause: the Dutch hunger winter families study. Hum Reprod 28(12):3328–3336
Zahran S, Snodgrass JG, Peek L, Weiler S (2010) Maternal hurricane exposure and fetal distress risk. Risk Anal 30(10):1590–1601
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This review is part of the special issue “Driving the Best Science to Meet Global Health Challenges” edited on the occasion of the 9th European Congress on Tropical Medicine and International Health 2015.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saulnier, D.D., Brolin, K. A systematic review of the health effects of prenatal exposure to disaster. Int J Public Health 60, 781–787 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00038-015-0699-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00038-015-0699-2