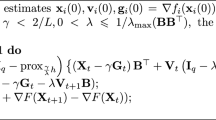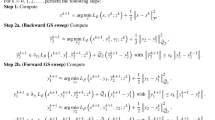Abstract
In this paper, we propose the diffusion sparse sign algorithm with variable step-size for distributed estimation in sparse and impulsive interference environments. Firstly, we address the problem of in-network distributed estimation for sparse vectors under the impulsive noise environment. In order to exploit the sparsity of the vector of interest, we incorporate the sparse norms (\({l_1}\)-norm and \(RW{l_1}\)-norm) into the cost function of the standard diffusion sign algorithm, which accelerates the convergence speed of zero or near-zero components. In addition, we propose the adaptive variable step-size to further improve the convergence rate of the proposed algorithm. The variable step-size is derived by the correlation entropy, which contains a modified Gaussian kernel function and is robust to impulsive noise. In this paper, every node combines its correlation entropy function with the information of its neighborhood to drive the variable step-size at each iteration. Simulation results show that the proposed algorithm outperforms the standard diffusion SA in the sparse and impulsive system and the convergence rate of the proposed algorithm is faster than constant step-size algorithms.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Arablouei, S. Werner, K. Dogancay, Diffusion-based distributed adaptive estimation utilizing gradient-descent total least-squares, in IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (IEEE, 2013), pp. 5308–5312
A. Bertrand, M. Moonen, Consensus-based distributed total least squares estimation in ad hoc wireless sensor networks. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 59(5), 2320–2330 (2011)
J.A. Bazerque, G.B. Giannakis, Distributed spectrum sensing for cognitive radio networks by exploiting sparsity. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 58(3), 1847–1862 (2010)
E.J. Cands, M.B. Wakin, S.P. Boyd, Enhancing sparsity by reweighted \({l_1}\), minimization. J. Fourier Anal. Appl. 14(5–6), 877–905 (2008)
F.S. Cattivelli, A.H. Sayed, Diffusion LMS strategies for distributed estimation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 58(3), 1035–1048 (2010)
F.S. Cattivelli, C.G. Lopes, A.H. Sayed, Diffusion strategies for distributed Kalman filtering: formulation and performance analysis, in Proceedings of the Iapr Workshop on Cognitive Information Processing (2008)
F.S. Cattivelli, A.H. Sayed, Diffusion strategies for distributed Kalman filtering and smoothing. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 55(9), 2069–2084 (2010)
F.S. Cattivelli, A.H. Sayed, Diffusion mechanisms for fixedpoint distributed Kalman smoothing, in Signal Processing Conference (2008)
T. Fan, Y. Lin, A variable step-size strategy based on error function for sparse system identification. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 36, 1301–1310 (2017)
S. Huang, C. Li, Distributed sparse total least-squares over networks. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 63(11), 2986–2998 (2015)
C. Li, P. Shen, Y. Liu, Z. Zhang, Diffusion information theoretic learning for distributed estimation over network. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 61(16), 4011–4024 (2013)
C.G. Lopes, A.H. Sayed, Diffusion least-mean squares over adaptive networks: formulation and performance analysis. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 56(7), 3122–3136 (2008)
C.G. Lopes, A.H. Sayed, Distributed adaptive incremental strategies: formulation and performance analysis. IEEE Int. Conf. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 3, 584–587 (2006)
M. Li, L. Li, H.M. Tai, Variable step size LMS algorithm based on function control. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 32, 3121–3130 (2013)
Y. Liu, C. Li, Z. Zhang, Diffusion sparse least-mean squares over networks. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 60(8), 4480–4485 (2012)
Z. Liu, Y. Liu, C. Li, Distributed sparse recursive least-squares over networks. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 62(6), 1386–1395 (2014)
K. Mayyas, A new variable step size control method for the transform domain LMS adaptive algorithm. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 24(6), 703–721 (2005)
R.K. Martin, W.A. Sethares, R.C. Williamson, C.R. Johnson Jr., Exploiting sparsity in adaptive filters. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 50(8), 1883–1894 (2002)
W. Ma, H. Qu, G. Gui, L. Xu, J. Zhao, B. chen, Maximum correntropy criterion based sparse adaptive filtering algorithms for robust channel estimation under non-Gaussian environments. J. Frankl. Inst. 352(7), 2708–2727 (2015)
J. Ni, J. Chen, Diffusion sign-error LMS algorithm: formulation and stochastic behavior analysis. Signal Process. 128, 142–149 (2016)
S.S. Ram, A. Nedic, V.V. Veeravalli, in Asilomar Conference on stochastic incremental gradient descent for estimation in sensor networks (IEEE, 2007), pp. 582–586
A. Singh, J. Principe, Using correntropy as a cost function in linear adaptive filters, in International Joint Conference on Neural Networks. (IEEE, 2009), pp. 2950–2955
B.W. Silverman, Density Estimation for Statistics and Data Analysis (Chapman and Hall, London, 1986)
I.D. Schizas, G. Mateos, G.B. Giannakis, Distributed LMS for consensus-based in-network adaptive processing. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 8(6), 2365–2381 (2009)
L. Shi, H. Zhao, Variable step size norm-constrained adaptive filtering algorithms. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 36(10), 1–14 (2017)
L. Shi, H. Zhao, Two diffusion proportionate sign subband adaptive filtering algorithms. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 36(10), 1–18 (2017)
S.S. Stankovic, M.S. Stankovic, D.S. Stipanovic, Decentralized parameter estimation by consensus based stochastic approximation. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 56(3), 531–543 (2007)
T. Shao, Y.R. Zheng, J. Benesty, An affine projection sign algorithm robust against impulsive interferences. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 17(4), 327–330 (2010)
X. Shao, F. Chen, Q. Ye, S. Duan, A robust diffusion estimation algorithm with self-adjusting step-size in WSNs. Sensors 17(4), 824 (2017)
W. Wang, J. Zhao, H. Qu, B. Chen, A correntropy inspired variable step-size sign algorithm against impulsive noises. Signal Process. 141, 168–175 (2017)
W. Wang, H. Zhao, B. Chen, Robust adaptive volterra filter under maximum correntropy criteria in impulsive environments. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 36, 4097–4117 (2017)
Z. Wu, S. Peng, B. Chen, H. Zhao, Robust hammerstein adaptive filtering under maximum correntropy criterion. Entropy 17(10), 7149–7166 (2015)
H. Zhu, G. Leus, G.B. Giannakis, Sparsity-cognizant total least-squares for perturbed compressive sampling. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 59(5), 2002–2016 (2011)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported in part by the Doctoral Fund of Southwest University (No. SWU113067), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant Nos. XDJK2017B053, XDJK2017D176, XDJK2017D180, XDJK2017D181) and Chongqing Research Program of Basic Research and Frontier Technology (No. cstc2017jcyjAX2065).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, F., Liu, X., Duan, S. et al. Diffusion Sparse Sign Algorithm with Variable Step-Size. Circuits Syst Signal Process 38, 1736–1750 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-018-0935-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-018-0935-0