Abstract
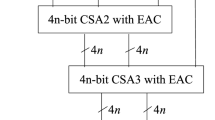
Speed and complexity of a reverse converter are two important factors that affect the performance of a residue number system. In this paper, two efficient reverse converters are proposed for the 4-moduli sets {2\(^{2n-1}-1\), 2\(^{n}\), 2\(^{n}+1\), 2\(^{n}-1\)} and {2\(^{2n-1}\), 2\(^{2n-1}-1\), 2\(^{n}+1\), 2\(^{n}-1\)} with 5\(n\)-bit and 6\(n\)-bit dynamic range, respectively. The proposed reverse converter for moduli set {2\(^{2n-1}-1\), 2\(^{n}\), 2\(^{n}+1\), 2\(^{n}-1\)} has been designed based on CRT and New CRT-I algorithms and in two-level structure. Also, an efficient reverse converter for moduli set {2\(^{2n-1}\), 2\(^{2n-1}-1\), 2\(^{n}+1\), 2\(^{n}-1\)} has been designed by applying New CRT-I algorithm. The proposed reverse converters are based on adders and hence can be simply implemented by VLSI circuit technology. The proposed reverse converters offer less delay and hardware cost when compared with the recently introduced reverse converters for the moduli sets {2\(^{n}+1\), 2\(^{n}-1\),2\(^{n}\), 2\(^{2n+1}-1\)} and {2\(^{n}+1\), 2\(^{n}-1\), 2\(^{2n}\), 2\(^{2n+1}-1\)}.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Andraros, H. Ahmad, A new efficient memory-less residue to binary converter. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. 35, 1441–1444 (1988)
J.C. Bajard, L. Imbert, Brief contributions: a full implementation RSA in RNS. IEEE Trans. Comput. 53(6), 769–774 (2004)
M. Bhardwaj, T. Srikanthan, C.T. Clarke, A reverse converter for the 4 moduli super set \(\{2^{n}-1, 2^{n}, 2^{n}+1, 2^{n+1}+1\}\). IEEE Conference on Computer Arithmetic, 1999, pp. 168–175
B. Cao, C.H. Chang, T. Srikanthan, An efficient reverse converter for the 4-moduli set \(\{2^{n}-1, 2^{n}, 2^{n}+1, 2^{2n}+1\}\) based on Chinese New Remainder Theorem. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I 50, 1296–1303 (2003)
B. Cao, C.H. Chang, T. Srikanthan, A residue to binary converter for a new five-moduli set. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I 54, 1041–1049 (2007)
B. Cao, T. Srikanthan, C.H. Chang, Efficient reverse converters for the four-moduli sets \(\{2^{n}-1, 2^{n}, 2^{n}+1, 2^{n+1}-1 {\rm and} 2^{n}-1, 2^{n}, 2^{n}+1, 2^{n-1}-1\}\). Proc. IEEE Comput. Digit. Tech. 152, 687–696 (2005)
C.H. Chang, S. Menon, B. Cao, T.A. Srikanthan, A configurable dual moduli multi-operand modulo adder. Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and System, 2005
M. Ciet, M. Nevel, E. Peetersl, J.J. Quisquater, in Parallel FPGA implementation of RSA with residue number systems, Proceedings of the 46th IEEE International Midwest Symposium on Circuits Systems, vol. 2, 2003, pp. 806–810
R. Conway, J. Nelson, Improved RNS FIR filter architectures. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II 51(1), 26–28 (2004)
A. Dhurkadas, Comments on a high speed realisation of a residue to binary number system converter. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II 45, 446–447 (1998)
L. Kalampoukas, D. Nikolos, C. Efstathiou, H.T. Vergos, J. Kalamatianos, High-speed parallel-prefix modulo 2\(^{n}\)-1 adders. IEEE Trans. Comput. 49, 673–679 (2000)
S.H. Lin, M.H. Sheu, C.H. Wang, Efficient VLSI design of residue-to-binary converter for the moduli set (2\(^{n}, 2^{n+1} -1, 2^{n} -1\)). IEICE Trans. E91–D, 2058–2060 (2008)
P.V.A. Mohan, Residue Number Systems: Algorithms and Architectures (Kluwer, Norwell, 2002)
P.V.A. Mohan, RNS-to-binary converter for a new three-moduli set \(\{2^{n+1} -1, 2^{n}, 2^{n} -1\}\). IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II 54(9), 775–779 (2007)
P.V.A. Mohan, New reverse converters for the moduli set \(\{2^{n} - 3, 2^{n}- 1, 2^{n}+1, 2^{n}+ 3\}\). J. Electron. Commun. 62, 643–658 (2008)
P.V.A. Mohan, A.B. Premkumar, RNS-to-binary converters for two four-moduli set \(\{2^{n}- 1, 2^{n}, 2^{n} + 1, 2^{n+1}- 1\}\) and \(\{2^{n} - 1, 2^{n}, 2^{n} + 1, 2^{n+1}+ 1\}\). IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I 54, 1245–1254 (2007)
A.S. Molahosseini, K. Navi, A reverse converter for the enhanced moduli set \(\{2^{n}-1, 2^{n} +1, 2^{2n}, 2^{2n+1} -1\}\) using CRT and MRC. Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Annual Symposium on VLSI (ISVLSI’10), Kefalonia, Greece, 2010, pp. 456–457
M.R. Noorimehr, M. Hosseinzadeh, R. Farshidi, An efficient reverse converter for the new four moduli set \(\{2^{2n}, 2^{n/2} -1, 2^{n/2} +1, 2^{n+1}-1\}\). J. Circuits Syst. 20(7), 1341–1355 (2011)
M.R. Noorimehr, M. Hosseinzadeh, H.R. Hosseini, A new four-moduli set \(\{2^{2n}, 2^{n+1} -1, 2^{n/2} +1, 2^{n/2}-1\}\) with an efficient residue to binary converter. J. Autom. Syst. Eng. 5, 165–175 (2011)
A. Omondi, B. Premkumar, Residue Number Systems: Theory and Implementations (Imperial College Press, London, 2007)
B. Parhami, Computer Arithmetic: Algorithms and Hardware Design (Oxford University Press, Oxford, 2000)
R.A. Patel, M. Benaissa, S. Boussakta, Fast modulo \(2^{n}-(2^{n-2}+1)\) addition: a new class of adder for RNS. IEEE Trans. Comput. 56(4), 572–576 (2007)
S.J. Piestrak, Design of residue generators and multioperand modular adders using carry-save adders. IEEE Trans. Comput. 423(1), 68–77 (1994)
S.J. Piestrak, A high speed realization of a residue to binary converter. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II 42(10), 661–663 (1995)
K.H. Rosen, Elementary Number Theory and Its Application (Addison-Wesley, Reading, 1988)
A. Sabbagh, Improving the delay of residue-to-binary converter for a four-moduli set. Adv. Electr. Comput. Eng. 11(2), 37–42 (2011)
A. Sabbagh, S. Jafarali Jassbi, S. Sorouri, Design and FPGA implementation of an improved RNS conveter. J. Basic Appl. Sci. Res. 2(6), 6167–6171 (2012)
A. Sabbagh, K. Navi, Ch. Dadkhah, S. Timarchi, Efficient reverse converter designs for the new 4-moduli sets \(\{2^{n}-1, 2^{n}, 2^{n} +1, 2^{2n+1}-1\}\) and \(\{2^{n}-1, 2^{n}+1, 2^{2n}, 2^{2n} +1\}\). IEEE Trans. Circuit Syst. 56(9), 1–13 (2009)
M.H. Sheu, S.H. Lin, C. Chen, S.W. Yang, An efficient VLSI design for a residue to binary converter for general balance moduli \((2^{n}-3, 2^{n}-1, 2^{n}+1, 2^{n}+3)\). IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. 51, 52–55 (2004)
M.A. Soderstrand, Residue Number System Arithmetic: Modern Applications in Digital Signal Processing (IEEE Press, Piscataway, 1986)
M.A. Soderstrand, R.A. Escott, VLSI implementation in multiple-valued logic of an FIR digital filter using residue number system arithmetic. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. 33(1), 5–25 (1986)
L. Sousa, S. Antão, MRC-based RNS reverse converters for the four-moduli sets \(\}2^{n}+1, 2^{n}-1, 2^{n}, 2^{2n+1}-1\}\) and \(\{2^{n} +1, 2^{n}-1,2^{2n}, 2^{2n+1} -1\}\). IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. 59(4), 244–248 (2012)
F. Taylor, A single modulus ALU for signal processing. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 33(5), 1302–1315 (1985)
F.J. Taylor, Residue arithmetic: a tutorial with examples. IEEE Comput. 17, 50–62 (1984)
A.P. Vinod, A.B. Premkumar, A residue to binary converter for the 4-moduli superset \(\{2^{n}-1, 2^{n}, 2^{n}+1, 2^{n+1}-1\}\). J. Circuits Syst. 10, 85–99 (2000)
W. Wang, M.N.S. Swamy, M.O. Ahmad, Moduli selection in RNS for efficient VLSI implementation. Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Circuits Systems, 2003, pp. 25–28
W. Wang, M.N.S. Swamy, M.O. Ahmad, RNS application for digital image processing. Proceedings of the 4th IEEE International Workshop on System-on-Chip for Real Time Applications, 2004, pp. 77–80
Y. Wang, Residue-to-binary converters based on new chinese remainder theorems. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. 47(3), 197–205 (2000)
Y. Wang, X. Song, M. Aboulhamid, H. Shen, Adder based residue to binary numbers converters for \(\{2^{n}-1, 2^{n}, 2^{n}+1\}\). IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 50(7), 1772–1779 (2002)
R. Zimmermann, Efficient VLSI implementation of modulo (\(2^{n} \pm 1\)) addition and multiplication. Proceedings of the 14th IEEE Symposium on Computer Arithmetic, Adelaide, 1999, 158–167
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Noorimehr, M.R., Hosseinzadeh, M. & Navi, K. Efficient Reverse Converters for 4-Moduli Sets {2\(^{2n-1}-1\), 2\(^{n}\), 2\(^{n}+1\), 2\(^{n}-1\)} and {2\(^{2n-1}\), 2\(^{2n-1}-1\), 2\(^{n}+1\), 2\(^{n}-1\)} Based on CRTs Algorithm. Circuits Syst Signal Process 33, 3145–3163 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-014-9798-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-014-9798-1